- Mailing Lists
- in
- 6 More Microservices Interview Questions
Archives
- By thread 5363
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 176
Top Reports of 2023
SmartWaste - Manager Application which is designed for managers to track and monitor all the activities of the Waste Collecting Vehicles.
6 More Microservices Interview Questions
6 More Microservices Interview Questions
Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: In this issue, we continue our exploration of microservices interview questions. We will cover the following topics:
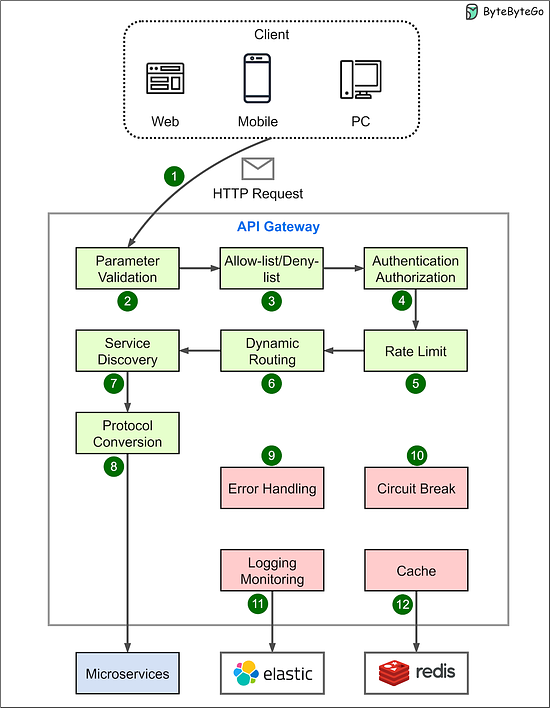
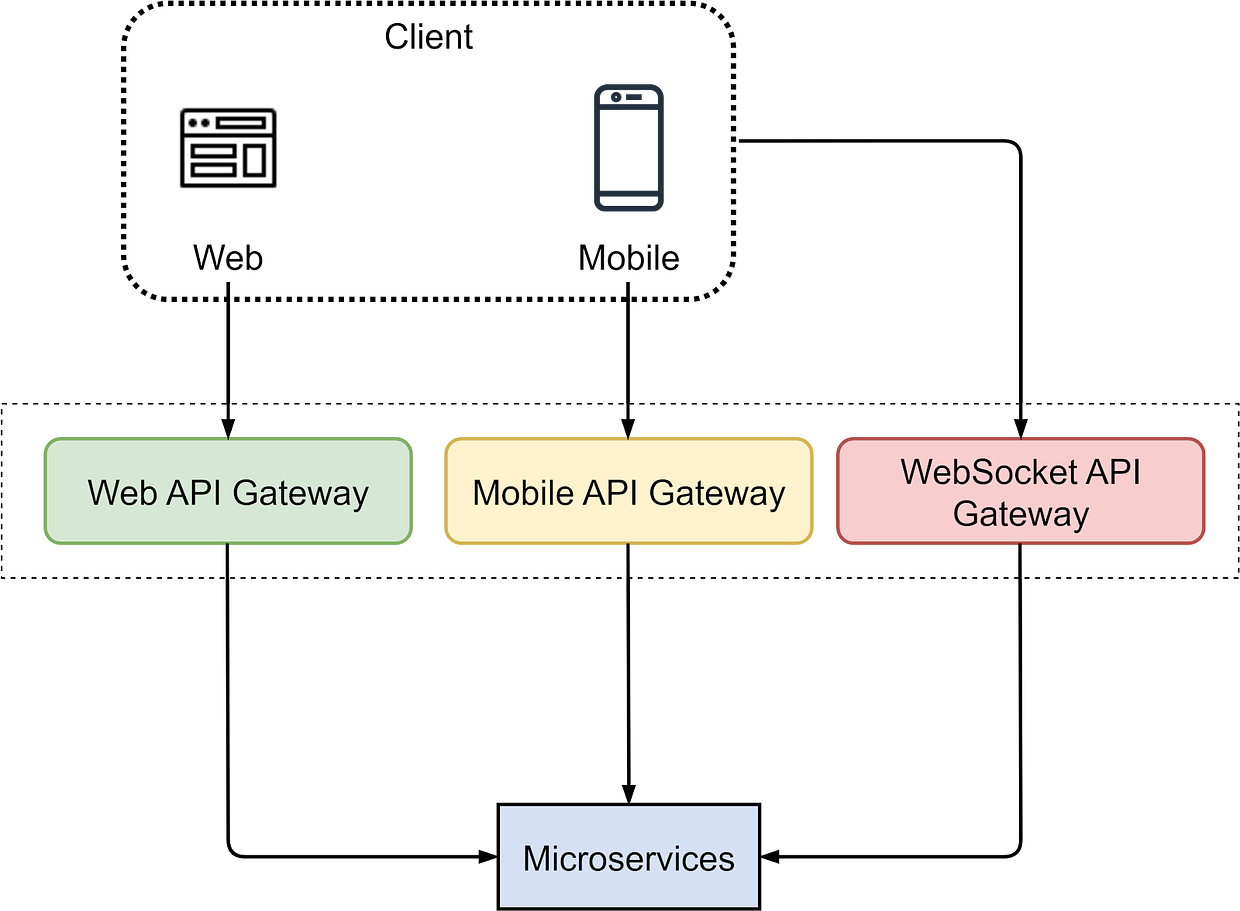
You can find more information on the definition of microservices and their basic components in our previous article. We will now dive into the API gateway, an important request entry point in a microservices architecture. 1. What is API Gateway?In a microservices architecture, an API gateway acts as a single entry point for client requests. The API gateway is responsible for request routing, composition, and protocol translation. It also provides additional features like authentication, authorization, caching, and rate limiting. The diagram below shows the key steps: Step 1: The client sends an HTTP request to the API gateway. Step 2: The API gateway parses and validates the attributes in the HTTP request. Step 3: The API gateway checks allow/deny lists. Step 4: The API gateway authenticates and authorizes through an identity provider. Step 5: Rate-limiting rules are applied. Requests over the limit are rejected. Steps 6 and 7: The API gateway routes the request to the relevant backend service by path matching. Step 8: The API gateway transforms the request into the appropriate protocol and forwards it to backend microservices. Step 9: The API gateway handles any errors that may arise during request processing for graceful degradation of service. Step 10: The API gateway implements resiliency patterns like circuit brakes to detect failures and prevent overloading interconnected services, avoiding cascading failures. Step 11: The API gateway utilizes observability tools like the ELK stack (Elastic-Logstash-Kibana) for logging, monitoring, tracing, and debugging. Step 12: The API gateway can optionally cache responses to common requests to improve responsiveness. Besides request routing, the API gateway can also aggregate responses from microservices into a single response for the client. The API gateway is different from a load balancer. While both handle network traffic, the API gateway operates at the application layer, mainly handling HTTP requests; the load balancer mostly operates at the transport layer, dealing with TCP/UDP protocols. The API gateway offers more functions as it sees the request payload. The API gateway differs from a load balancer in that it typically operates at the application layer to handle HTTP requests and understand message payloads, while traditional load balancers work at the transport layer to handle TCP/UDP connections without looking at the application data. However, the lines can blur between these two types of infrastructure. Some advanced load balancers are gaining application layer visibility and routing capabilities resembling API gateways. But in general, API gateways focus on application-level concerns like security, routing, composition, and resilience based on the payload, while traditional load balancers map requests to backend servers mainly based on transport-level metadata like IP and port numbers. We often have separate API gateways tailored for different clients and their user experience requirements. The diagram below shows a typical architecture. We have different API gateways to handle requests from mobile devices and web applications because they have unique requirements for user experiences. Additionally, we separate WebSocket API Gateway because it has different connection persistence and rate-limiting requirements compared to HTTP gateways. Some recent API gateway trends:
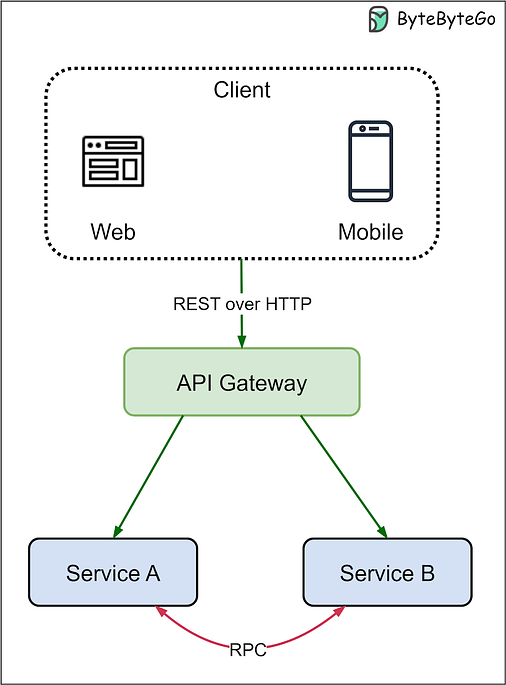
2. What Are the Differences Between REST and RPC?REST (Representational State Transfer) and RPC (Remote Procedure Call) are two common architectural patterns used for communications in distributed systems. REST is used for client-server communications, and RPC is used for server-server communications, as illustrated in the diagram below. Keep reading with a 7-day free trialSubscribe to ByteByteGo Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives. A subscription gets you:
© 2023 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:39 - 21 Dec 2023