- Mailing Lists
- in
- A Crash Course in Kubernetes
Archives
- By thread 5316
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 128
3 steps to platform engineering mastery
Learn the can’t-miss guiding principles for successful GenAI initiatives.
A Crash Course in Kubernetes
A Crash Course in Kubernetes
This is a sneak peek of today’s paid newsletter for our premium subscribers. Get access to this issue and all future issues - by subscribing today. Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
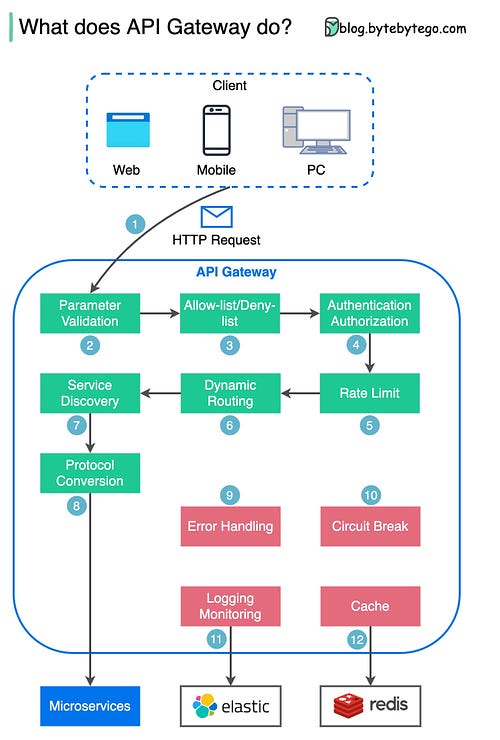
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: In today's world of complex, web-scale application backends made up of many microservices and components running across clusters of servers and containers, managing and coordinating all these pieces is incredibly challenging. That's where Kubernetes comes in. Kubernetes (also known as "k8s") is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. With Kubernetes, you don't have to worry about manually placing containers or restarting failed ones. You simply describe your desired application architecture and Kubernetes makes it happen and keeps it running. In this two-part series, we'll dive deep into Kubernetes and cover:
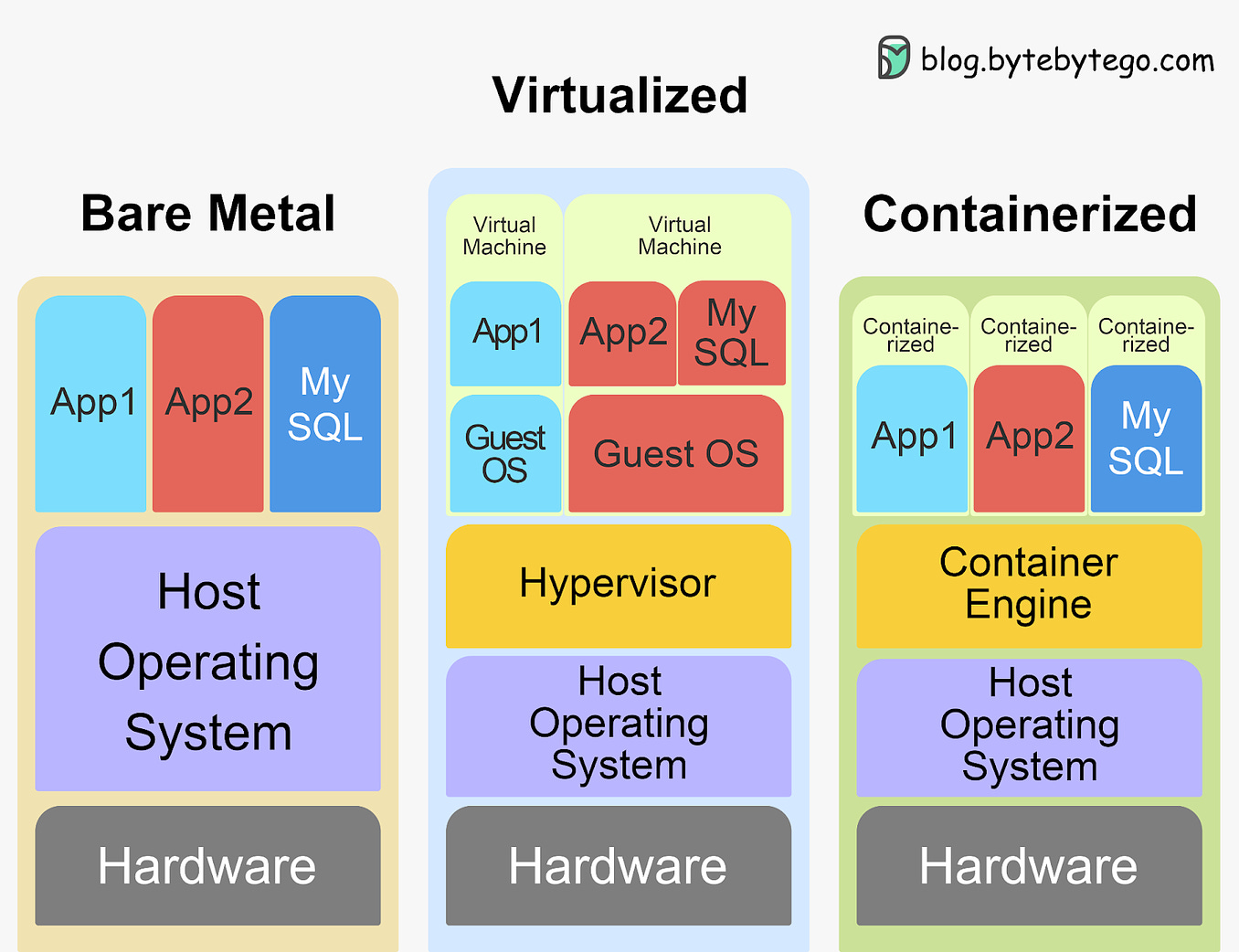
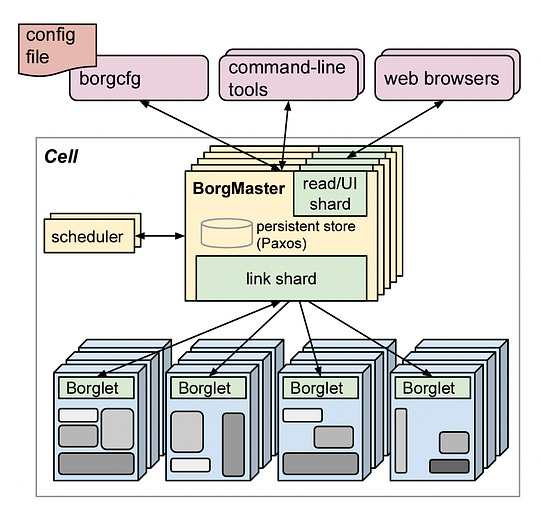
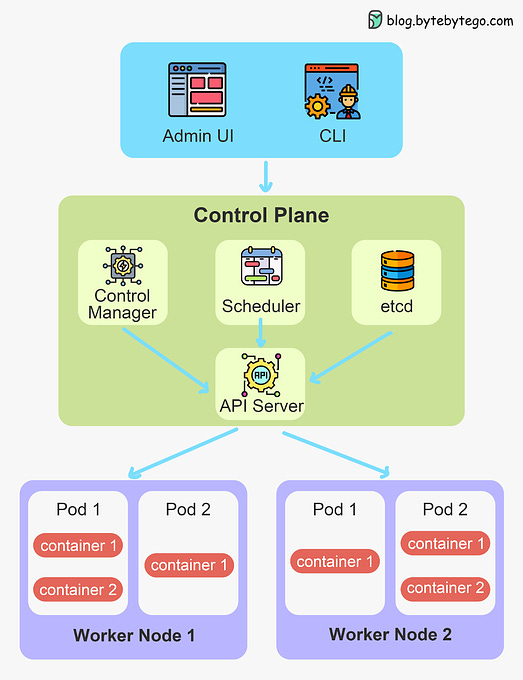
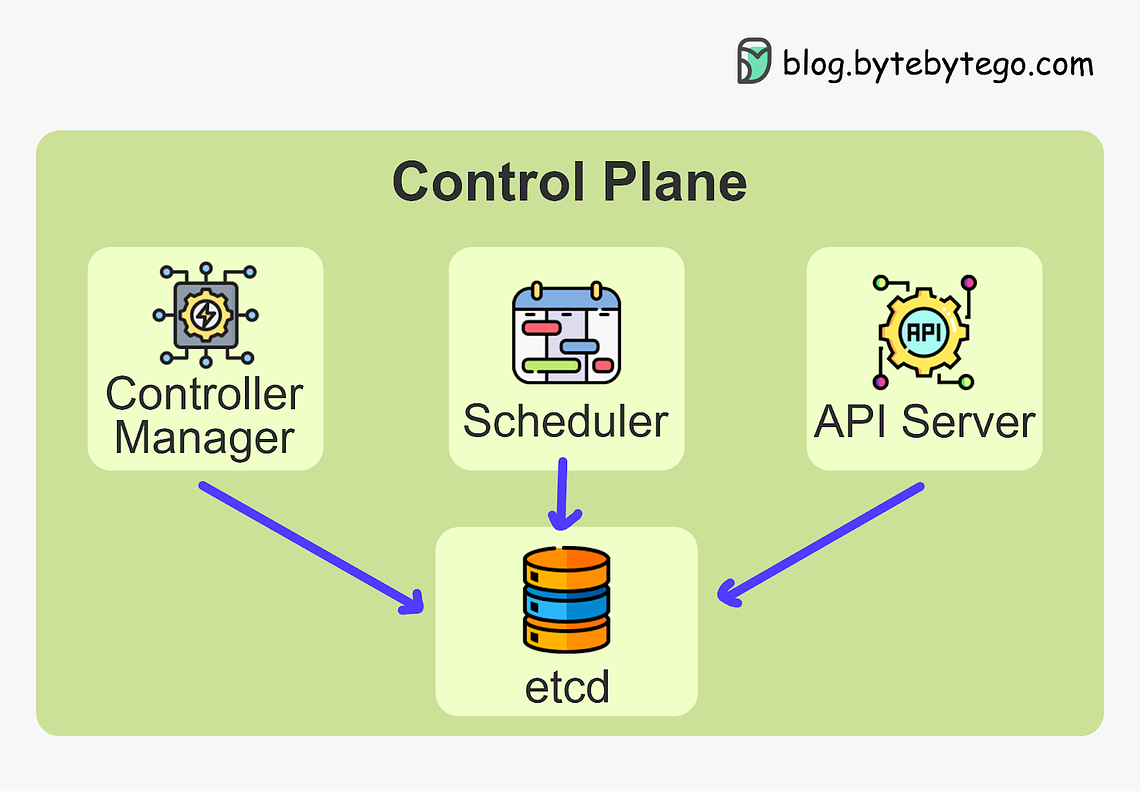
We'll demystify Kubernetes and equip you with everything you need to determine if and when Kubernetes could be the right solution for your applications. You'll walk away with a clear understanding of what Kubernetes is, how it works, and how to put it into practice. Whether you're a developer, ops engineer, or technology leader, you'll find invaluable insights in this deep dive into Kubernetes. Let's get started! Brief HistoryKubernetes can be traced back to Google's internal container orchestration system, Borg, which managed the deployment of thousands of applications within Google. Containers are a method of packaging and isolating applications into standardized units that can be easily moved between environments. Unlike traditional virtual machines (VMs) which virtualize an entire operating system, containers only virtualize the application layer, making them more lightweight, portable and efficient. In 2014, Google open-sourced a container orchestration system based on its learnings from Borg. This is Kubernetes. Kubernetes provides automated deployment, scaling and management of containerized applications. By leveraging containers rather than VMs, Kubernetes provides benefits like increased resource efficiency, faster deployment of applications, and portability across on-prem and cloud environments. Why is it also called k8s? This is a somewhat nerdy way of abbreviating long words. The number 8 in k8s refers to the 8 letters between the first letter “k” and the last letter “s” in the word Kubernetes. Kubernetes Architecture and Key ComponentsAt its core, Kubernetes follows a client-server architecture. There are two core pieces in a Kubernetes cluster - control plane and worker nodes. The control plane is responsible for managing the state of the cluster. In production environments, the control plane usually runs on multiple nodes that span across several data center zones. In other words, the control plane manages worker nodes and the containers running on them. The containerized applications run in a Pod. Pods are the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes. A pod hosts one or more containers and provides shared storage and networking for those containers. Pods are created and managed by the Kubernetes control plane. They are the basic building blocks of Kubernetes applications. Let’s dive deeper into the main pieces. Kubernetes Control PlaneThe control plane is the brain of Kubernetes. It consists of various components that, together, make global decisions about the cluster. The control plane components run on multiple servers across availability zones to provide high availability. The key components are:
Keep reading with a 7-day free trialSubscribe to ByteByteGo Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.A subscription gets you:
© 2023 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:38 - 26 Oct 2023