- Mailing Lists
- in
- CAP, PACELC, ACID, BASE - Essential Concepts for an Architect’s Toolkit
Archives
- By thread 5343
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 156
CAP, PACELC, ACID, BASE - Essential Concepts for an Architect’s Toolkit
CAP, PACELC, ACID, BASE - Essential Concepts for an Architect’s Toolkit
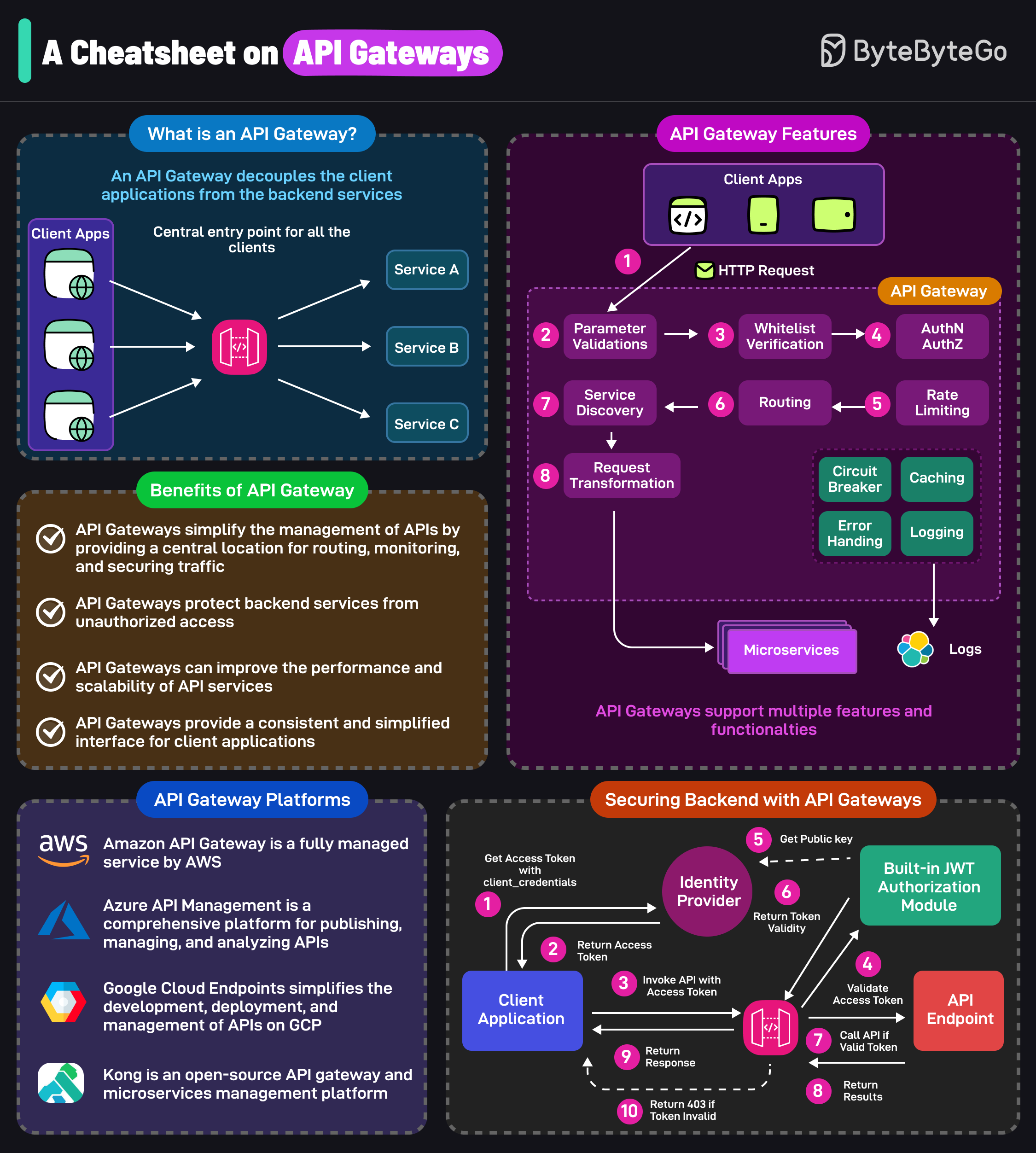
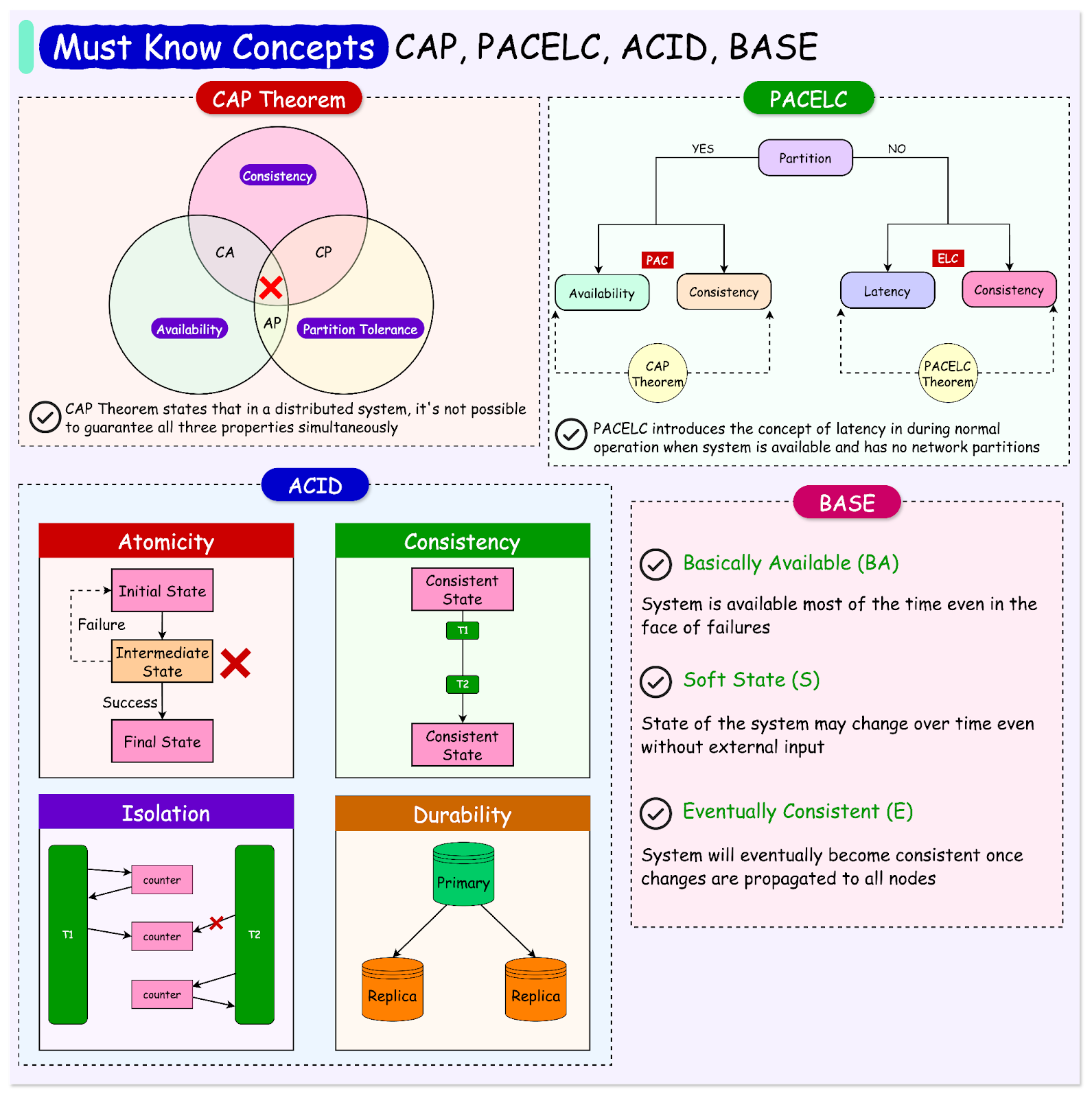
Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month. To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: In today's world, distributed systems have become ubiquitous, powering everything from social media platforms and e-commerce websites to financial systems and healthcare applications. As these systems grow in complexity and scale, it becomes increasingly important for software architects and developers to understand the inherent trade-offs and challenges associated with designing and building such systems. One of the key challenges in distributed systems is ensuring data consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. These properties are often in tension with one another, and achieving all three simultaneously is impossible, as stated by the famous CAP theorem. This theorem has become a fundamental principle in distributed systems design, guiding architects in making informed decisions about the trade-offs between consistency, availability, and partition tolerance. Building upon the CAP theorem, other frameworks and models have emerged to help reason about the trade-offs in distributed systems. The PACELC theorem extends the CAP theorem to provide a more nuanced understanding of the trade-offs between consistency and availability during normal operations and network partitions. In addition to CAP and PACELC, the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) and BASE (Basically Available, Soft-state, Eventually Consistent) models provide guidance for designing transactional systems and dealing with the challenges of eventual consistency in distributed databases. By carefully considering the implications of CAP, PACELC, ACID, and BASE, architects can make informed choices that align with the specific requirements and constraints of their applications. In this article, we will dive deep into these concepts, exploring their definitions and implications. We will also discuss the limitations of these models and the factors to consider when choosing the right approach for a given use case. The CAP Theorem... Continue reading this post for free in the Substack app© 2024 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:37 - 10 Oct 2024