- Mailing Lists
- in
- Dark Side of Distributed Systems: Latency and Partition Tolerance
Archives
- By thread 5036
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 149
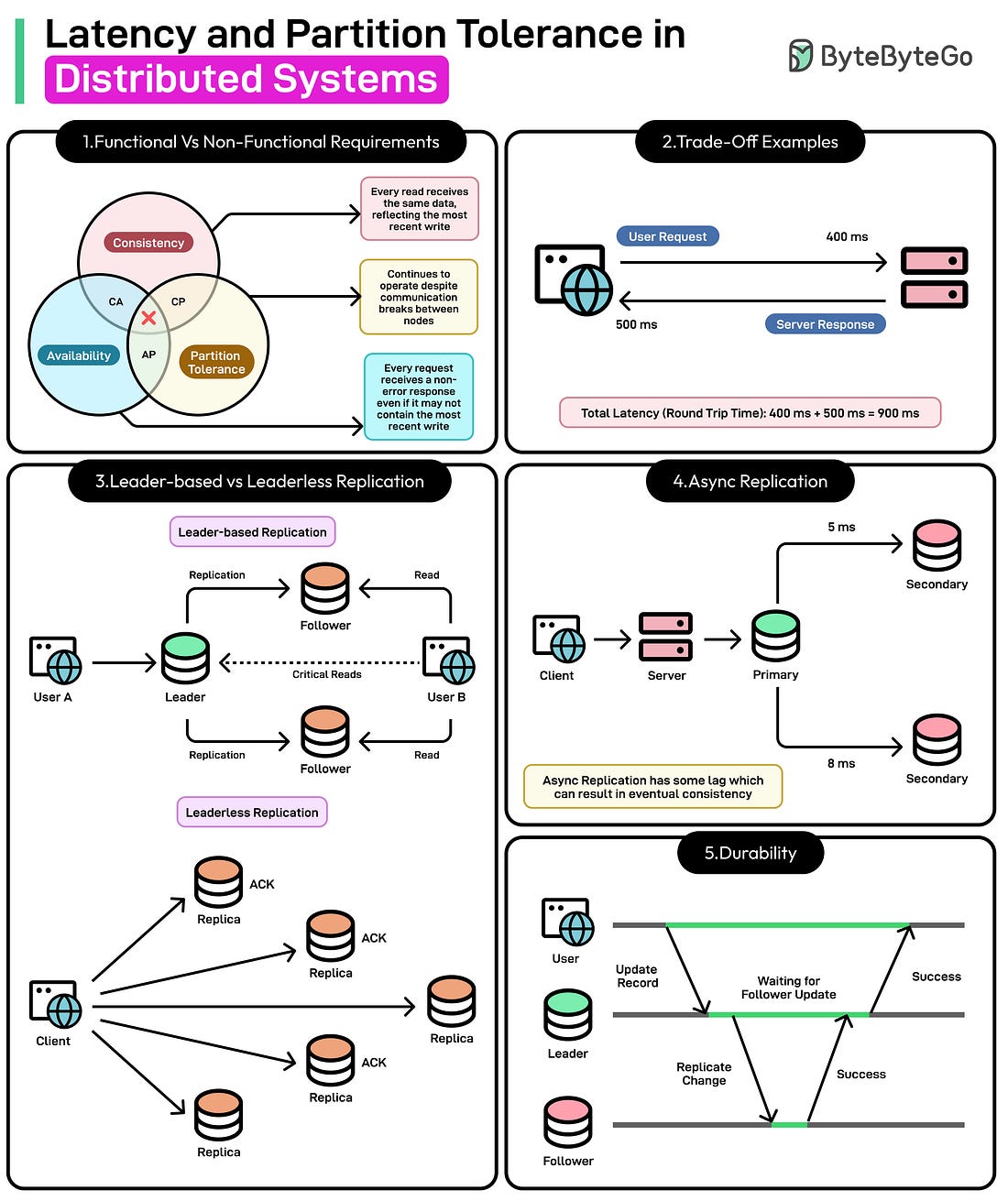
Dark Side of Distributed Systems: Latency and Partition Tolerance
Dark Side of Distributed Systems: Latency and Partition Tolerance
Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
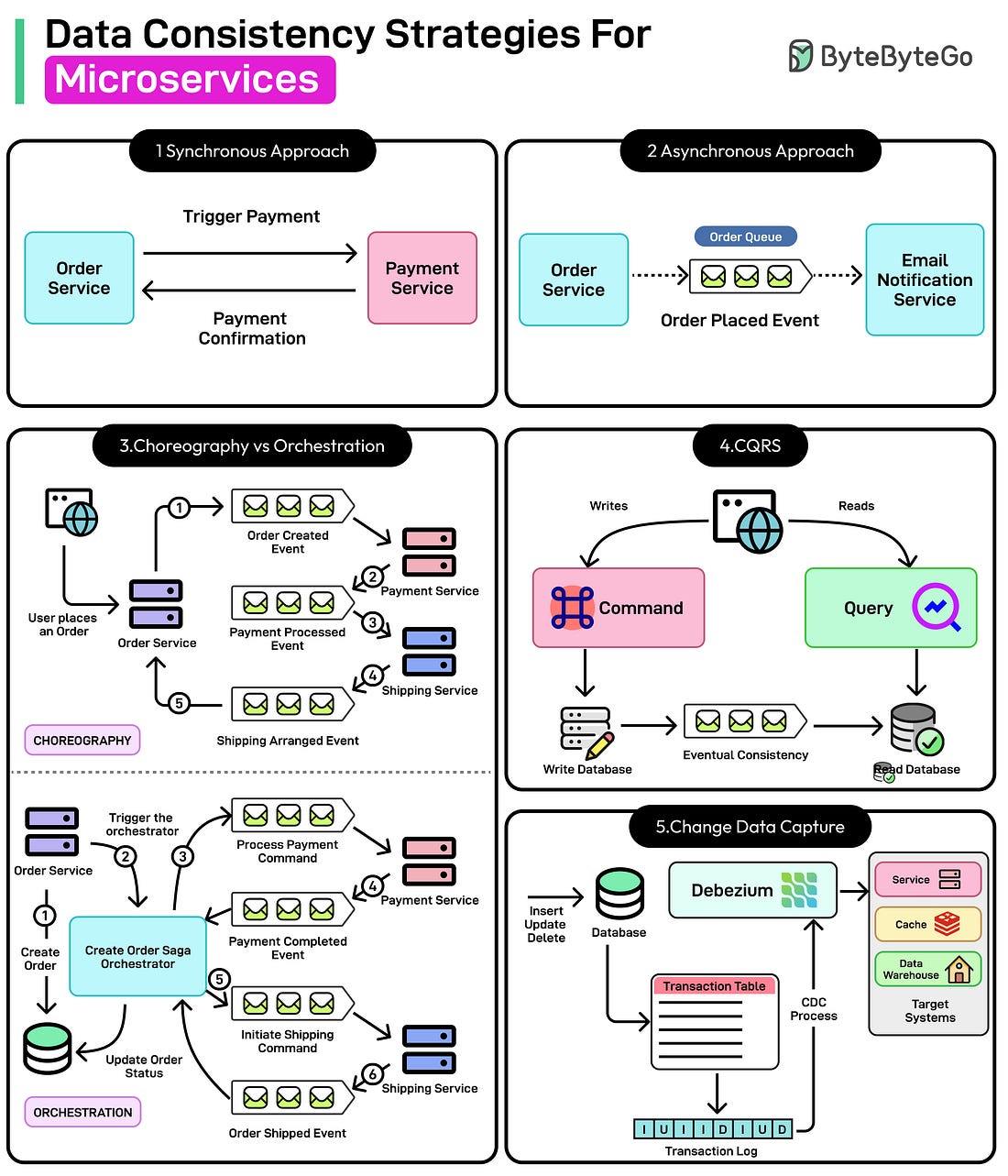
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: Distributed systems are collections of independent computing resources that work together to present a unified, cohesive service or application to the user. Rather than relying on a single powerful machine, these systems spread workloads across multiple nodes, often deployed across different servers, regions, or continents. Building distributed systems is popular because it offers improved scalability, enabling organizations to handle growing traffic by adding more nodes as needed. It also enhances fault tolerance. If one node goes down, the system can often continue serving requests, minimizing downtime and user impact. However, with these benefits come complexities—what many refer to as the “dark side” of distributed systems.
Two critical considerations that consistently arise in distributed systems are latency and partition tolerance. Latency, or the delay in communication between nodes, can degrade user experience and complicate real-time processing. Partition tolerance, the capacity of a system to continue operating despite communication breakdowns among nodes, highlights the trade-offs between maintaining availability and ensuring data consistency. In this article, we’ll understand how latency and partition tolerance impact distributed systems and discuss strategies for addressing them effectively. Understanding the CAP Theorem... Continue reading this post for free in the Substack app© 2025 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:36 - 6 Mar 2025