This week’s system design refresher:
Session Vs JWT: The Differences You May Not Know! (Youtube video)
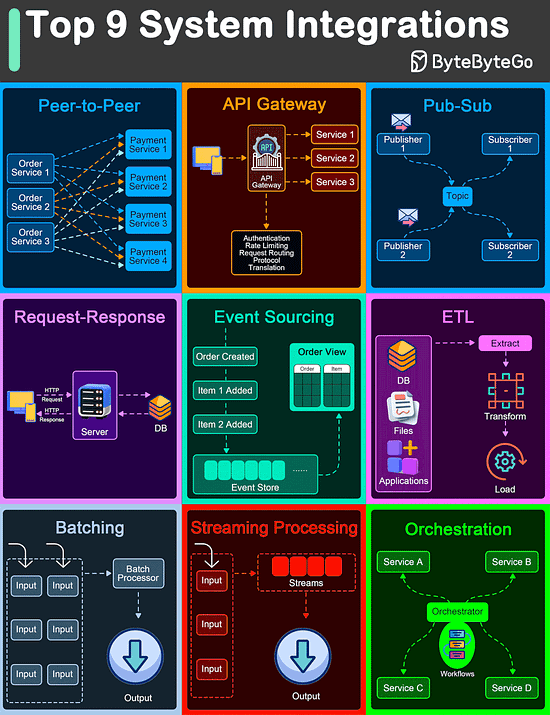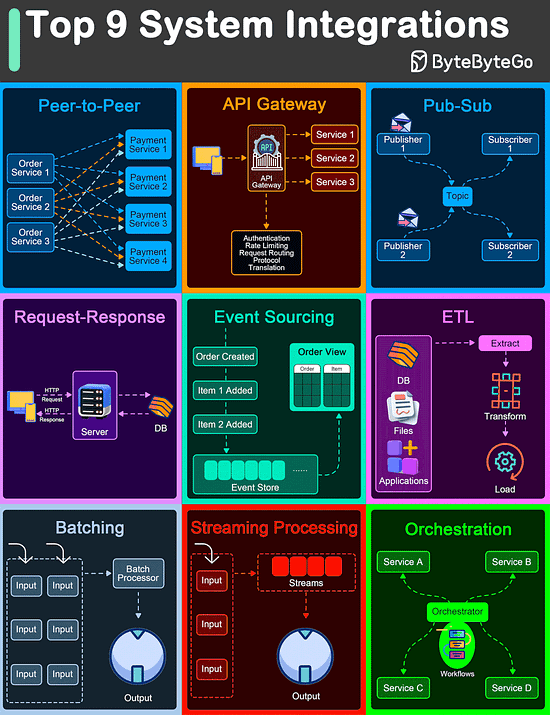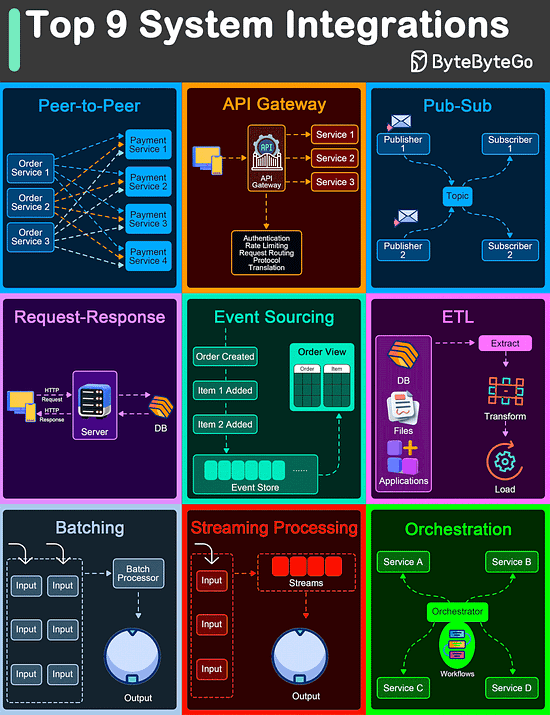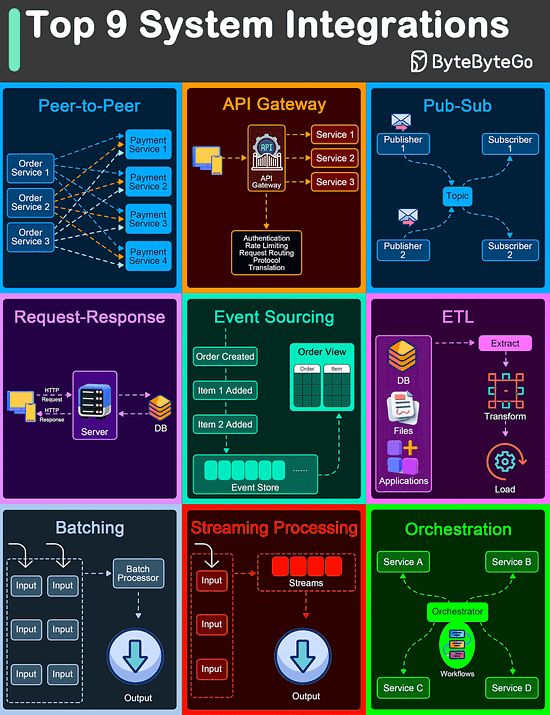
Top 9 Architectural Patterns for Data and Communication Flow
API Gateway 101
Why are Content Delivery Networks (CDN) so Popular?
A Roadmap for Full-Stack Development
SPONSOR US
Get practical tips for building low latency, high throughput apps with ScyllaDB
ScyllaDB in Action is a practical guide to everything you need to know about ScyllaDB, from your first queries to running it in a production environment. It’s written by Discord Staff Engineer Bo Ingram, author of the famous blog on how Discord migrated trillions of messages from Cassandra to ScyllaDB.
This early access preview covers:
Working with ScyllaDB vs. working with other databases
How ScyllaDB runs in practice
What matters most in real-world deployments
How to launch your first cluster, add tables, and run queries
How to perform effective data modeling in ScyllaDB
Free Book Download
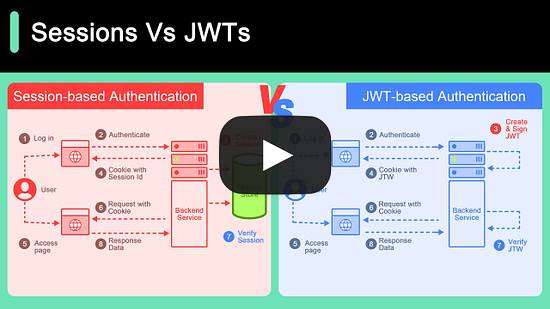
Session Vs JWT: The Differences You May Not Know!
Top 9 Architectural Patterns for Data and Communication Flow
Peer-to-Peer
The Peer-to-Peer pattern involves direct communication between two components without the need for a central coordinator.
API Gateway
An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for all client requests to the backend services of an application.
Pub-Sub
The Pub-Sub pattern decouples the producers of messages (publishers) from the consumers of messages (subscribers) through a message broker.
Request-Response
This is one of the most fundamental integration patterns, where a client sends a request to a server and waits for a response.
Event Sourcing
Event Sourcing involves storing the state changes of an application as a sequence of events.
ETL
ETL is a data integration pattern used to gather data from multiple sources, transform it into a structured format, and load it into a destination database.
Batching
Batching involves accumulating data over a period or until a certain threshold is met before processing it as a single group.
Streaming Processing
Streaming Processing allows for the continuous ingestion, processing, and analysis of data streams in real-time.
Orchestration
Orchestration involves a central coordinator (an orchestrator) managing the interactions between distributed components or services to achieve a workflow or business process.
Latest articles
If you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed.
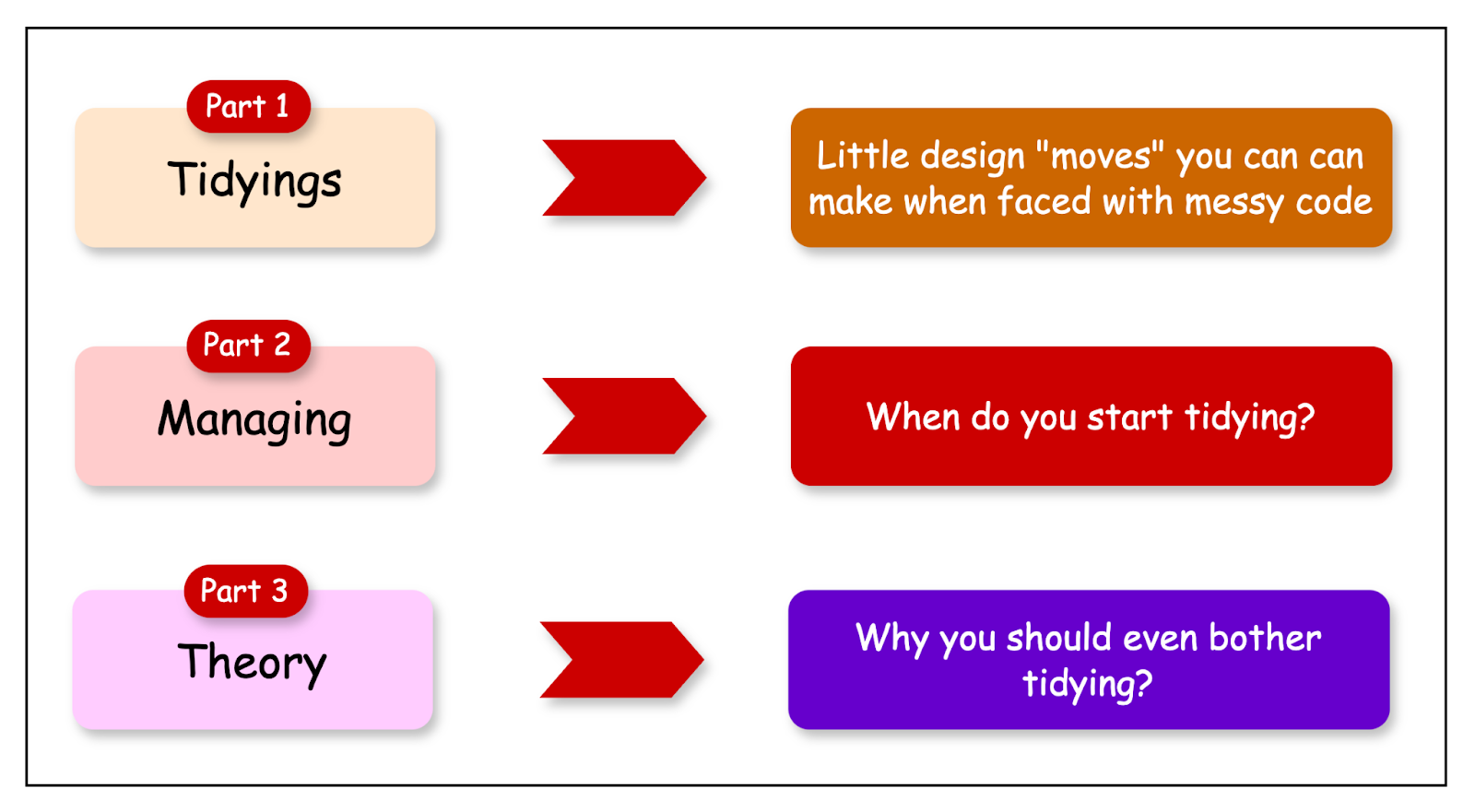
"Tidying" Code
A Crash Course on Relational Database Design
A Crash Course on Distributed Systems
A Crash Course in Database Scaling Strategies
A Crash Course in Database Sharding
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
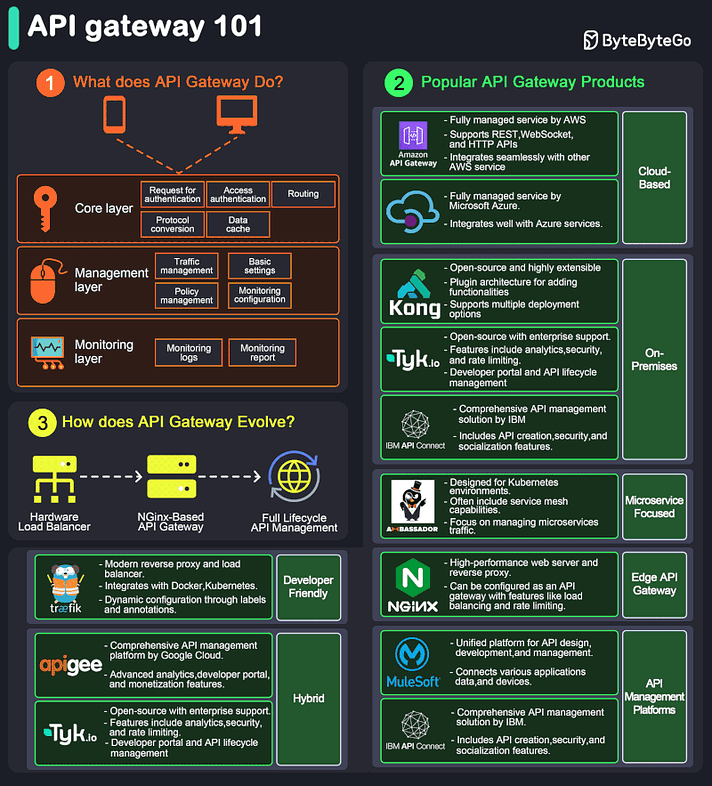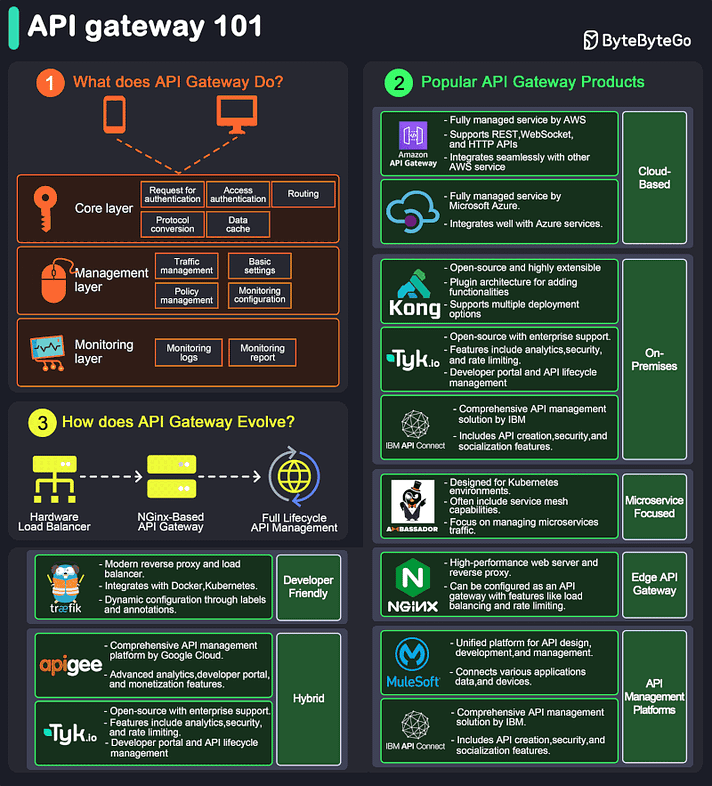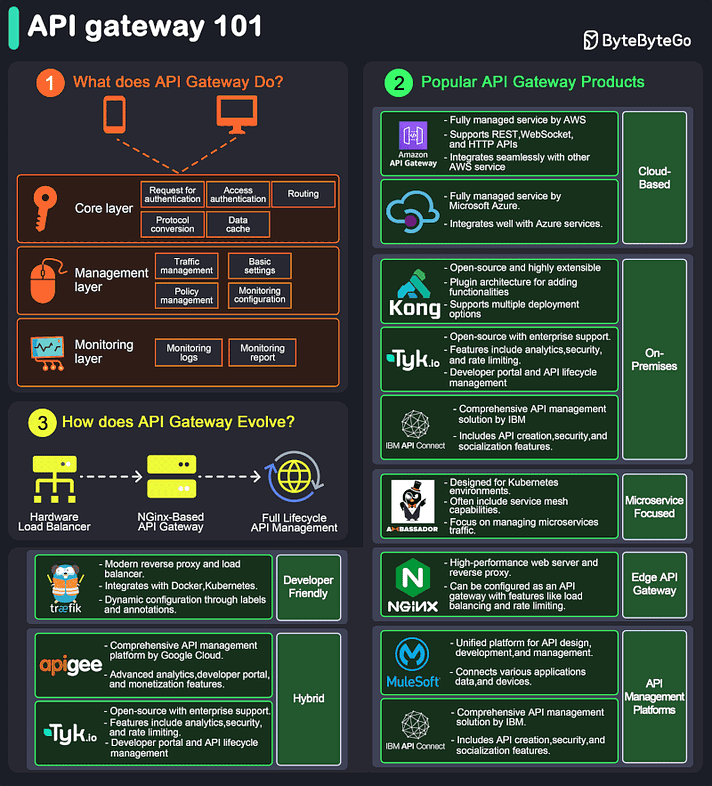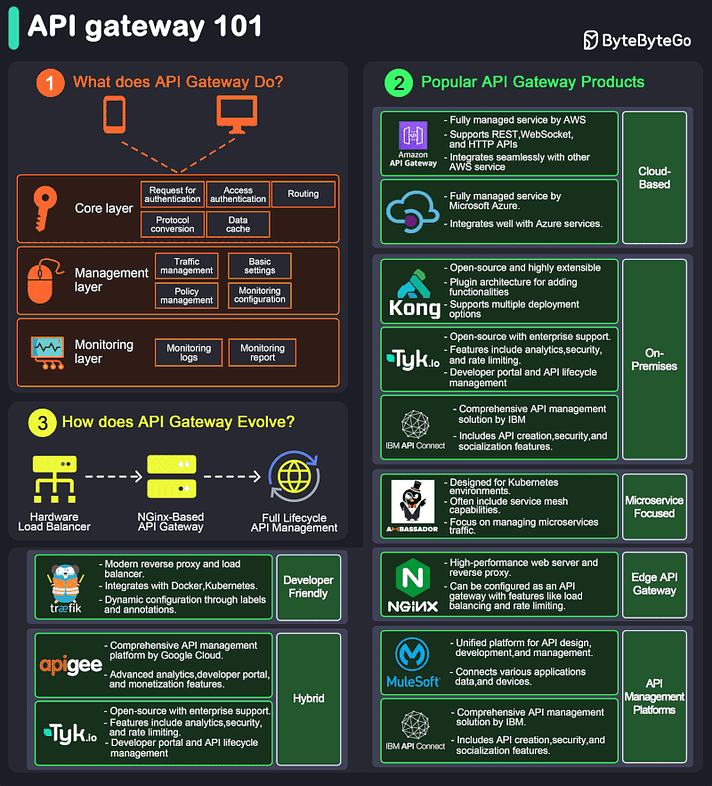
API Gateway 101
An API gateway is a server that acts as an API front-end, receiving API requests, enforcing throttling and security policies, passing requests to the back-end service, and then returning the appropriate result to the client.
It is essentially a middleman between the client and the server, managing and optimizing API traffic.
Key Functions of an API Gateway:
Request Routing: Directs incoming API requests to the appropriate backend service.
Load Balancing: Distributes requests across multiple servers to ensure no single server is overwhelmed.
Security: Implements security measures like authentication, authorization, and data encryption.
Rate Limiting and Throttling: Controls the number of requests a client can make within a certain period.
API Composition: Combines multiple backend API requests into a single frontend request to optimize performance.
Caching: Stores responses temporarily to reduce the need for repeated processing.
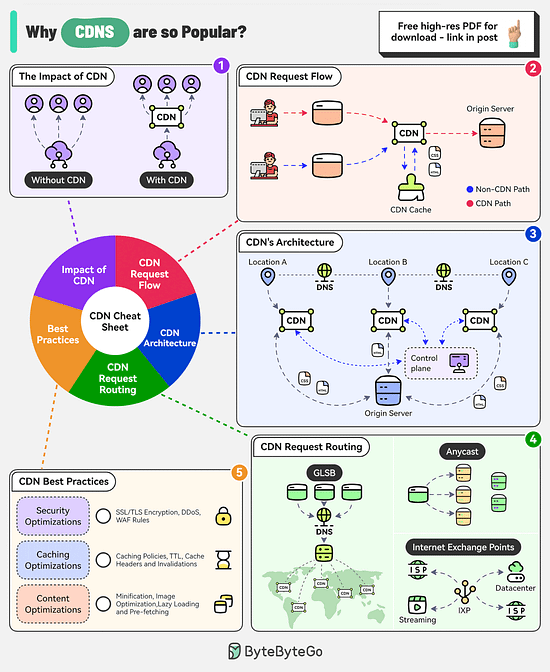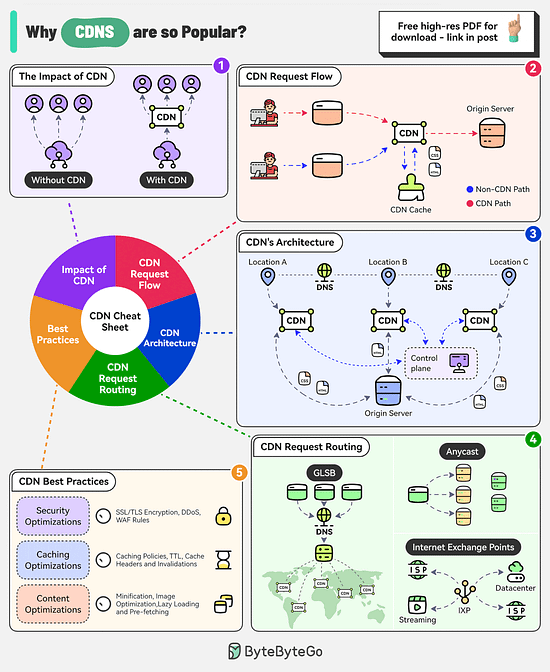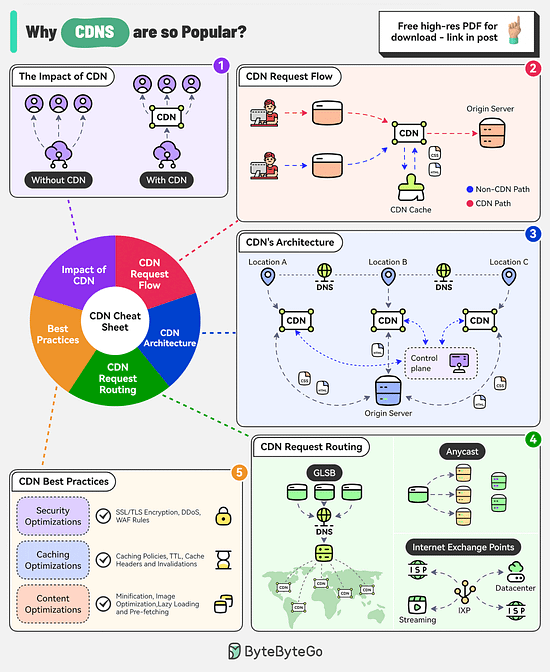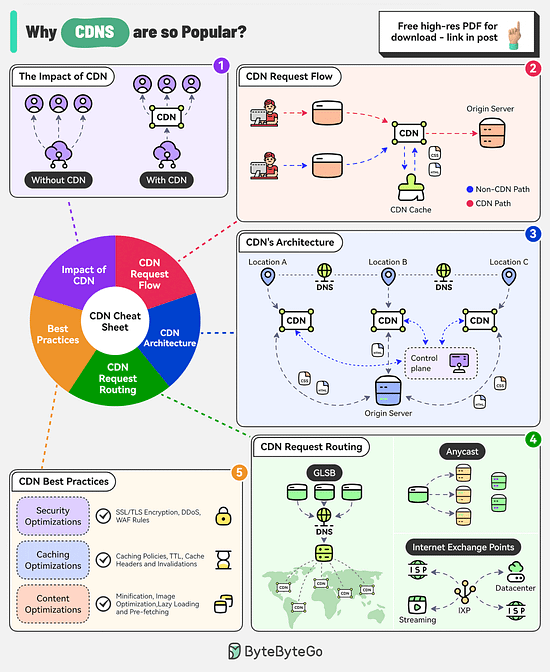
Why are Content Delivery Networks (CDN) so Popular?
The CDN market is expected to reach nearly $38 billion by 2028. Companies like Akamai, Cloudflare, and Amazon CloudFront are investing heavily in this area.
There are several factors behind the popularity of CDNs
The Impact of CDN
CDNs improve performance, increase availability, and enhance bandwidth costs. With the use of CDN, there is a significant reduction in latency.
CDN Request Flow
After DNS resolution, the user’s device sends the content request to the CDN edge server.
The edge server checks its local cache for the content. If found, the edge server serves the content to the user.
If not found, the edge server forwards the request to the origin server.
After receiving the content from the origin server, the edge server stores a copy in its cache and delivers it to the user.
The Architecture of CDN
There are multiple components in a CDN’s architecture:
Origin Server: This is the primary source of content.
Edge Servers: They cache and server content to the users and are distributed across the world.
DNS: The DNS resolves the domain name to the IP address of the nearest edge server
Control Plane: Responsible for configuring and managing the edge servers.
CDN Request Routing
GSLB: Routes user requests to the server based on factors like geographic proximity, server load, network conditions
Anycast DNS: Allows multiple servers to share the same IP address. It helps route incoming traffic to the nearest data center.
Internet Exchange Points: CDN providers establish a presence at major IXPs, allowing them to exchange traffic directly with ISPs and other networks.
Best Practices
Some key best practices to optimize CDN performance are related to security aspects, caching optimizations, and content optimizations.
Over to you: What do you think makes CDNs popular?
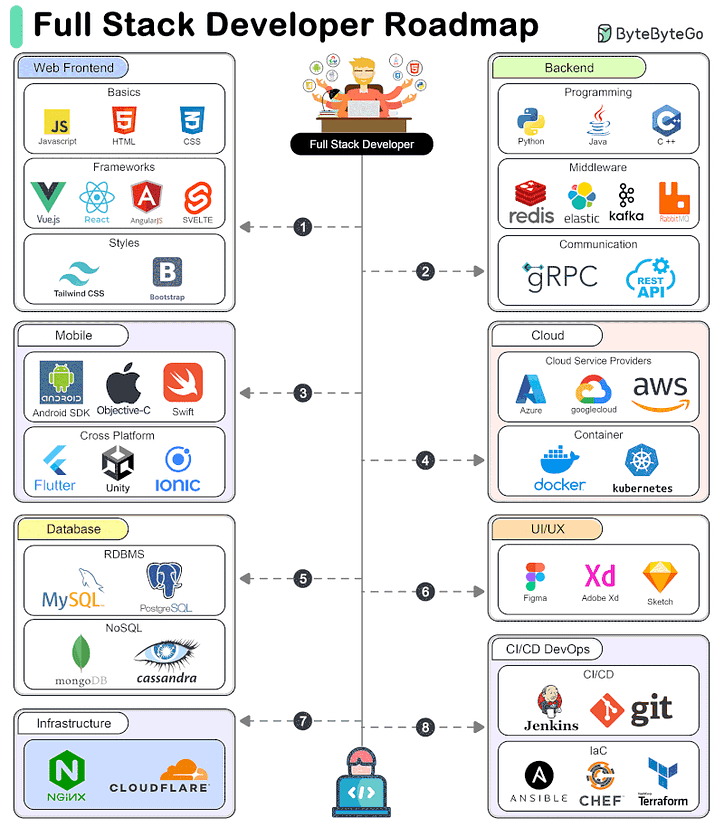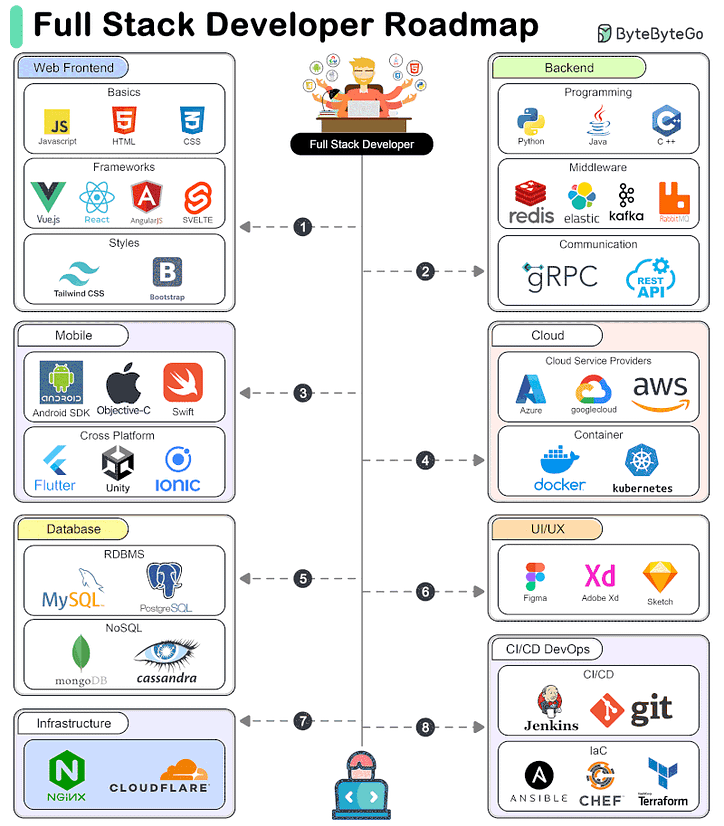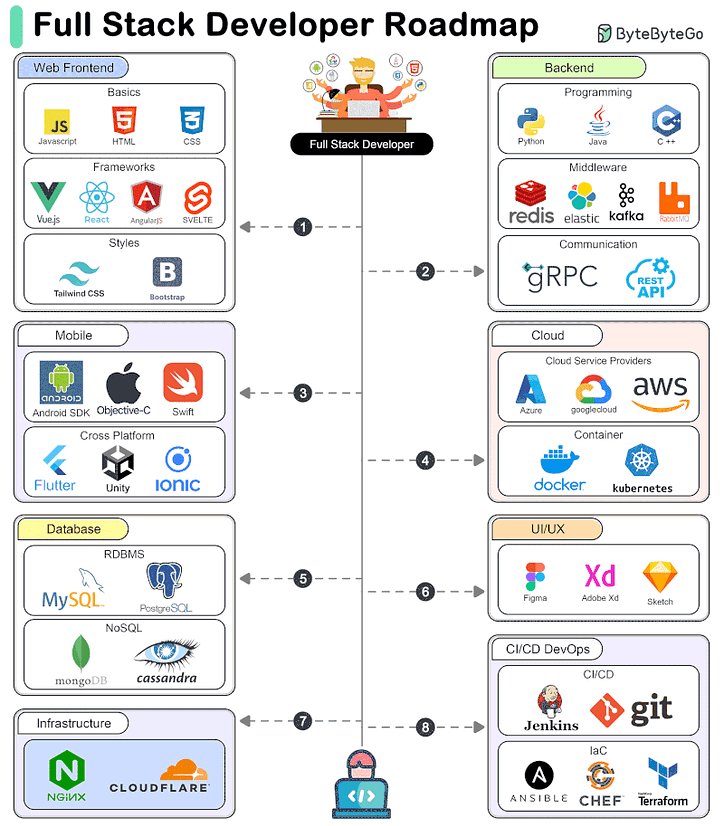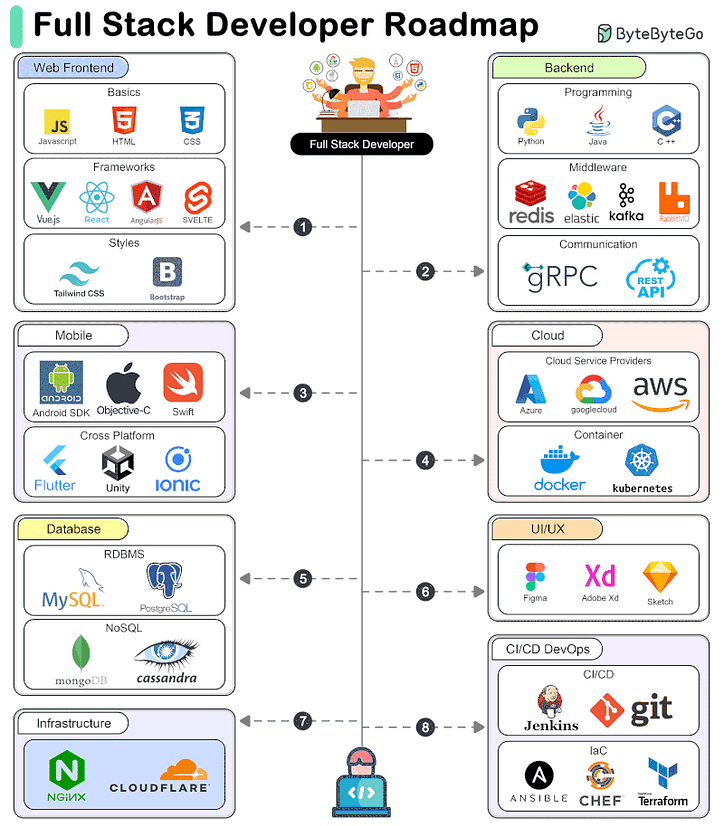
A Roadmap for Full-Stack Development
A full-stack developer needs to be proficient in a wide range of technologies and tools across different areas of software development. Here’s a comprehensive look at the technical stacks required for a full-stack developer.
Frontend Development
Frontend development involves creating the user interface and user experience of a web application.
Backend Development
Backend development involves managing the server-side logic, databases, and integration of various services.
Database Development
Database development involves managing data storage, retrieval, and manipulation.
Mobile Development
Mobile development involves creating applications for mobile devices.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing involves deploying and managing applications on cloud platforms.
UI/UX Design
UI/UX design involves designing the user interface and experience of applications.
Infrastructure and DevOps
Infrastructure and DevOps involve managing the infrastructure, deployment, and continuous integration/continuous delivery (CI/CD) of applications.
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com