- Mailing Lists
- in
- EP148: DeepSeek 1-Pager
Archives
- By thread 5399
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 213
EP148: DeepSeek 1-Pager
EP148: DeepSeek 1-Pager
Build the API your users deserve (Sponsored)Creating a best in class API experience for your partners and customers shouldn't require an army of engineers. Speakeasy’s platform automates the generation of idiomatic SDKs, custom-branded docs, and robust test suites that are as good as what you'd build yourself. That means you can unlock API revenue while keeping your team focused on what matters most: shipping new products. All you need to get started is your OpenAPI document. This week’s system design refresher:
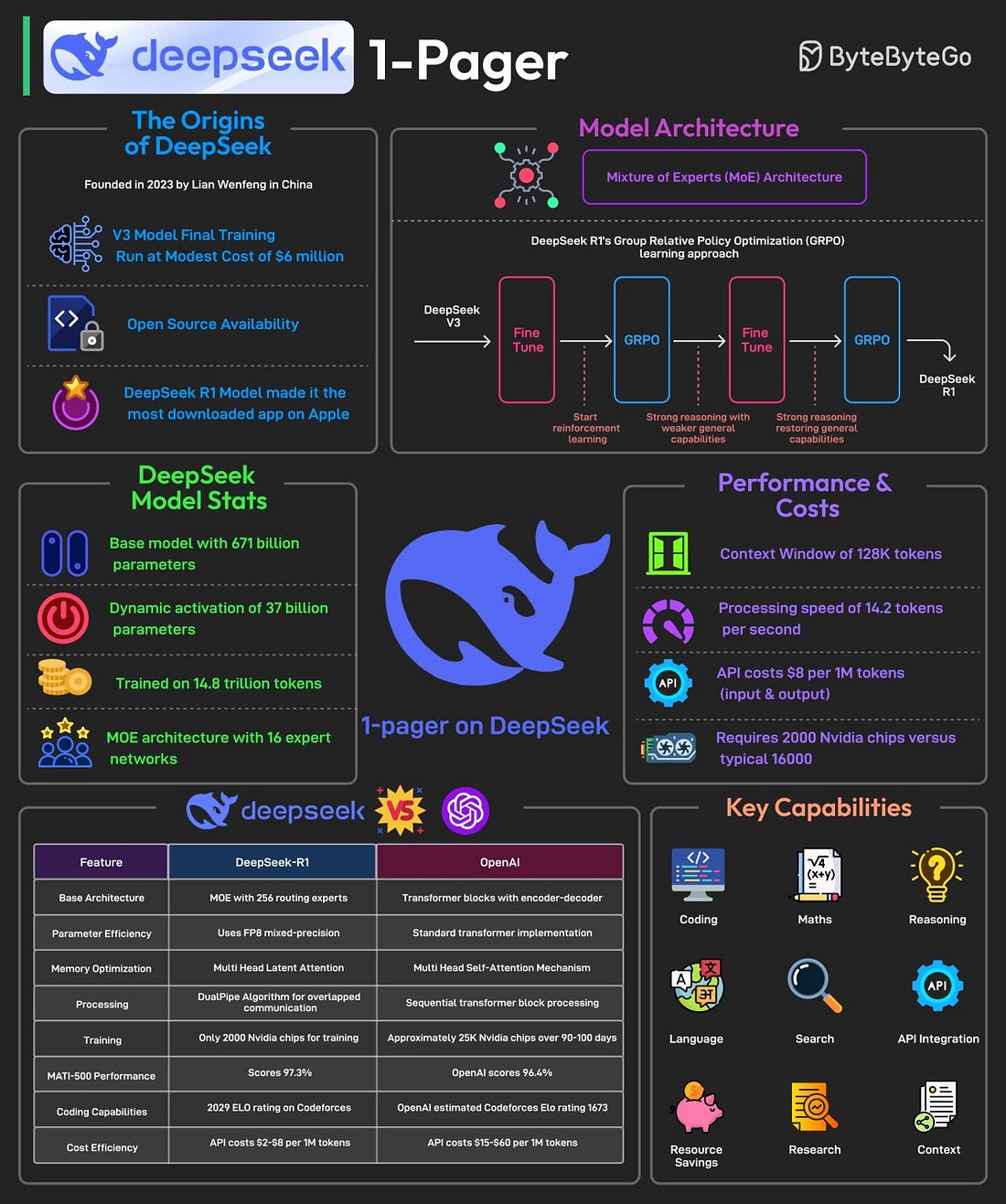
DeepSeek 1-PagerIt is said to have developed a powerful AI model at a remarkably low cost, approximately $6 million for the final training run. In January 2025, it is said to have released its latest reasoning-focused model known as DeepSeek R1. The release made it the No. 1 downloaded free app on the Apple Play Store. Most AI models are trained using supervised fine-tuning, meaning they learn by mimicking large datasets of human-annotated examples. This method has limitations.
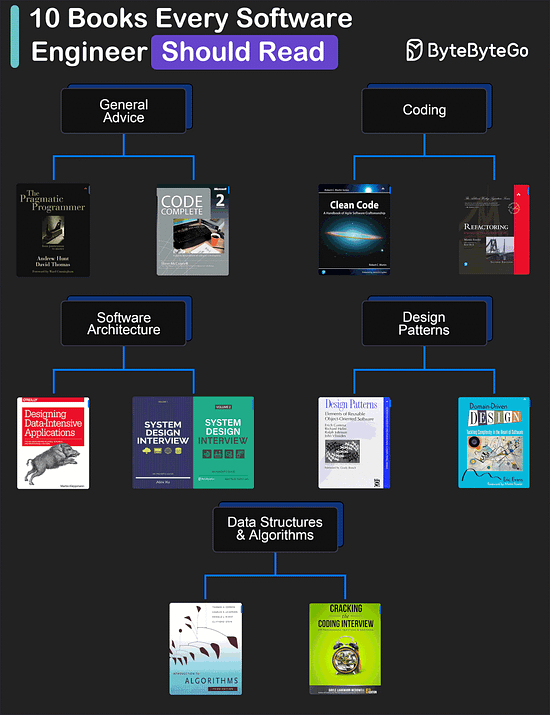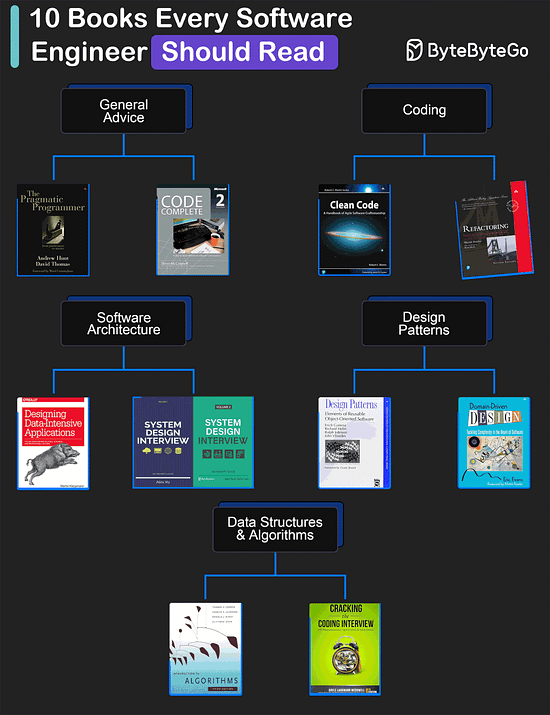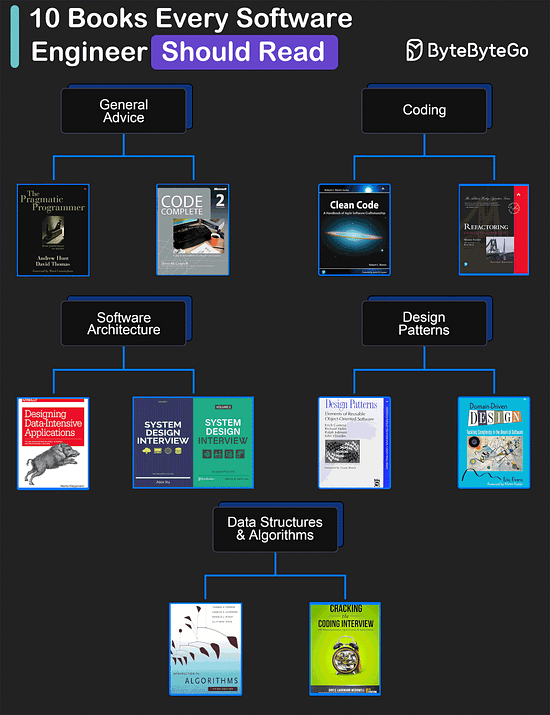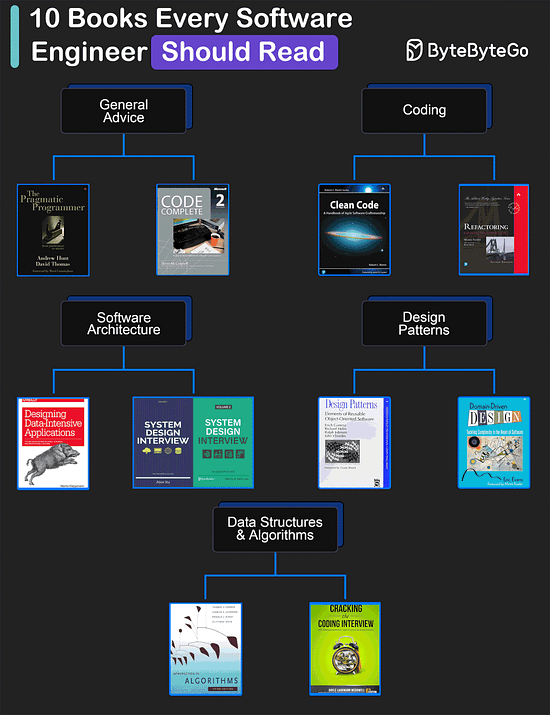
Over to you: Have you tried DeepSeek? Download the high-resolution image here. My Favorite 10 Books for Software DevelopersGeneral Advice
Coding
Software Architecture
Design Patterns
Data Structures and Algorithms
Over to you: What is your favorite book? How I use 20+ AI models in one app(PRESENTED BY YOU.COM)I routinely have ChatGPT, Claude, and DeepSeek open side-by-side because each model excels at tasks that the others don't. That’s why I like using You.com, the tool that combines the most popular AI models in one app:
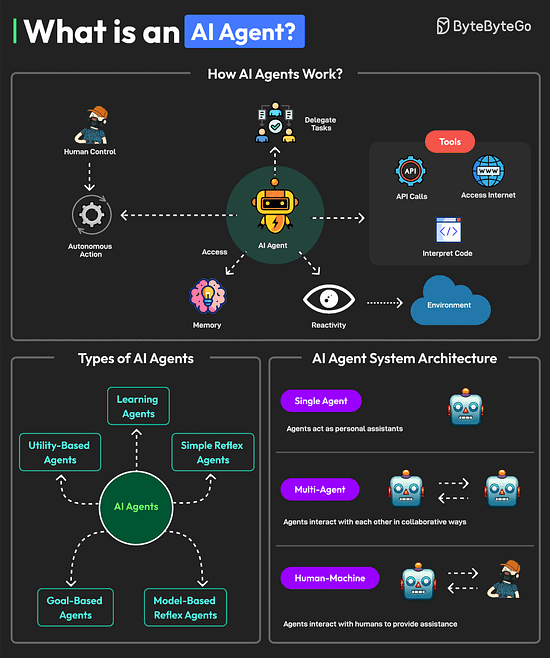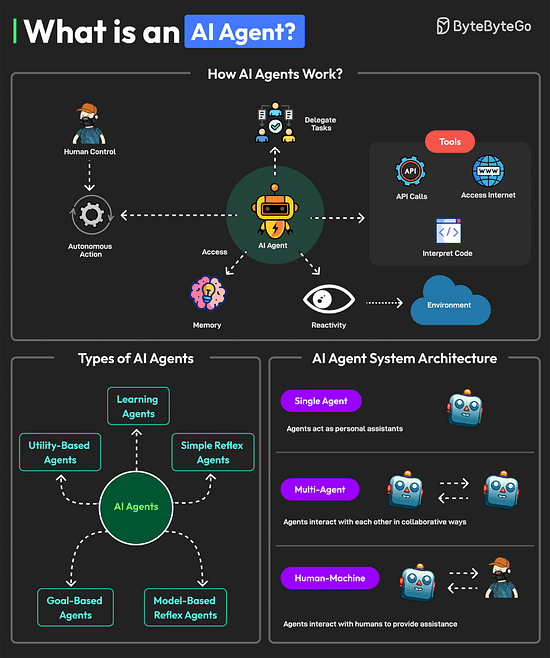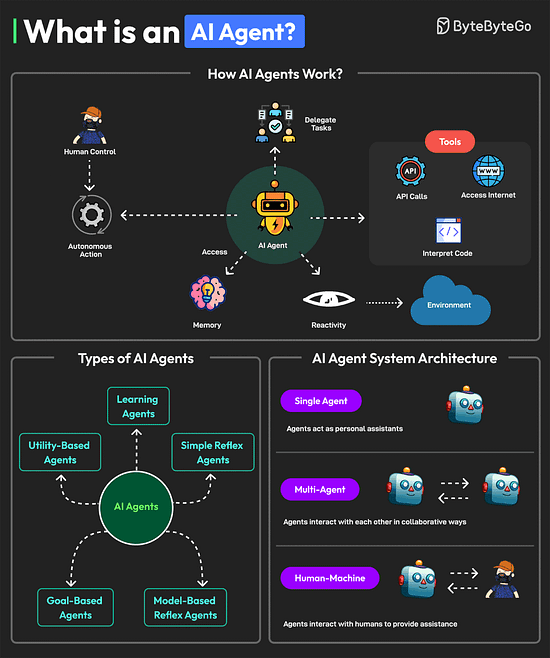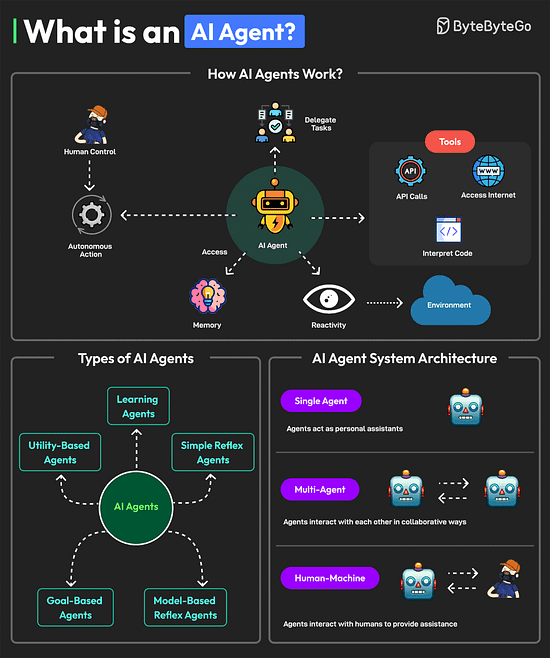
Ends soon: Access 12 months of Pro at no cost ($180 value). Just visit the offer page to redeem your special offer as a ByteByteGo newsletter subscriber. What is an AI Agent?An AI agent is a software program that can interact with its environment, gather data, and use that data to achieve predetermined goals. AI agents can choose the best actions to perform to meet those goals. Key characteristics of AI agents are as follows: An agent can perform autonomous actions without constant human intervention. Also, they can have a human in the loop to maintain control.
Multiple types of AI agents are available such as learning agents, simple reflex agents, model-based reflex agents, goal-based agents, and utility-based agents. A system with AI agents can be built with different architectural approaches.
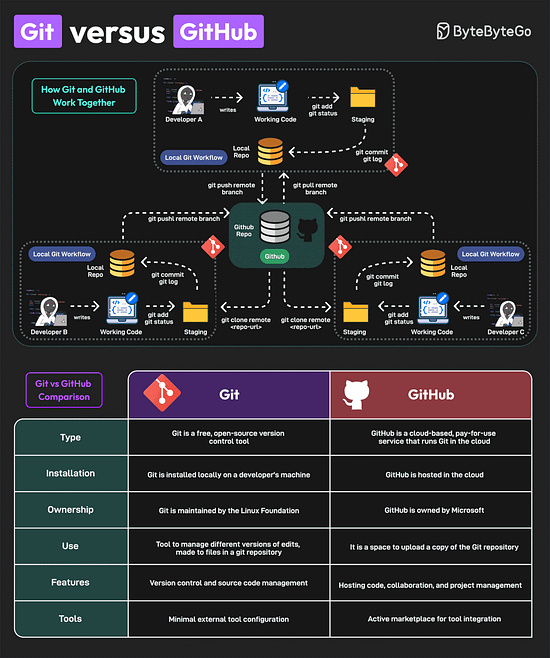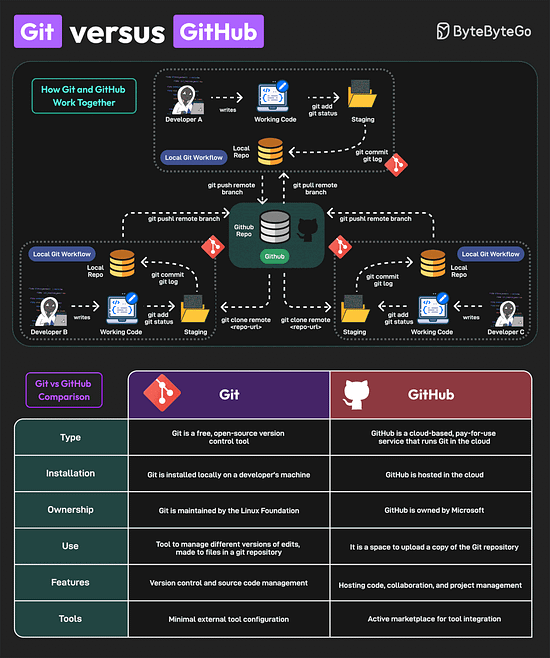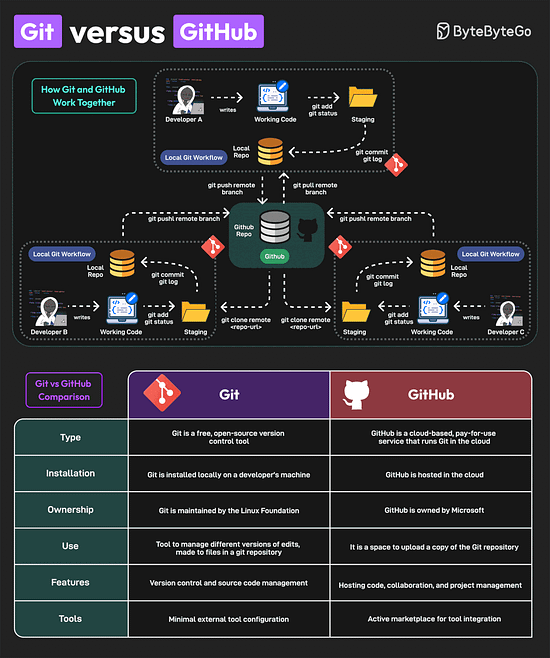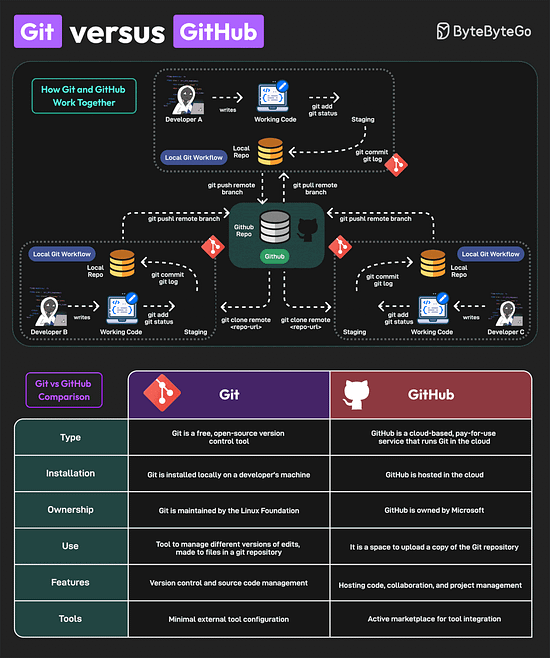
Over to you: Have you used AI Agents? Git vs GitHubGit and GitHub are popular tools for version control. They work together and complement each other to provide effective source control management. On a high level, Git is focused on version control and code sharing, whereas GitHub is focused on centralized source code hosting for sharing with other developers. However, they have some key differences
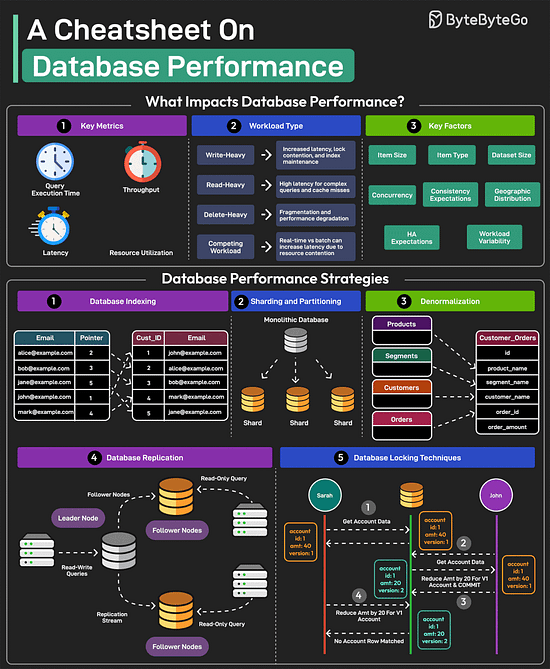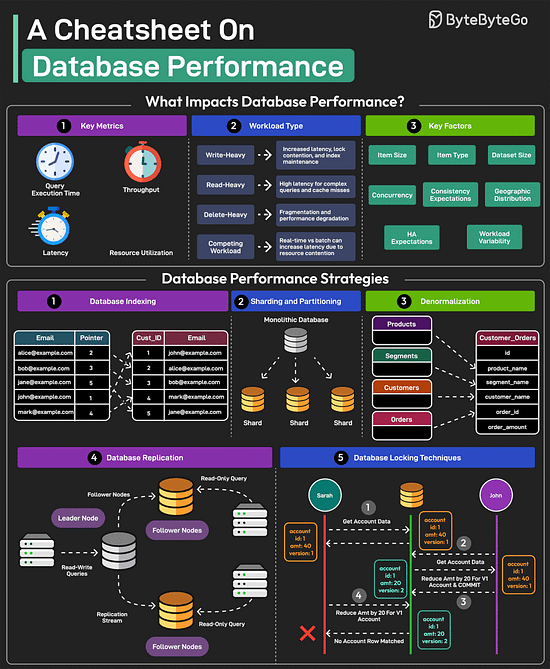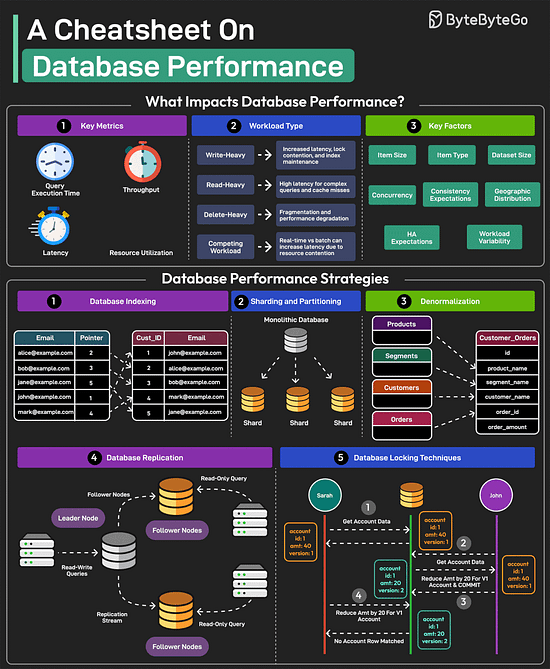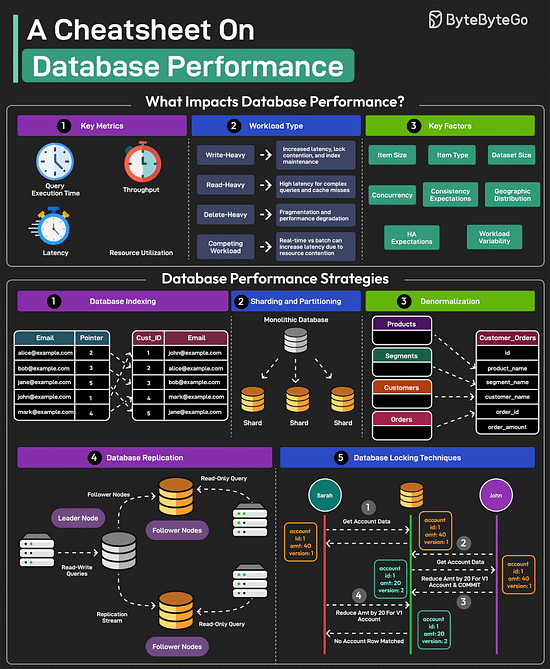
Lastly, you can use Git without GitHub but you cannot use GitHub without Git. A Cheatsheet on Database PerformanceGood database performance is critical since it directly impacts user experience, operational costs, and scalability. But what impacts database performance? Evaluating database performance depends on key metrics such as query execution time, throughput, latency, and resource utilization. Other factors that impact performance are item size, item type, dataset size, concurrency expectations, consistency requirements, HA expectations, and geographic distribution.
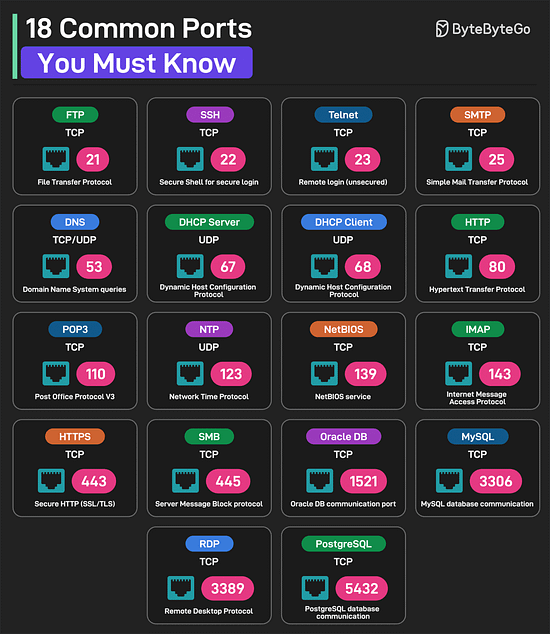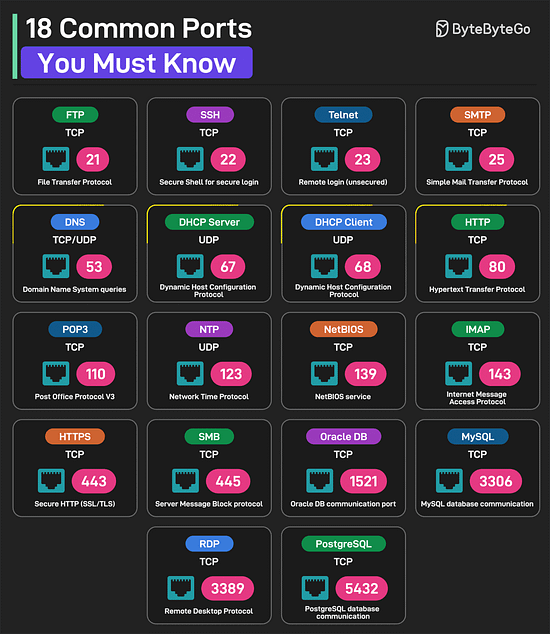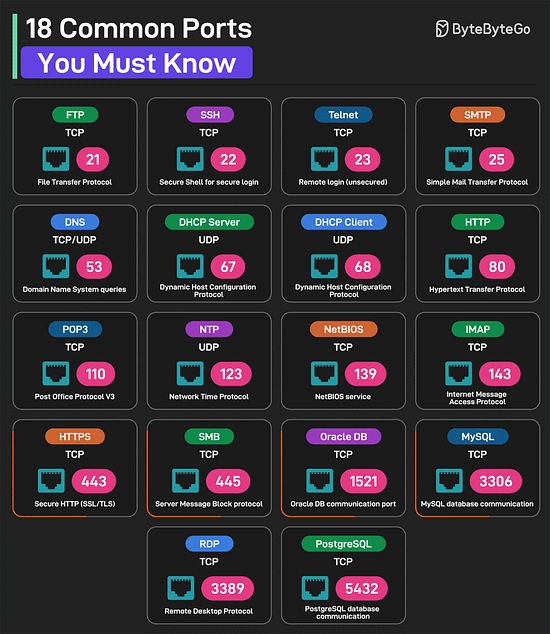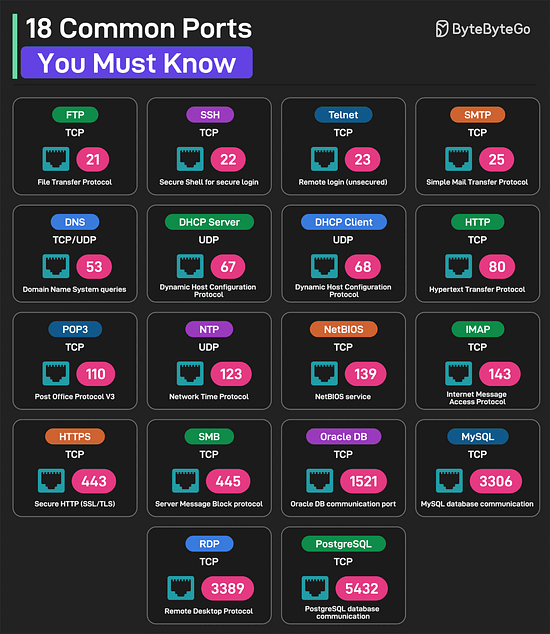
Over to you: Which other database performance strategy will you add to the list? 18 Common Ports Worth Knowing
Over to you: Which other port will you add to the list? SPONSOR USGet your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals. Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases. Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com. © 2025 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:36 - 1 Feb 2025