- Mailing Lists
- in
- EP90: How do SQL Joins Work?
Archives
- By thread 5315
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 127
The year’s most popular articles from the McKinsey Quarterly
Giving customers what they want requires getting personal
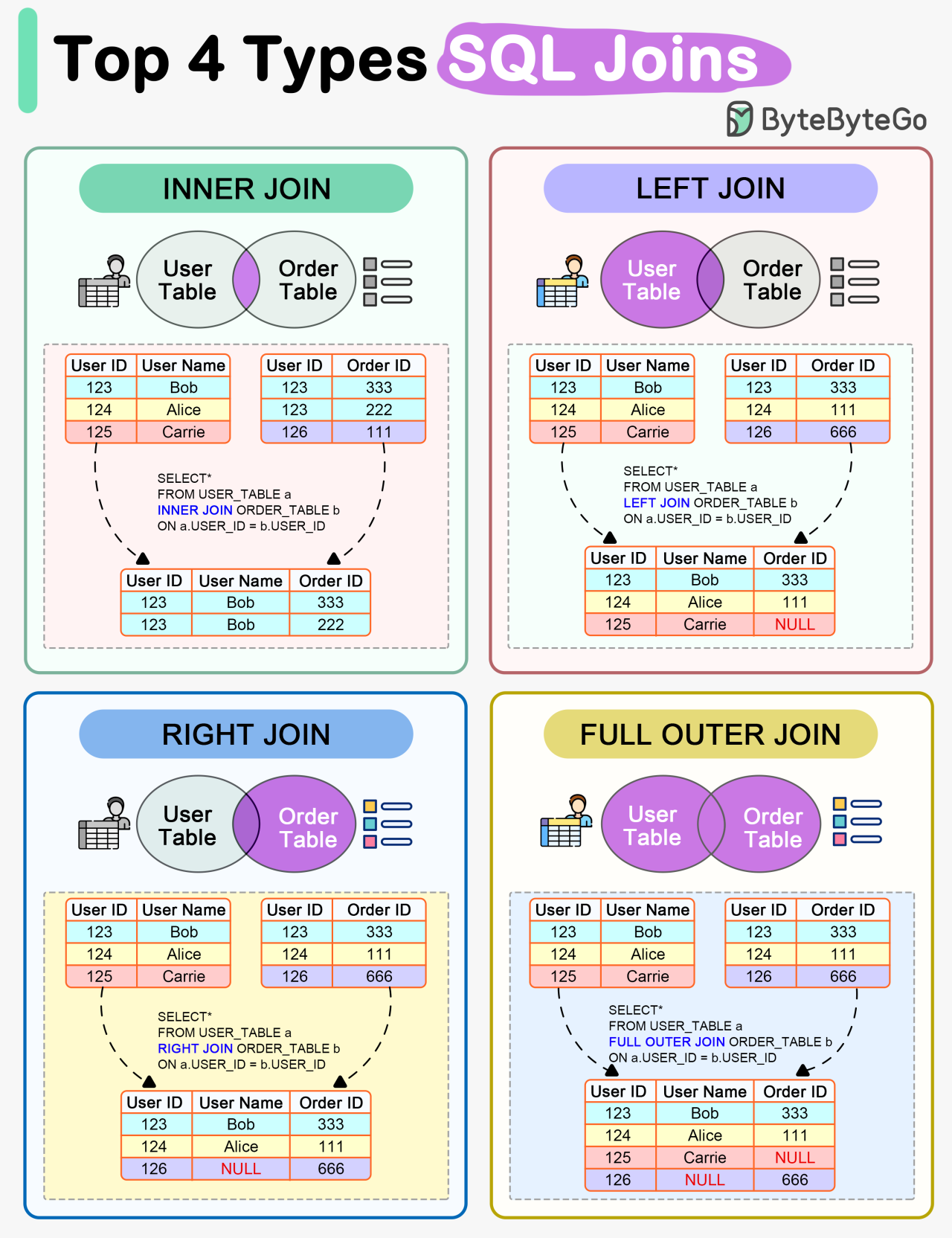
EP90: How do SQL Joins Work?
EP90: How do SQL Joins Work?
This week’ system design refresher:
Get paid to build full-stack Zero-Knowledge applications on Aleo (Sponsored)Unlock the future of dApps with Aleo's Layer-1 blockchain, where zero-knowledge tech is baked in—not tacked on. Enjoy the best of both worlds: bulletproof privacy and scalable performance, no crypto PhD required. Our language, Leo, and web-friendly SDK make it a breeze to integrate. Aleo has deployed over $1 Million in grants. How Does Linux Boot Process Work? How do SQL Joins Work?The diagram below shows how 4 types of SQL joins work in detail.
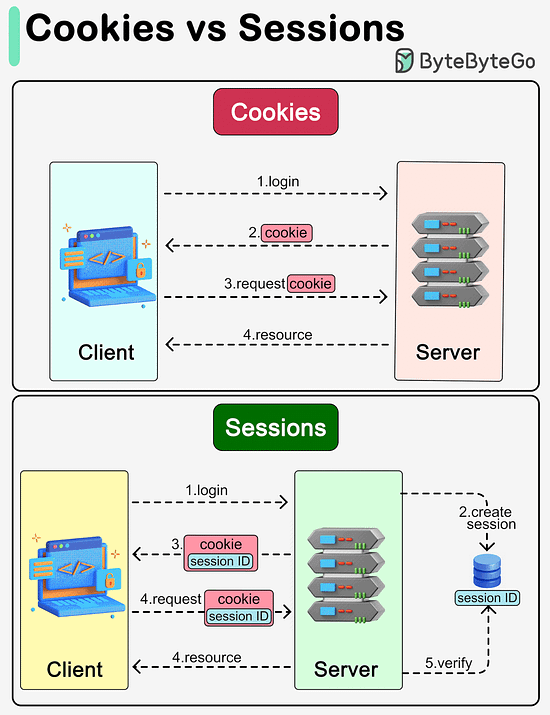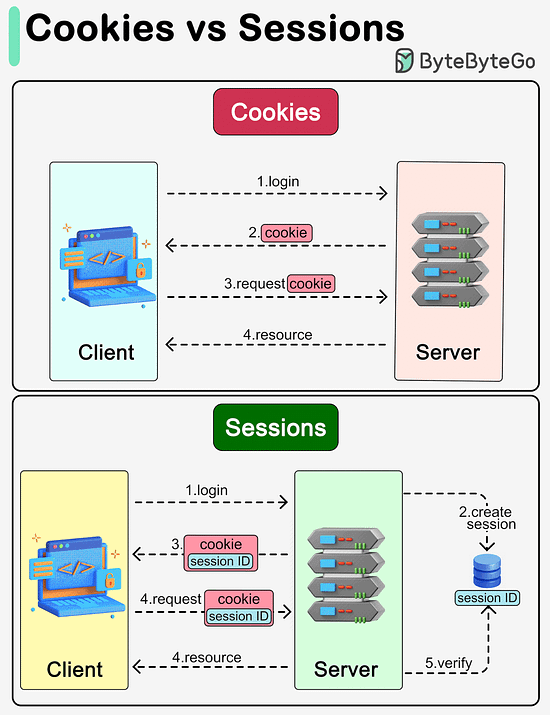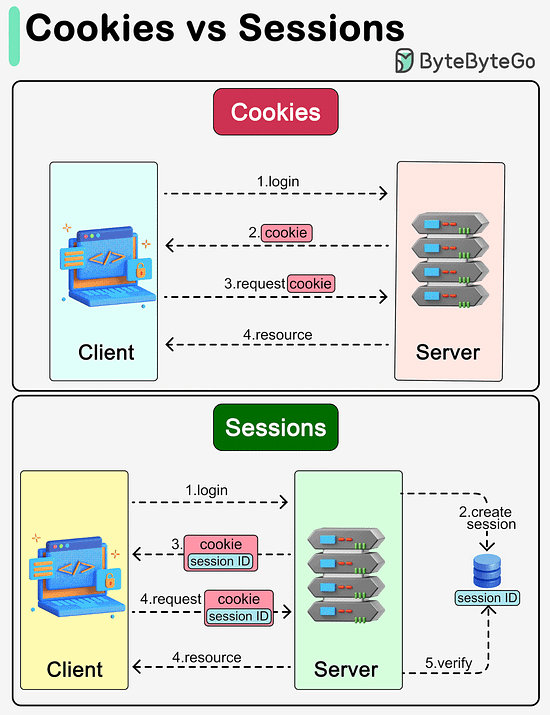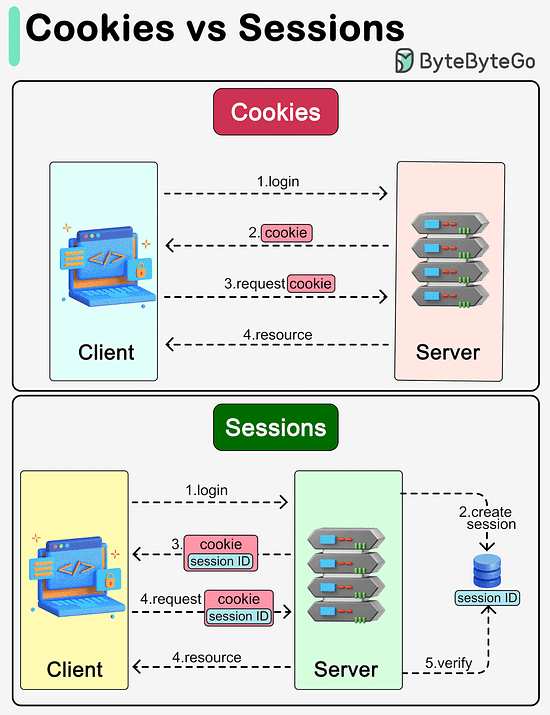
Latest articlesIf you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed this month. To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: What are the differences between cookies and sessions?The diagram below shows how they work. Cookies and sessions are both used to carry user information over HTTP requests, including user login status, user permissions, etc.
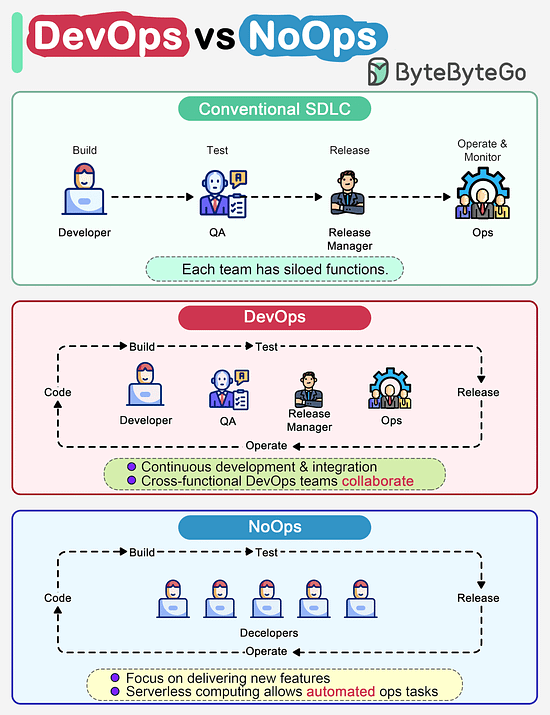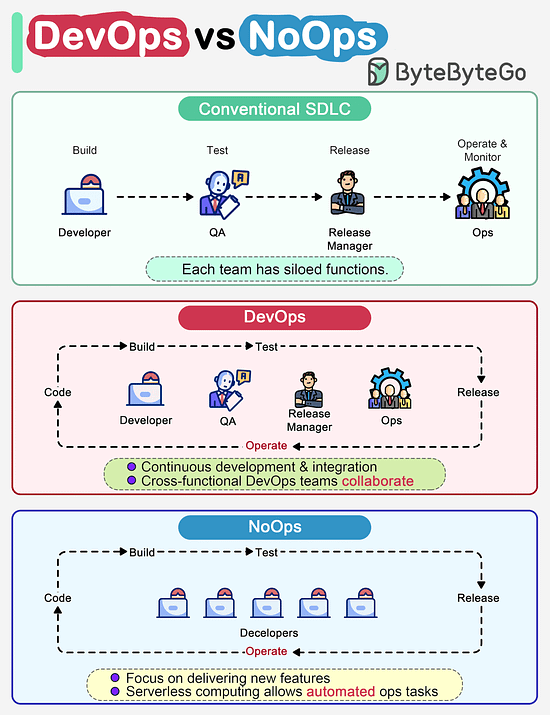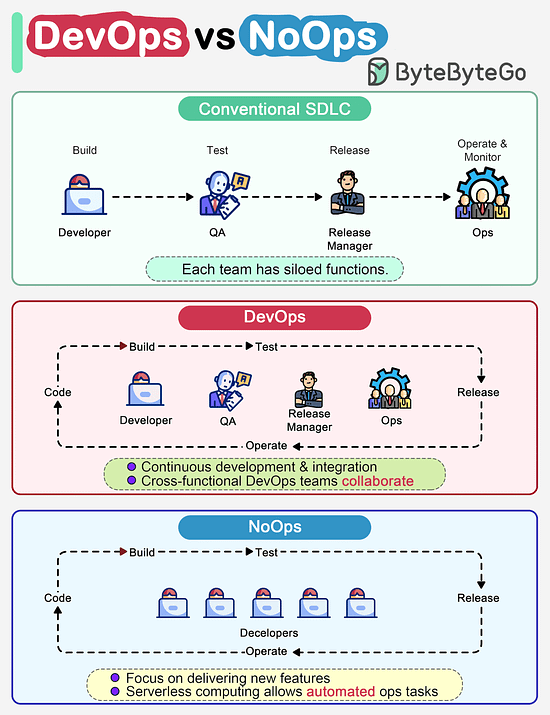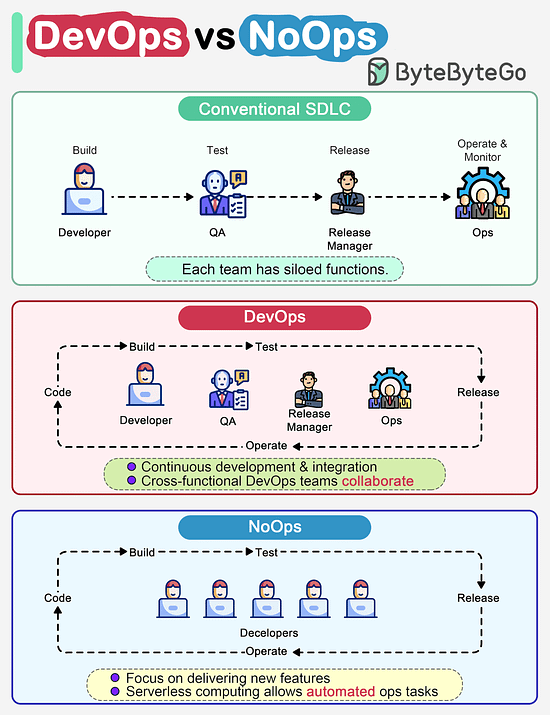
How do DevOps, NoOps change the software development lifecycle (SDLC)?The diagram below compares traditional SDLC, DevOps and NoOps. In a traditional software development, code, build, test, release and monitoring are siloed functions. Each stage works independently and hands over to the next stage. © 2023 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:36 - 16 Dec 2023