Archives
- By thread 5295
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 107
-
How to size up and increase your talent’s productivity
Only McKinsey
Measurements and tactics that make a difference
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:30 - 24 Jul 2024 -
Your company needs a superpower. Do you have what it takes to build one?
Intersection
Get your briefing Companies know they need new capabilities to thrive, but many struggle to build them. Identifying a superpower—a distinct institutional capability to enable them to excel—can help, say Brad Mendelson, Harald Fanderl, Homayoun Hatami, and Liz Hilton Segel. To learn how to build your superpower, check out the latest edition of the Five Fifty.
McKinsey helps companies develop their own superpowers, turning their ideas into impact. Learn more about how we’re moving companies forward.
Share these insights
Did you enjoy this newsletter? Forward it to colleagues and friends so they can subscribe too. Was this issue forwarded to you? Sign up for it and sample our 40+ other free email subscriptions here.
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to our McKinsey Quarterly Five Fifty alert list.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey Quarterly Five Fifty" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 05:03 - 23 Jul 2024 -
How Stripe Scaled to 5 Million Database Queries Per Second
How Stripe Scaled to 5 Million Database Queries Per Second
WorkOS: modern identity platform for B2B SaaS (Sponsored) Start selling to enterprises with just a few lines of code. → WorkOS provides a complete User Management solution along with SSO, SCIM, RBAC, & FGA. → Unlike other auth providers that rely on user-centric models, WorkOS is designed for B2B SaaS with an org modeling approach.͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreWorkOS: modern identity platform for B2B SaaS (Sponsored)
Start selling to enterprises with just a few lines of code.
→ WorkOS provides a complete User Management solution along with SSO, SCIM, RBAC, & FGA.
→ Unlike other auth providers that rely on user-centric models, WorkOS is designed for B2B SaaS with an org modeling approach.
→ The APIs are flexible, easy-to-use, and modular. Pick and choose what you need and integrate in minutes.
→ Best of all, User Management is free up to 1 million MAUs and comes standard with RBAC, bot protection, impersonation, MFA, & more.
Disclaimer: The details in this post have been derived from the Stripe Engineering Blog. All credit for the architectural details goes to Stripe’s engineering team. The links to the original articles are present in the references section at the end of the post. We’ve attempted to analyze the details and provide our input about them. If you find any inaccuracies or omissions, please leave a comment, and we will do our best to fix them.
As of 2023, only 19 countries had a GDP surpassing $1 trillion. Also, in 2023, Stripe alone processed $1 trillion in total payment value.
To make the achievement even more remarkable, they managed these numbers while supporting 5 million database queries per second at five-nines (99.999%) of availability.
What was behind the success of Stripe’s infrastructure?
The secret lies in the horizontal scaling capabilities of their database.
Stripe’s database infrastructure team built an internal database-as-a-service (DBaaS) offering called DocDB. It was created as an extension of MongoDB’s community edition because of MongoDB’s flexibility and ability to handle a massive volume of real-time data at scale.
In this post, we’ll explore how DocDB works and the various features it provides that allow Stripe to operate at such an incredible scale.
Why the Need for DocDB?
The first question while looking at DocDB is this: what forced Stripe to build a DBaaS offering?
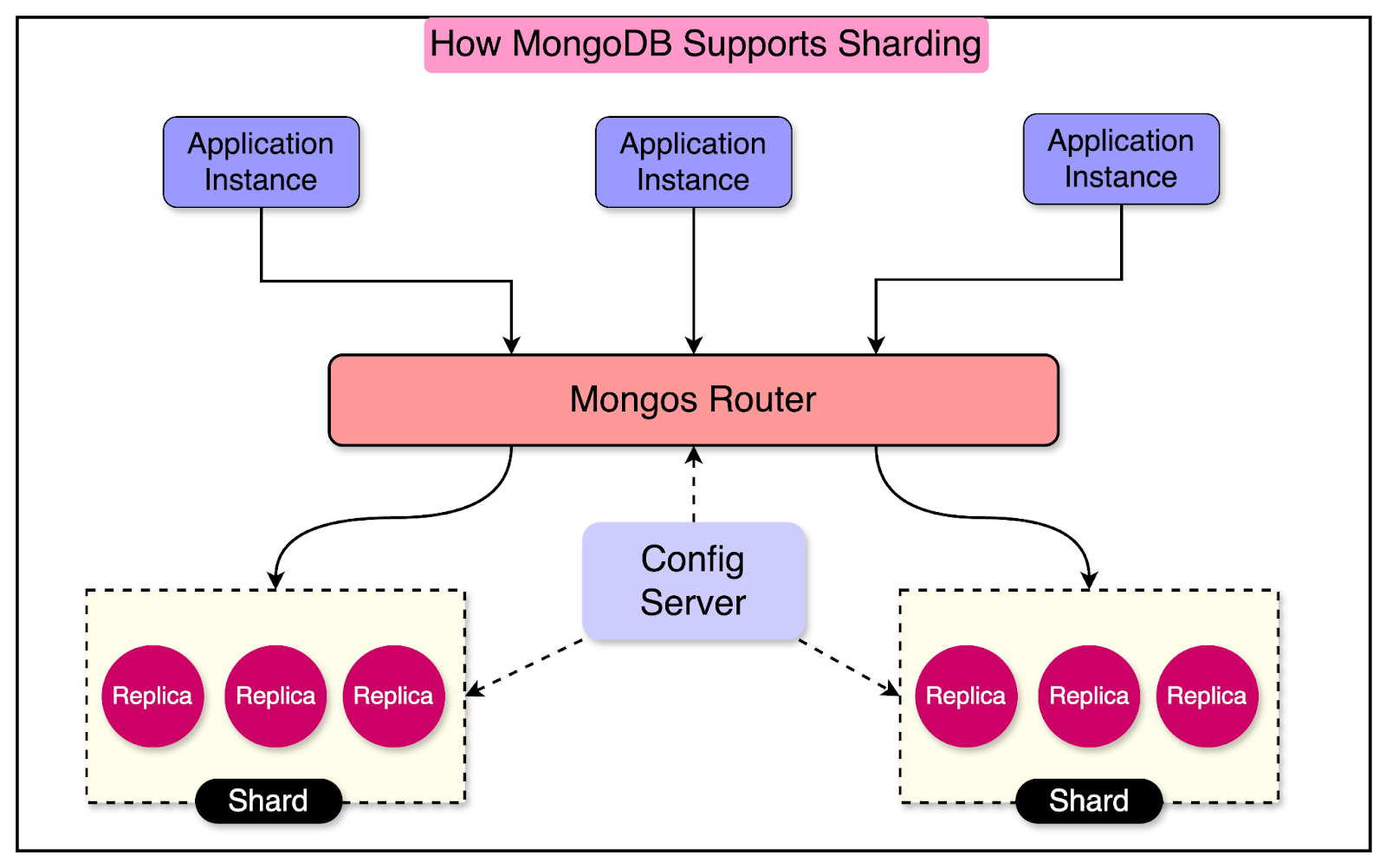
Stripe launched in 2011. At the time, they chose MongoDB as the online database because its schema-less approach made it more productive for developers than standard relational databases. MongoDB also supports horizontal scaling through its robust sharding architecture, which is shown in the diagram below:
However, to unlock the best developer experience, Stripe needed a database service that could work like a product for the development teams. MongoDB Atlas didn’t exist in 2011 and they couldn’t find an off-the-shelf DBaaS that met key requirements such as:
Maintain the highest standards of availability, durability, and performance.
Expose a minimal set of database functions to prevent issues from suboptimal client queries. For example, queries running on a large collection based on a specific field that does not have a corresponding index. It also includes unbounded queries on large result sets and complex aggregations.
Support horizontal scalability with sharding.
First-class support for multi-tenancy with quotas
Strong security with authorization policies.
The solution was to build DocDB with MongoDB as the underlying storage engine. The DocDB deployment was also highly customized to provide low latency and diverse access. Some interesting stats related to DocDB are as follows:
It supports over 10,000 distinct query types that run over petabytes of important financial data.
The data is spread across 5000+ collections.
The collections are distributed over 2000 database shards.
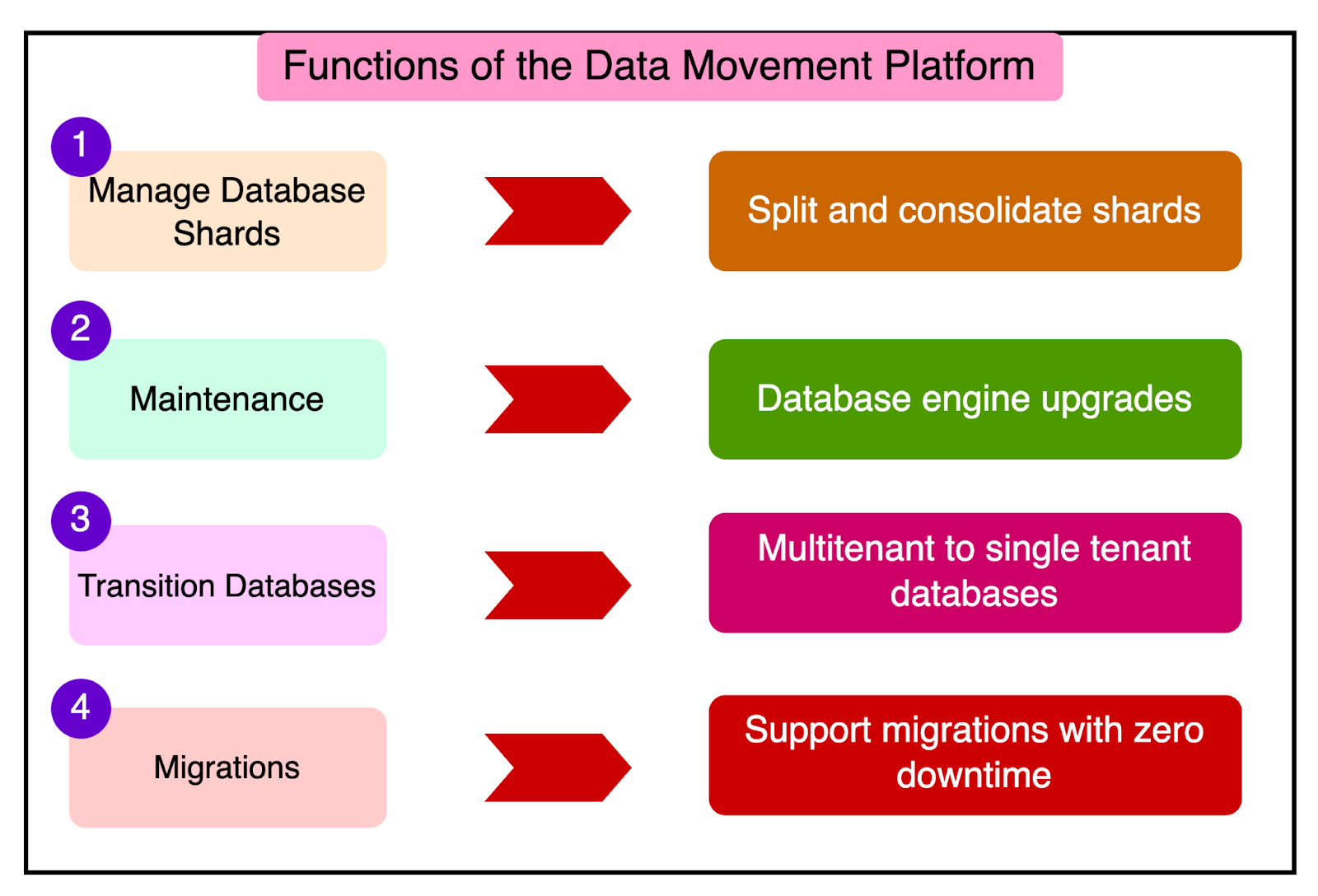
At the heart of DocDB is the Data Movement Platform. It was originally built as a horizontal scaling solution to overcome the vertical scaling limits of MongoDB.
The Data Movement Platform made it possible to transition from running a small number of database shards (each storing tens of terabytes of data) to thousands of database shards (each with a fraction of the original data).
The platform performs multiple functions such as:
Handling maintenance tasks like database engine upgrades.
Transitioning databases from a multitenant arrangement to single tenancy for large users. In a multitenant database arrangement, multiple users or applications share the same resources. In contrast, single tenancy means that a user or application has dedicated database resources for better isolation, customization, and performance.
Supporting migrations with zero downtime and no impact on the clients.
Splitting database shards during traffic surges and consolidating thousands of databases through bin packing when traffic is low.
For reference, bin packing is an optimization problem where the goal is to pack a set of objects (in this case, data) into a minimum number of bins (database shards) of a fixed capacity. The objective is to minimize the number of bins used while ensuring that the total size or weight of the objects in each bin does not exceed its capacity.
How Applications Access DocDB?
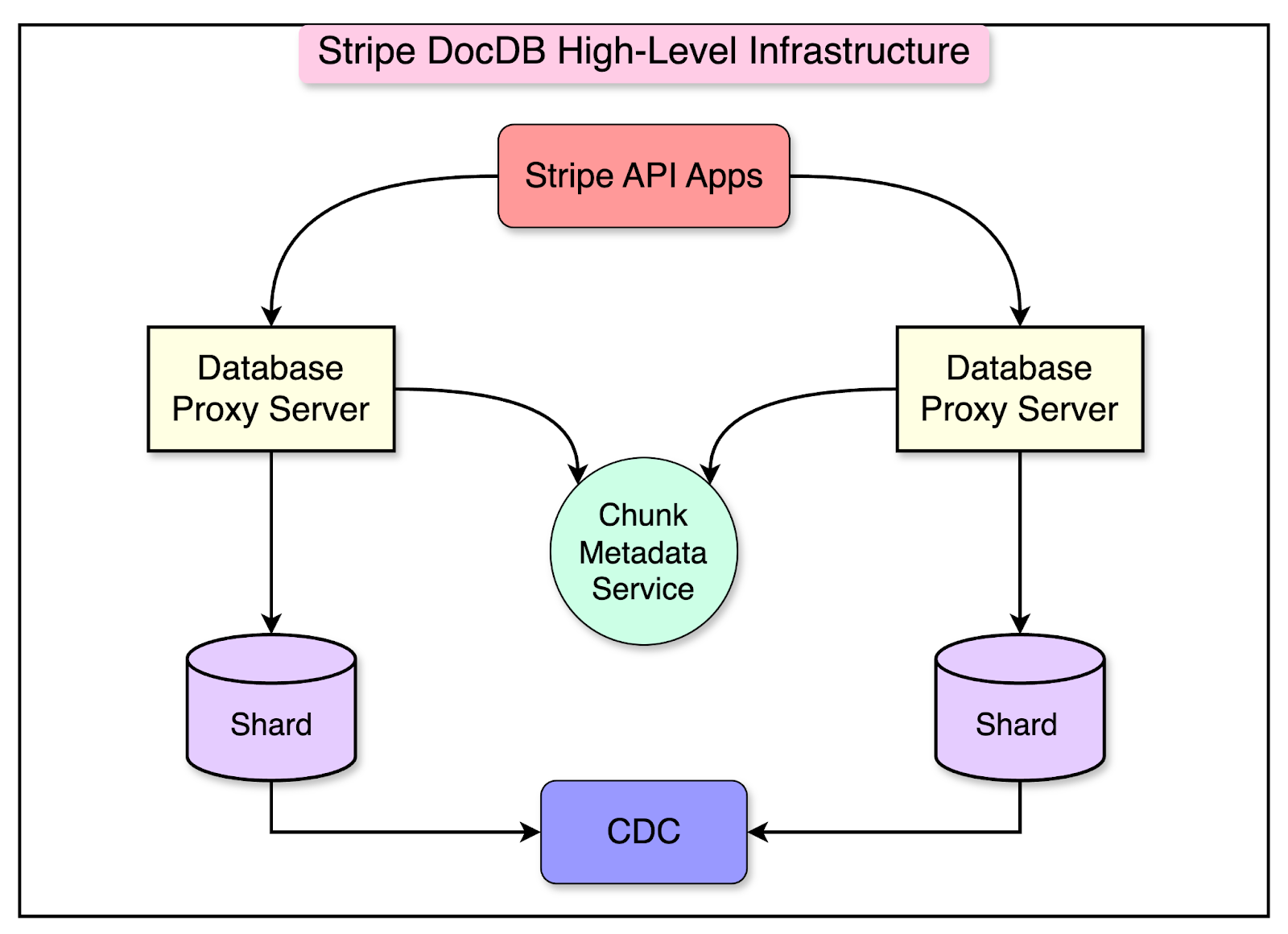
DocDB leverages sharding to achieve horizontal scalability for its database infrastructure. With thousands of database shards distributed across Stripe’s product applications, sharding enables efficient data distribution and parallel processing.
However, the use of database sharding introduces a challenge for applications when determining the appropriate destination shard for their queries.
To address this issue, Stripe’s database infrastructure team developed a fleet of database proxy servers implemented in Golang. These proxy servers handle the task of routing queries to the correct shard.
The diagram shows DocDB’s high-level infrastructure overview.
When an application sends a query to a database proxy server, it performs the following steps:
Parsing the query
Routing it to one or more shards
Combining the results received from the shards
Returning the final result to the application
But how do database proxy servers make the routing decisions?
The database proxy servers rely on the chunk metadata service to make routing decisions.
A chunk represents a small subset of data within a larger collection. Each shard contains a fraction of the total data, and these fractions are referred to as chunks.
For example, consider that Stripe has a large collection called “Transactions” that contains millions of documents representing financial transactions. To scale this collection horizontally, they might split the data into chunks based on a sharding key, such as customer ID or the transaction timestamp. Each chunk would then be assigned to a specific database shard.
The chunk metadata service manages the mapping between these chunks and their corresponding shards. It keeps track of which chunk resides on which shard, allowing the proxy servers to route queries and requests to the appropriate shard.
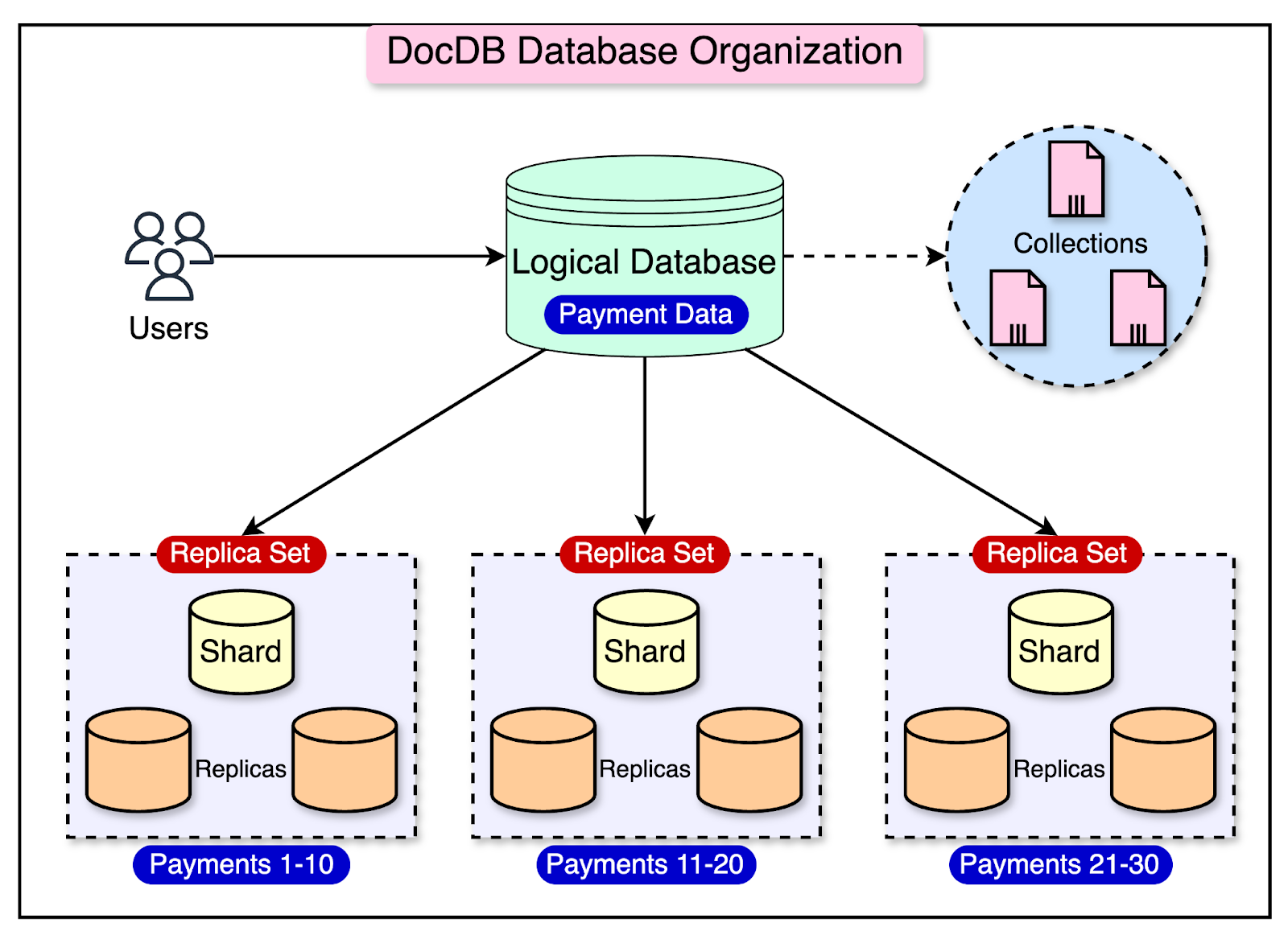
Data Organization in DocDB
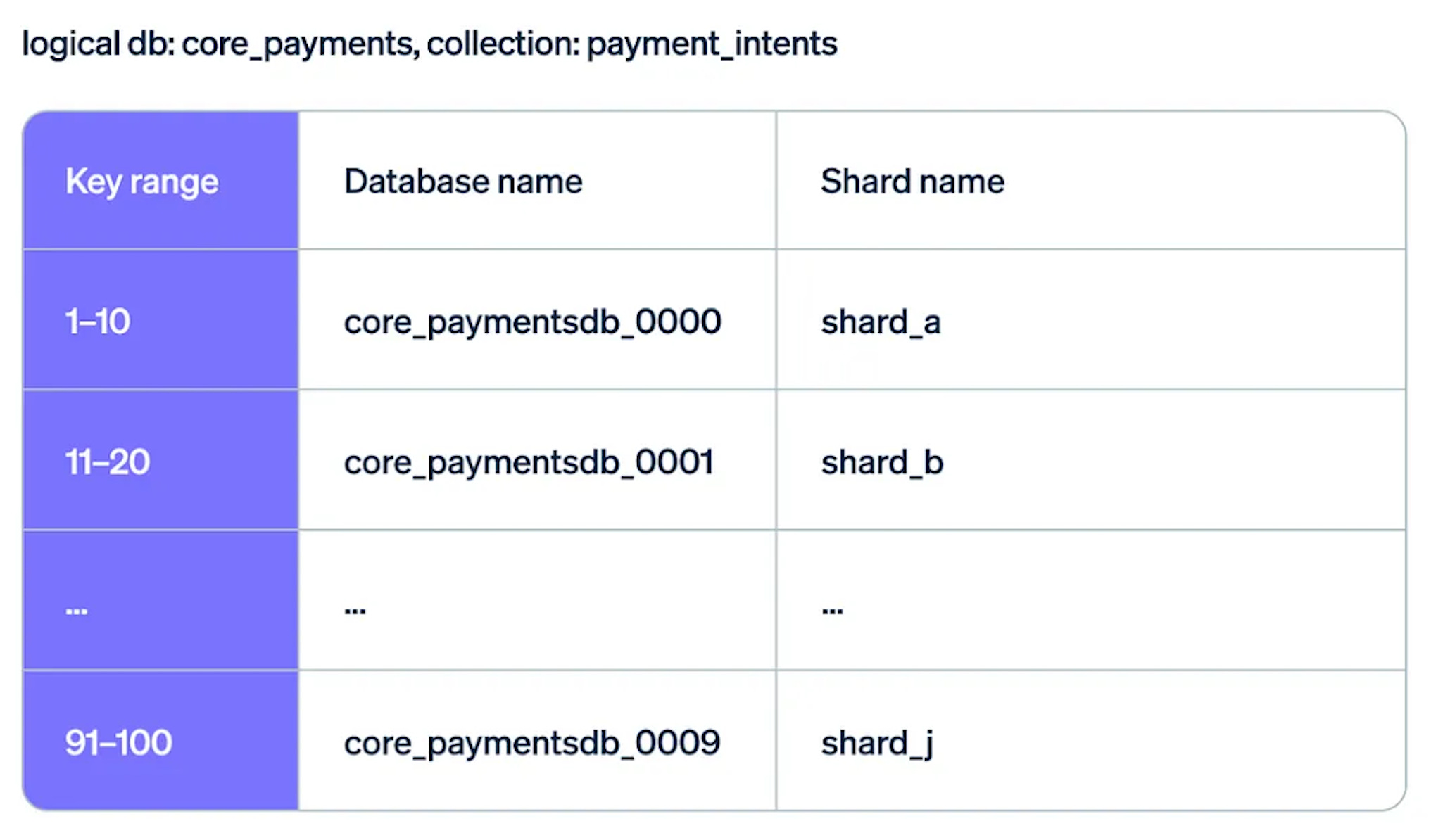
At Stripe, product teams use an in-house tool called the document database control plane to create and manage their databases. When a team provisions a new database using this tool, they are creating a “logical database.”
A logical database is like a virtual container holding one or more data collections known as DocDB collections. Each DocDB collection contains related documents that serve a specific purpose for the product team.
Even though a logical database appears as a single entity to the product team, the data within the collections is spread across multiple physical databases behind the scenes. These physical databases are the actual databases running on Stripe’s infrastructure.
The diagram below shows this arrangement:
Each physical database contains a small portion (or “chunk”) of the data from the DocDB collection and is deployed on a shard. The shard consists of a primary database node and several secondary database nodes. These nodes work together as a replica set.
The primary node handles all the write operations and replicates the data to the secondary nodes. If the primary node fails, one of the secondary nodes automatically takes over as the new primary, ensuring continuous operation and availability.
The diagram below shows a different representation of the database hierarchy
Source: Stripe Engineering Blog Latest articles
If you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
The Data Movement Platform
What’s the most important ability required to build a DBaaS platform that is horizontally scalable and highly elastic?
It’s the ability to migrate data across database shards with zero downtime and no impact on the client.
Stripe achieved this ability with their Data Movement Platform. The platform had a few important requirements such as:
Ensure that the data getting migrated is consistent and complete across both the source and target shards.
Prevent a situation of prolonged downtime. Millions of businesses rely 24/7 on Stripe to accept payments from their customers.
Support the migration of an arbitrary number of chunks from any number of sources to target shards. Moreover, the migration should take place at a high throughput.
Prevent any performance impact on the source shard during the migration process.
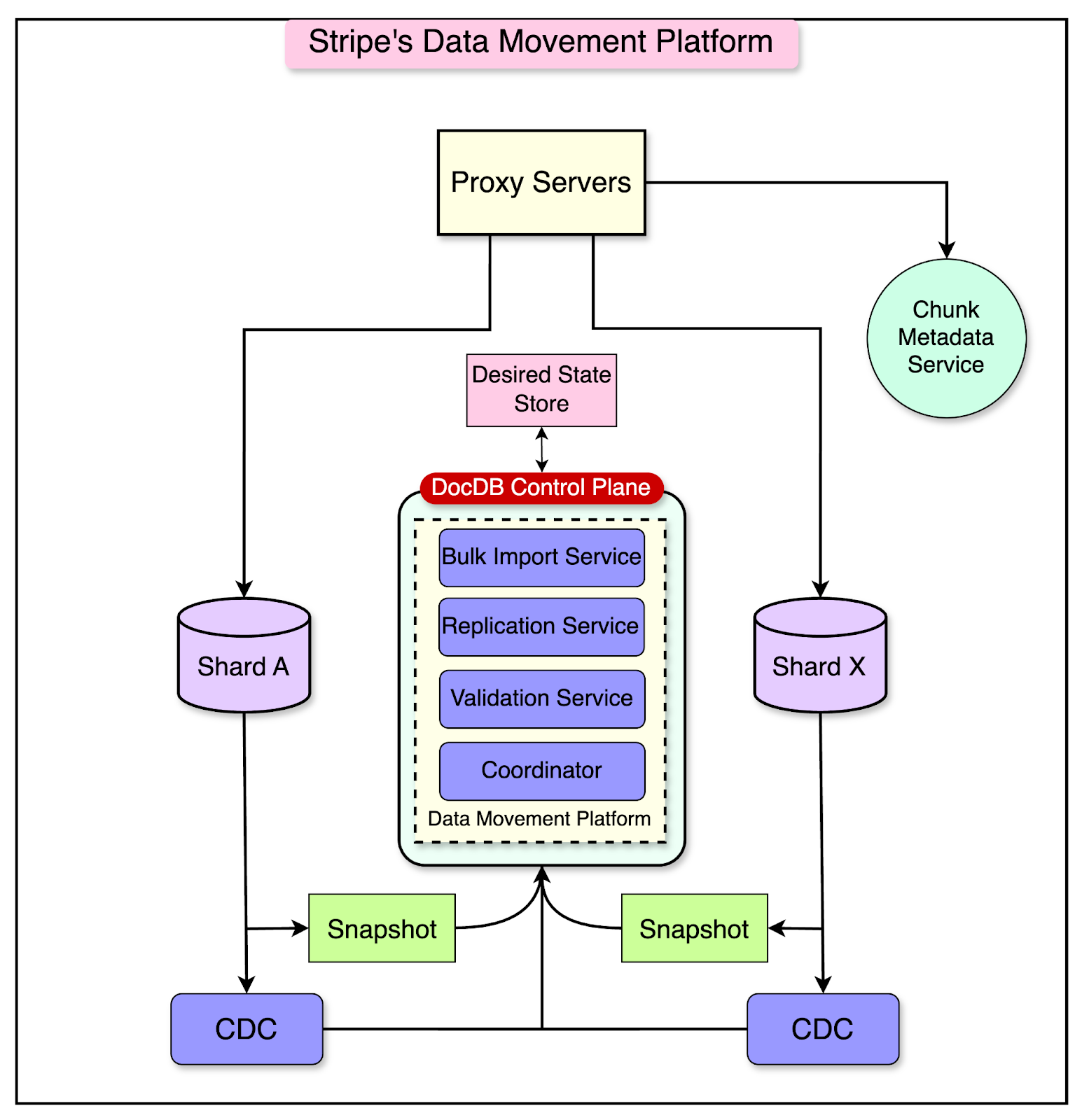
The diagram below shows the architecture of the Data Movement Platform:
The heart of the platform is the Coordinator component, which is responsible for orchestrating the various steps involved in online data migrations.
Step 1: Chunk Migration Registration
The first step is registering a request to migrate database chunks from source shards to target shards.
Once the request is created, indexes are built on the target shards.
An index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table or collection. Building the index first on the target shard has some advantages:50
Query Performance: By creating indexes on the target shards before data migration, Stripe ensures that the target shards are ready to handle queries efficiently as soon as the data is available. Without pre-built indexes, queries on the newly migrated data would have to perform full collection scans, leading to slower query response times until the indexes are created.
Consistency: Building indexes on the target shards before data migration helps maintain consistency between the source and target shards. If indexes were created after the data migration, it would result in inconsistent query behavior for some time.
Seamless Transition: Having the indexes ready on the target shards minimizes the impact on the applications and users querying the data.
Step 2: Bulk Data Import
The next step involves using a snapshot of the chunks on the source shard at a specific point in time. This snapshot is used to load the data onto one or more target database shards.
The service performing the bulk data import accepts data filters, allowing for the selective import of chunks that satisfy the specified filtering criteria. This step initially appeared straightforward. However, Stripe’s infra team encountered throughput limitations when they tried to bulk load data onto a DocDB shard.
Efforts to address the issue by batching writes and adjusting DocDB engine parameters were not successful.
A significant breakthrough came when the team explored methods to optimize the insertion order by using the fact that DocDB organizes its data using a B-tree data structure. By sorting the data based on the most common index attributes in the collections and inserting it in sorted order, the write proximity was enhanced, resulting in a 10X boost in write throughput.
Step 3: Async Replication
After the bulk data import step is completed, the next step ensures that any subsequent writes or mutations that occur on the source shard after time T are replicated to the target shard.
This is where async replication comes into play.
Stripe’s async replication systems rely on the Change Data Capture (CDC) mechanism to capture and replicate the mutations from the source shards to the target shards.
Here’s how it works:
Operations Log (Oplog): Each DocDB shard maintains a special collection called the Oplog, which records all the operations that modify data on the shard. Wherever a write operation occurs on the source shard, it is logged in the Oplog.
Oplog Transport: Oplog entries from each DocDB shard are transported to Kafka which acts as a message broker, allowing Oplog events to be consumed by downstream systems. Additionally, these events are archived in a cloud object storage service like Amazon S3 for durability and long-term storage.
Replication Service: Stripe built a dedicated service to handle the replication of mutations from the source shards to the target shards. This service consumes Oplog events from Kafka and S3 and applies the corresponding writes to the target shards. By relying on Oplog events from the CDC systems, the replication service avoids impacting the performance of user queries on the source shard. It doesn’t consume read throughput on the source shard, which would otherwise be available for serving user queries.
Bidirectional Replication: Mutations are replicated bidirectionally, meaning that writes are replicated from the source shards to the target shards and vice versa. This is done to provide flexibility in case there is a need to revert traffic to the source shards if any issues arise when directing traffic to the target shards.
Step 4: Correctness Check
After the replication sync between the source and target shard, the Coordinator conducts a comprehensive check for data completeness and correctness.
This is done by comparing point-in-time snapshots. It was a deliberate design choice to avoid impacting the shard’s throughput.
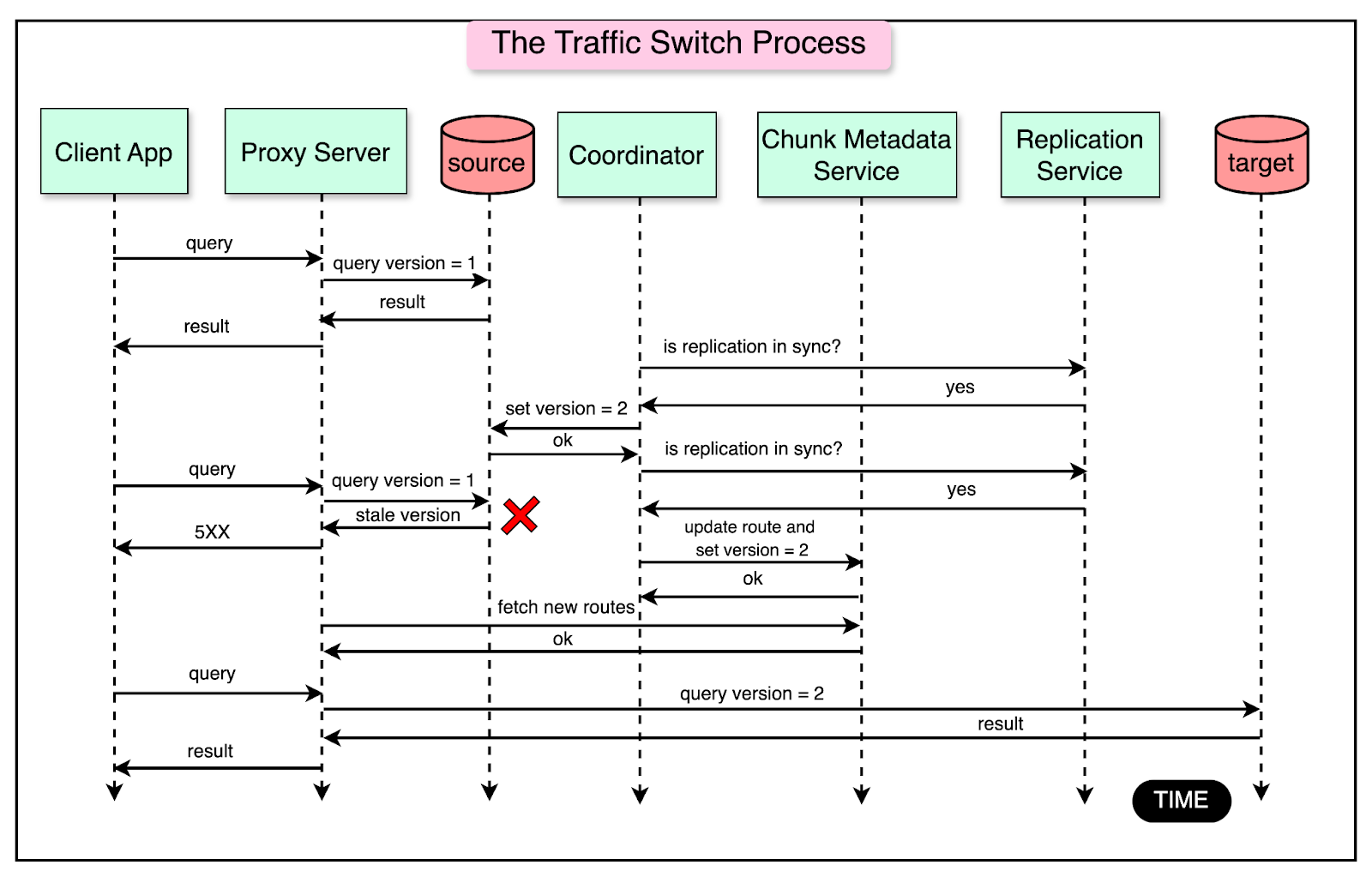
Step 5: Traffic Switch
The next step is to switch the traffic of incoming requests from the source shard to the target shard.
The Coordinator orchestrates the traffic switch after the data is imported to the target shard and the mutations are replicated. The process consists of three steps:
Stop the traffic on the source shard for a brief period
Update the routes in the chunk metadata service
Make the proxy server redirect reads and writes to the target shards.
The traffic switch protocol uses the concept of versioned gating.
To support this, the infra team added a custom patch to MongoDB that allows a shard to enforce a version number check before serving a request. Each proxy server annotates requests to the DocDB shard with a version token number. The shard first checks the version token number and serves the request only if the token number is newer than the earlier one.
The diagram below shows the detailed process flow for the traffic switch protocol:
Here’s how the process works:
The version token number is stored in a document in a special collection in DocDB. They increase the token number on the source DocDB shard. This allows all reads and writes on the chunk on the source shard to be rejected.
Then, they wait for the replication service to replicate any outstanding writes on the source.
Once the replication is over, they update the route for the chunk to point to the target shard. Also, the version token number in the chunk metadata service is updated.
The proxy servers fetch the updated routes for the chunk along with the most up-to-date token number from the chunk metadata service. Using the updated routes, the proxy servers route the traffic to the target shard.
The entire traffic switch protocol takes less than two seconds to execute. Any failed reads and writes to the source shard succeed on retries that go to the target shard.
Step 6: Chunk Migration Deregistration
Finally, the migration process is concluded by marking the migration as complete in the chunk metadata service.
Also, the chunk data is dropped from the source shard to reclaim the resources.
Conclusion
Stripe’s custom-built database-as-a-service, DocDb, and its Data Movement Platform have been instrumental in achieving 99.999% uptime while enabling zero-downtime data migrations.
Some key takeaways are as follows:
DocDB extends the MongoDB Community edition to provide a highly available and scalable database solution.
Sharding is employed to horizontally scale the database, with data distributed across thousands of shards.
The Data Movement Platform enables online migrations across shards while ensuring data consistency, availability, and adaptability.
The six-step migration process consists of chunk migration registration, bulk data import, async replication, correctness checks, traffic switching, and chunk migration deregistration.
The Data Movement Platform is used for various purposes such as splitting DocDB shards for size and throughput, bin-packing underutilized databases, and upgrading the database infrastructure fleet.
References:
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing hi@bytebytego.com
Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 23 Jul 2024 -
How can leaders effectively scale generative AI?
Only McKinsey
3 actions that can help •
Difficulties with data. Data and AI leaders have been working feverishly on gen AI use cases for more than a year. There’s considerable value at stake and also some challenges in getting to scale, particularly with managing data. (Managing data remains one of the main barriers to value creation from gen AI.) In fact, 70% of top performers in a recent McKinsey survey say that they have encountered difficulties integrating data into AI models, McKinsey senior partner Kayvaun Rowshankish and coauthors explain.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 11:08 - 22 Jul 2024 -
See you at Black Hat, Las Vegas, on August 6! 👋
Sumo Logic
Securing the future – together.

 Black Hat 2024 is the heart of cybersecurity innovation. This year, Sumo Logic will be dealing our best hand yet, and we want you at the table.
Black Hat 2024 is the heart of cybersecurity innovation. This year, Sumo Logic will be dealing our best hand yet, and we want you at the table.
Cybersecurity stakes are higher than ever and it's time to place your bet on a sure thing.
Sumo Logic is leading the charge with cutting-edge solutions that transform data chaos into cybersecurity clarity. Think of it as your security royal flush.
Book a meeting with our team before your schedule is spoken for.
Sumo Logic, Aviation House, 125 Kingsway, London WC2B 6NH, UK
© 2024 Sumo Logic, All rights reserved.Unsubscribe 
by "Sumo Logic" <marketing-info@sumologic.com> - 06:02 - 22 Jul 2024 -
Gearing up for small-business success: A leader’s guide
Leading Off
Growing pains Definitions of what constitutes a small business vary across countries and regions—for example, some microenterprises may employ fewer than ten workers and generate only modest revenues. But regardless of their size, small and medium-size businesses (SMEs) have been the backbone of most economies for decades, accounting for 70 percent of all jobs around the world. The COVID-19 pandemic took a heavy toll on these businesses. Although they have recovered somewhat, many SMEs may lack the resources, talent, and capabilities to expand over the long term. This week, we look at what it may take for this key segment of the world economy to thrive.
Small businesses account for more than 90 percent of all global enterprises, but their productivity is only about half that of large companies. New research led by McKinsey senior partners Marco Piccitto and Olivia White and colleagues reveals ways to narrow the productivity gap: doing so could equal 2–15 percent of GDP across advanced and emerging economies. The gap tends to vary most among subsectors—for example, in one country, “small businesses engaged in the manufacture of tobacco products are only 35 percent as productive as larger counterparts, while those manufacturing basic metals are 85 percent as productive,” the McKinsey researchers observe. “This granular view at the subsector level is important when setting aspirations for, and thinking about ways to boost, [small business] productivity.”
That’s the number of trends that banks may want to consider to better serve their small-business clients. Our survey of more than 1,200 US businesses with up to $50 million in annual revenue reveals that SMEs can be a notable growth engine and source of stability for financial institutions. For example, SMEs generally prefer to get all their financial needs fulfilled from a single source. “Typically, the larger a small business grows, the more complex its financial needs become and the more it becomes interested in comprehensive solutions,” note McKinsey senior partner Marukel Nunez Maxwell and partner Abhilash Sridharan, coauthors of our survey report. “To meet these needs, banks could offer bundled cash flow management tools and explore partnerships with specialized fintechs.”
That’s McKinsey partner Anu Madgavkar on the results of our latest analysis of small to midsize companies. Spanning 16 countries and more than 200 subsectors, the research reveals some “universal principles”—for example, identifying differentiators such as capital, skills, or technology—to raise productivity, Madgavkar says. But partnering with larger companies could be the most effective way for small businesses to perform better. “Often, they are interacting with a larger company, as a consumer or a buyer,” she says. “Understanding those kinds of networks is, I think, the most powerful idea that came from this research.”
Scaling may be one of the most persistent difficulties for small businesses—but discipline and structure enabled digital-coaching provider CoachHub to achieve it quickly. “From the beginning [in 2018], it was clear that we had to operate this business at scale to have the impact we wanted,” says cofounder and CEO Matti Niebelschütz in a discussion with McKinsey’s Alexander Baranov and Gisa Springer. “But even when you have a big vision, you begin with small steps.” That meant setting just three initial targets: building a minimal viable product, acquiring 30 coaches, and getting ten paying clients. Staying focused on those goals enabled CoachHub to expand within Europe over the next three years and eventually to 90 countries. “I’m a start-up guy at heart,” says Niebelschütz. “I like to build things and break them. But once we had several hundred employees, I realized that . . . I had to steer the business with our long-term objectives in mind.”
It’s back—and it’s better than ever. Our 2024 annual book recommendations list includes more than 90 books spanning ten genres, with suggestions from global leaders across six continents. Fiction is a hot favorite, but books on longevity (“Should we start thinking that we might live a lot longer?” asks McKinsey senior partner Sven Smit) and technology are not far behind. And whether your organization is small or large, you can’t go wrong by reading up on leadership. Our brand-new book, The Journey of Leadership: How CEOs Learn to Lead from the Inside Out, comes out this fall. “Using many intimate stories, the book brings to life the personal inner struggles of CEOs on their way to the top,” says McKinsey senior partner Homayoun Hatami.
Lead by supporting small businesses.
— Edited by Rama Ramaswami, senior editor, New York
Share these insights
Did you enjoy this newsletter? Forward it to colleagues and friends so they can subscribe too. Was this issue forwarded to you? Sign up for it and sample our 40+ other free email subscriptions here.
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to the Leading Off newsletter.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey Leading Off" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 04:50 - 22 Jul 2024 -
What does India’s future hold?
Only McKinsey
Challenges and opportunities in India •
Extraordinary growth. Could this be India’s century? With leaders of the world’s fifth-largest economy renewing their commitment to several economic goals, the private sector will be a key partner in helping India achieve growth and bolster economic inclusion. A McKinsey analysis reveals that between 2012 and 2022, one in five publicly traded Indian companies doubled its revenue every five years and quadrupled it in ten, McKinsey senior partner Jaidit Brar and coauthors share.
•
Accelerating equality. Technological innovation has a major role to play in accelerating equality in India, including in agriculture, which could boost the economy and significantly improve farmers’ livelihoods and income. The agricultural-technology ecosystem has the potential to increase Indian farmers’ incomes by up to 35 percent, McKinsey has found. Read “What does the future hold for India?,” a new McKinsey Explainer that explores seven themes that could influence India for years to come. And for more insights on India’s challenges and opportunities, read this interview with McKinsey global managing partner Bob Sternfels and McKinsey’s India managing partner Rajat Dhawan.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:39 - 22 Jul 2024 -
JASA PENAWARAN PENERBITAN JAMINAN BANK GARANSI DAN ASURANSI TANPA AGUNAN
Kepada Yth,
Perusahaan Kontraktor BUMN & Swasta PT, LTD, TBKUp : Bagian Keuangan/Finance Manager
Perihal : Penawaran Jasa Penerbitan Bank Garansi & Surety Bond Tanpa Agunan
Dengan Hormat,
Kami dari PT. BERDIKARI BINA GARANSI (BBG) dengan NO NPWP : 92.067.813.2-001.000 dimana perusahaan kami telah resmi ditunjuk untuk memasarkan penerbitan BANK GARANSI dan SURETY BOND, dan Bank Garansi maupun Surety Bond yang Kami terbitkan telah diterima di lingkungan instansi BUMN, BUMD, BUMS, KPS, OIL& GAS,MABES TNI-POLRI,PERTAMINA,PLN, CHEVRON, CONOCO PHILIPS, STAR ENERGY DLL, Kami juga memberikan prosedur yang relative mudah yaitu TANPA AGUNAN (NON COLLATERAL) untuk semua jenis jaminan, serta proses cepat dan polis jaminan kami antar langsung ke perusahaaan bapak/ibu, dan dibawah ini kami informasikan tabel untuk rate dan Bank penerbit adalah sebagai berikut.
Tabel.1. LIST PENERBIT BANK GARANSI & PENERBIT JAMINAN ASURANSI
NAMA BANK
NAMA ASURANSI
BANK BTN
BANK BRI
Asuransi Jamsyar
Asuransi Askrindo
BANK BNI
BANK BCA
Asuransi Ramayana
Asuransi Jasindo
BANK MANDIRI
BANK JATIM
Asuransi bumida Asuransi Jasa Raharjaputra
BANK EXIM
BANK SINARMAS
Asuransi Vidie
Asuransi Jamkrindo
BANK BUKOPIN
BANK DLL
Asuransi Bosowa
Asuransi Aswata Dll
Tabel 2 . RATE (Service Charge)
Jenis Jaminan
Rate Bank Garansi
Rate Asuransi(Surety Bond)
Bid Bond
2,50 % / Tiga Bulan
0.25 % Pertiga Bulan
Performance Bond
3, % / Tahun
0.30% Pertiga Bulan
Advancepayment Bond
4. % / Tahun
0.35 % Pertiga Bulan
Maintenance Bond
3.50 % / Tahun
0.40 % Pertiga Bulan
Payment Bond
1.30% Pertiga Bulan
Kami juga dapat membantu proses penerbitan Asuransi Umum Lainnya dengan Rate negosiasi, adapun Produk Asuransi dimaksud adalah sebagai berikut :
a
Contaktor All Risk (CAR) + Third Party Liability (TPL)
b
Liability Insurance : Comprehensive General Liability (CGL)
Automobile Liability Insurance (AL)
Employer’s Liability Insurance (EL)
Workman Compensation Insurance(WCI)
c
Erection All Risk (EAR) Insurance
d
Personal Accident (PA) Insurance
Kami berharap penawaran ini dapat berakhir dengan kerjasama yang baik yang dapat memberikan keuntungan terhadap kedua belah pihak.Demikian penawaran ini kami buat, atas perhatian dan kerjasamanya kami ucapkan terimakasih.Hormat Kami.
PT. BERDIKARI BINA GARANSI
Jasa Bank Garansi & Surety Bond
Jl. Rawamangun MukaTimur No.43 Pulo Gadung Jakarta Timur
Kantor : +62 21. 22483622
HP/wa : 0878 3478 3854Email : dadangpramanaberdikari@gmail.com
by "dadangpramana berdikari" <dadangpramanaberdikari@gmail.com> - 09:57 - 21 Jul 2024 -
https://www.odoo.com/
HiI am working with a company where we buy 100 the post in 1 monthPlease let me know about the following questions1)What is the sponsored post price=https://www.odoo.com/2)Are you allowed links in the old post? If yes then tell me a price for link insertion3)Do you accept CBD posts or not?4)Please tell me your site's original traffic?5)What is the price of link insertion?Hope you also want to work with usI am waiting for your replyThanks
by "Muhammad Hussain" <muhammadhussainseo786@gmail.com> - 01:02 - 21 Jul 2024 -
The week in charts
The Week in Charts
An aging labor force, AI transformations, and more Share these insights
Did you enjoy this newsletter? Forward it to colleagues and friends so they can subscribe too. Was this issue forwarded to you? Sign up for it and sample our 40+ other free email subscriptions here.
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to The Week in Charts newsletter.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey Week in Charts" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 03:02 - 20 Jul 2024 -
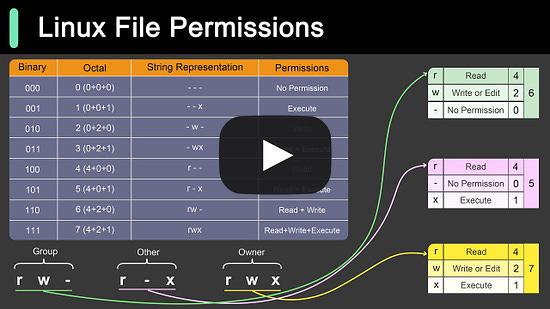
EP121: 9 Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application
EP121: 9 Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application
This week’s system design interview: Linux Crash Course - Understanding File Permissions (Youtube video) 9 Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application Iterative, Agile, Waterfall, Spiral Model, RAD Model... What are the differences?͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreHow to monitor AWS container environments at scale (Sponsored)
In this eBook, Datadog and AWS share insights into the changing state of containers in the cloud and explore why orchestration technologies are an essential part of managing ever-changing containerized workloads.
Learn more about:Strategies for successfully tracking containerized AWS applications at scale
Key metrics to monitor for Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS) and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Enabling comprehensive monitoring for AWS container environments with Datadog
This week’s system design interview:
Linux Crash Course - Understanding File Permissions (Youtube video)
9 Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application
Iterative, Agile, Waterfall, Spiral Model, RAD Model... What are the differences?
Design Patterns Cheat Sheet - Part 1 and Part 2
SPONSOR US
✂️Cut your QA cycles down to minutes with automated testing (Sponsored)
Are slow test cycles bottlenecking your dev teams’ release velocity? With QA Wolf, your organization can run entire test suites in minutes for faster feedback and developer confidence to ship.
QA Wolf takes testing off your plate. They can get you:
80% automated test coverage in weeks—not years
24-hour maintenance and on-demand test creation
Zero flakes, guaranteed
The benefit? No more manual E2E testing. No more slow QA cycles. No more bugs reaching production.
With QA Wolf, Drata’s team of 80+ engineers achieved 4x more test cases and 86% faster QA cycles.
🌟Rated 4.8/5 on G2
Linux Crash Course - Understanding File Permissions
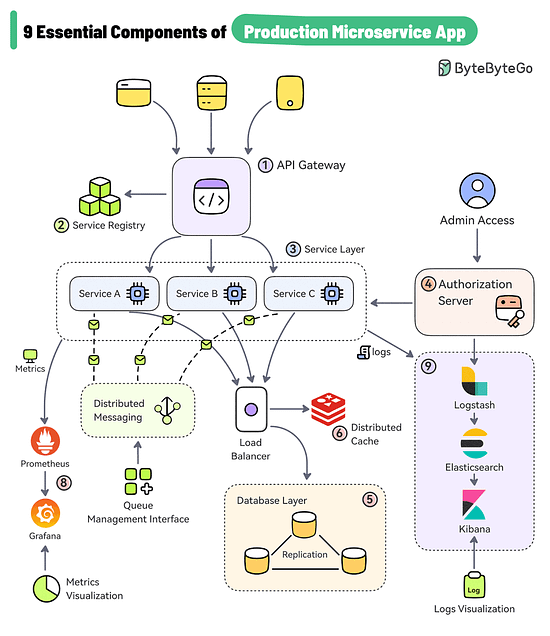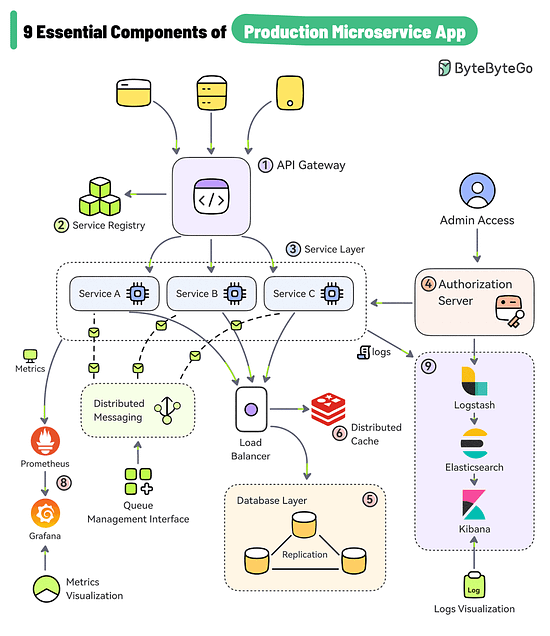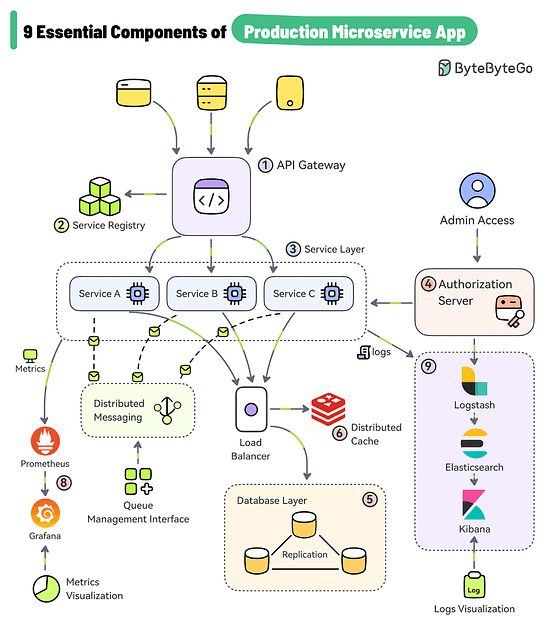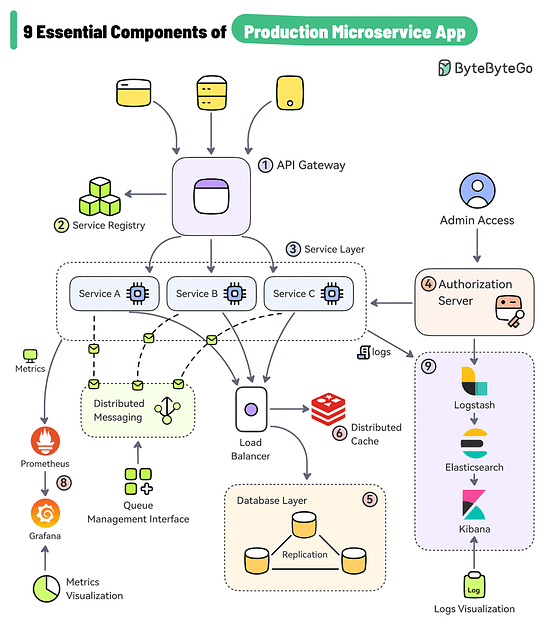
9 Essential Components of a Production Microservice Application
API Gateway
The gateway provides a unified entry point for client applications. It handles routing, filtering, and load balancing.Service Registry
The service registry contains the details of all the services. The gateway discovers the service using the registry. For example, Consul, Eureka, Zookeeper, etc.Service Layer
Each microservices serves a specific business function and can run on multiple instances. These services can be built using frameworks like Spring Boot, NestJS, etc.Authorization Server
Used to secure the microservices and manage identity and access control. Tools like Keycloak, Azure AD, and Okta can help over here.Data Storage
Databases like PostgreSQL and MySQL can store application data generated by the services.Distributed Caching
Caching is a great approach for boosting the application performance. Options include caching solutions like Redis, Couchbase, Memcached, etc.Async Microservices Communication
Use platforms such as Kafka and RabbitMQ to support async communication between microservices.Metrics Visualization
Microservices can be configured to publish metrics to Prometheus and tools like Grafana can help visualize the metrics.Log Aggregation and Visualization
Logs generated by the services are aggregated using Logstash, stored in Elasticsearch, and visualized with Kibana.
Over to you: What else would you add to your production microservice architecture?
Latest articles
If you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
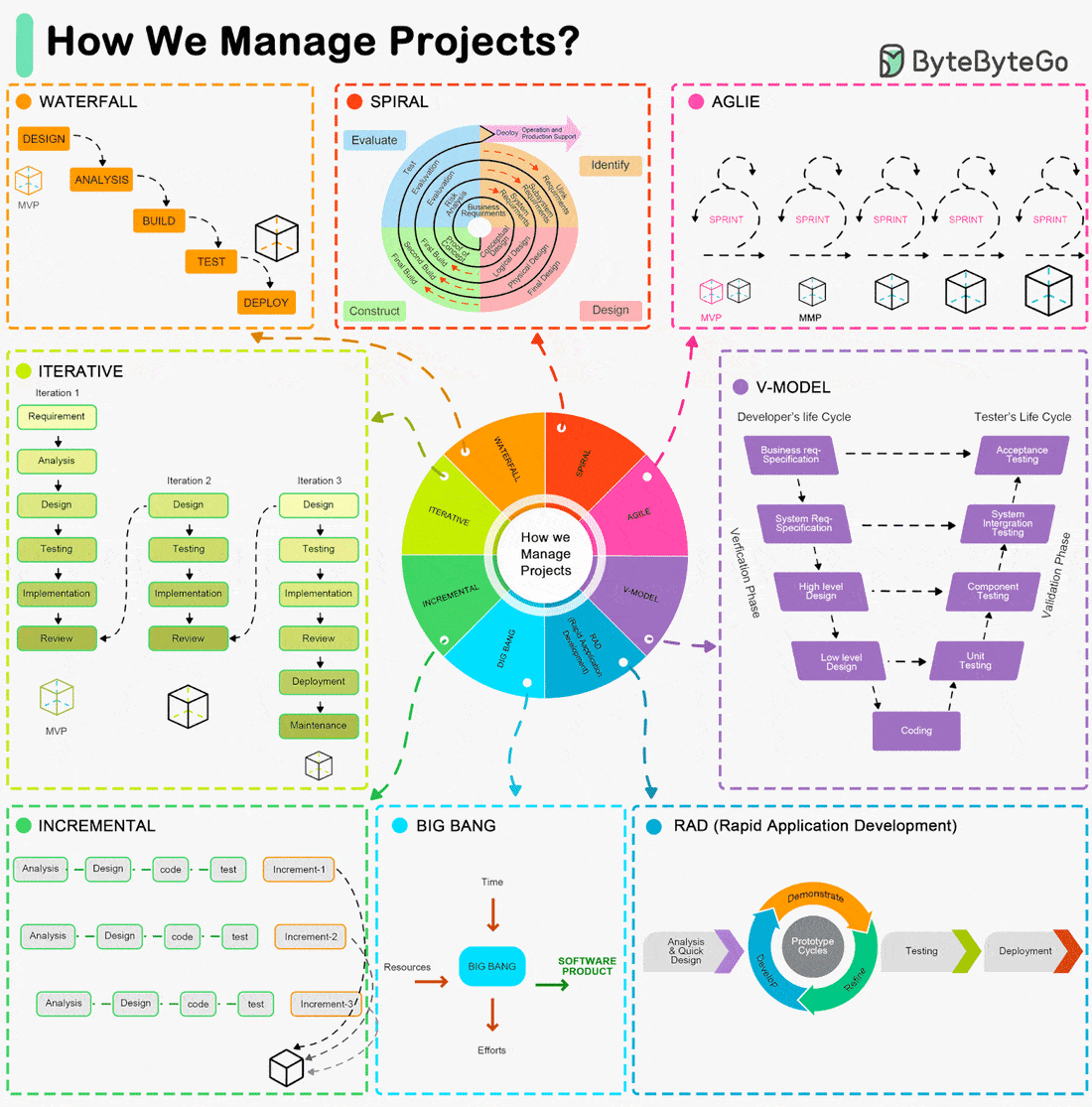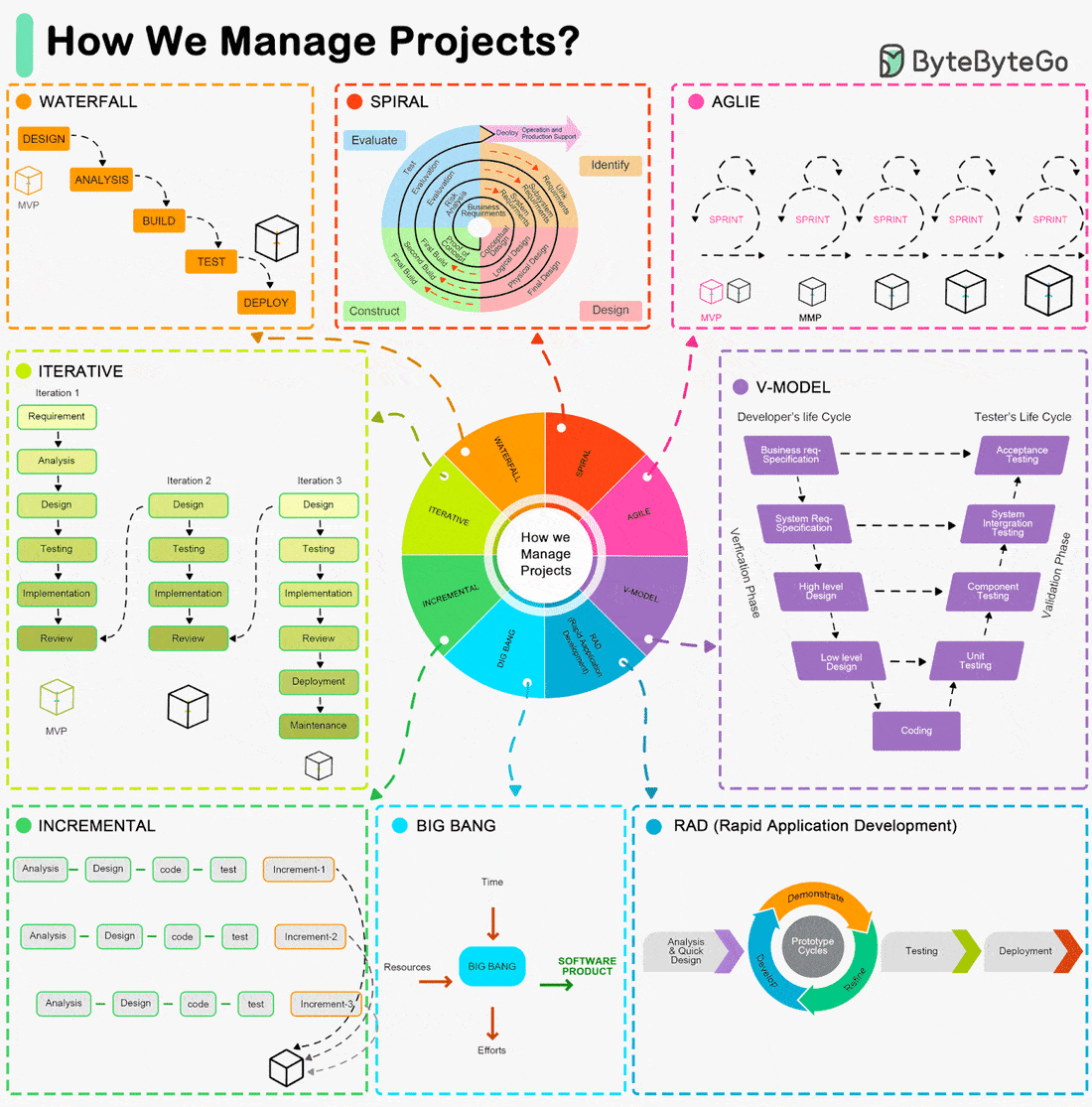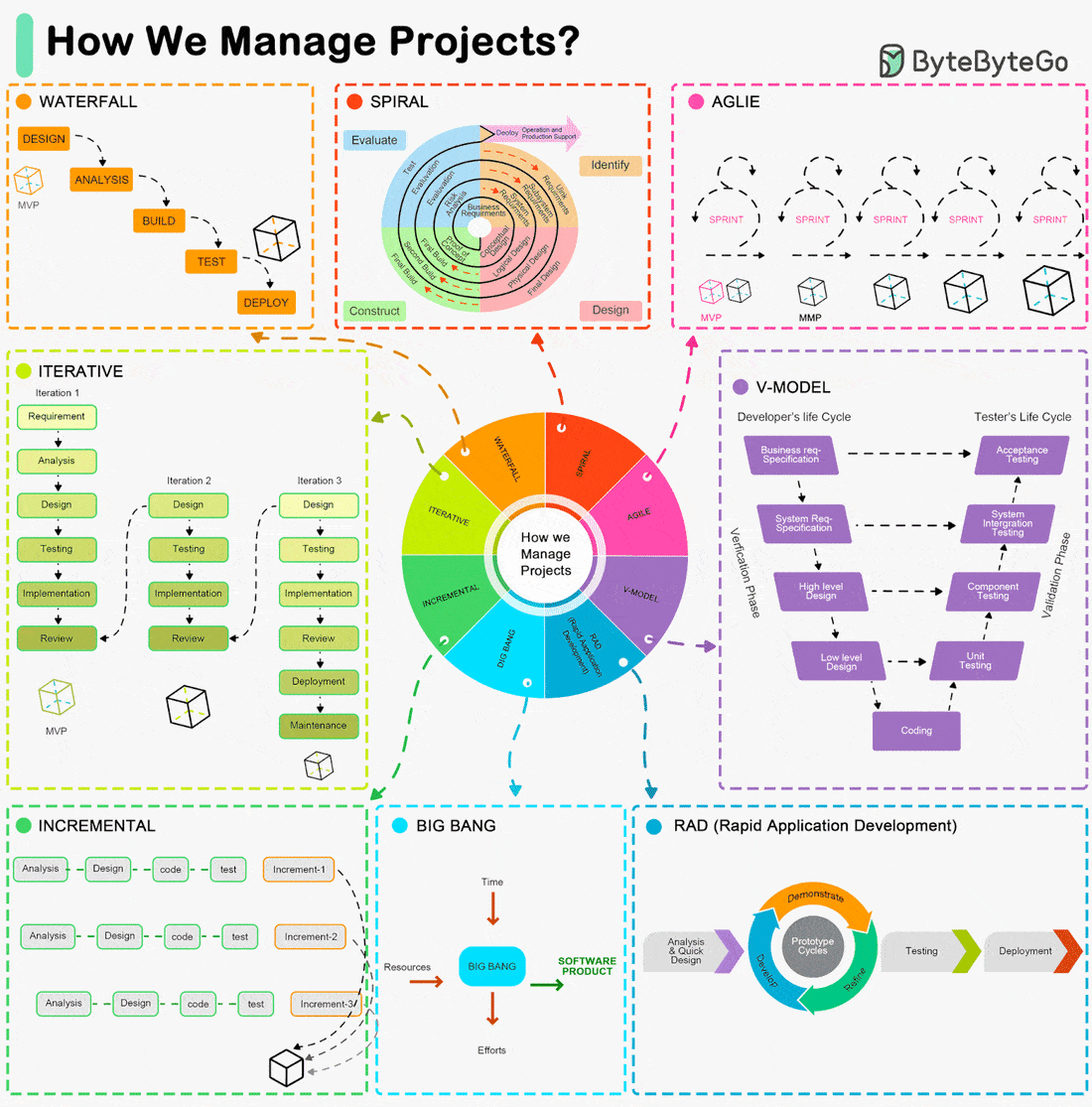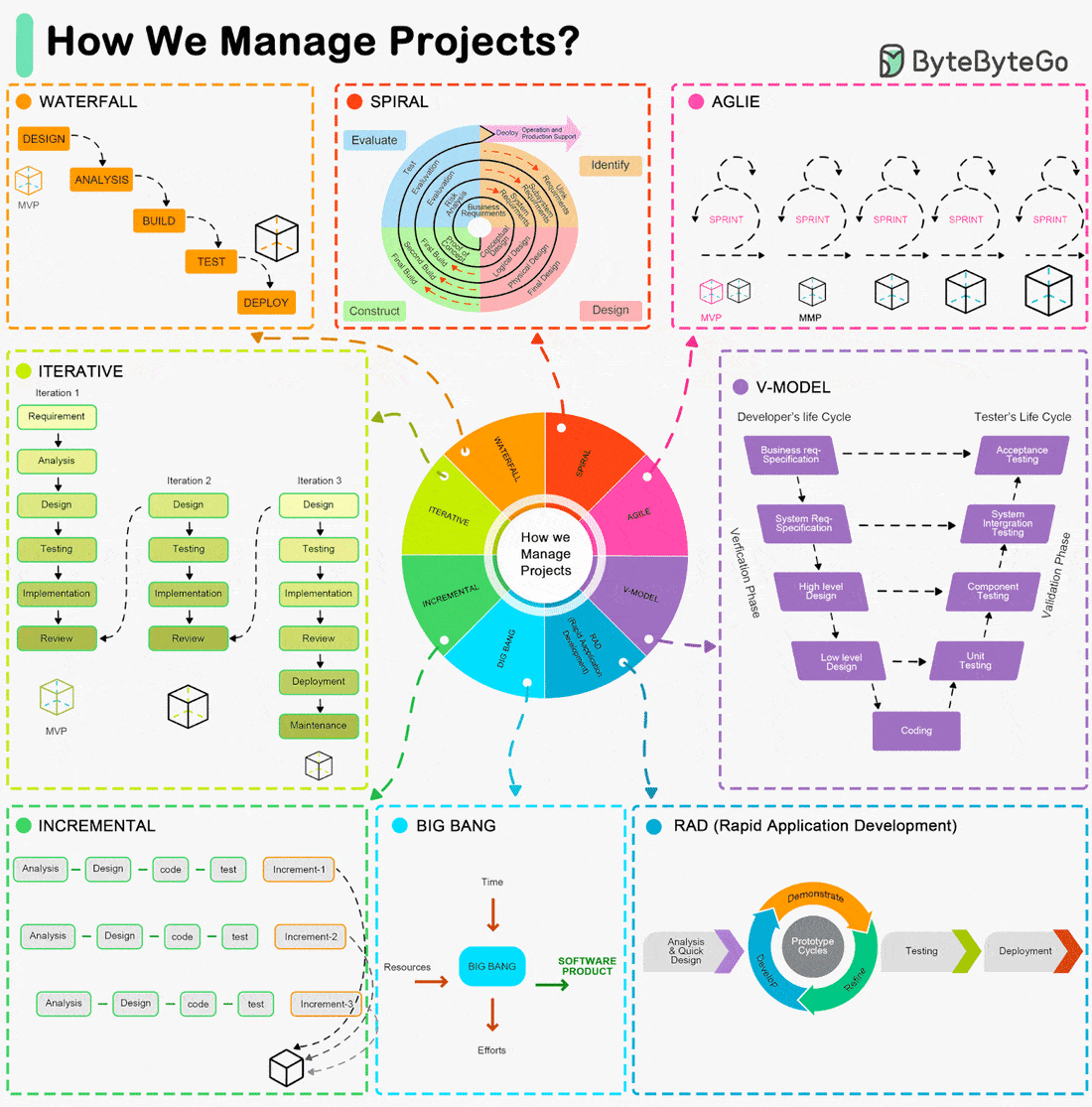
Iterative, Agile, Waterfall, Spiral Model, RAD Model... What are the differences?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a framework that outlines the process of developing software in a systematic way. Here are some of the most common ones:
Waterfall Model:
- A linear and sequential approach.
- Divides the project into distinct phases: Requirements, Design, Implementation, Verification, and Maintenance.Agile Model:
- Development is done in small, manageable increments called sprints.
- Common Agile methodologies include Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP).V-Model (Validation and Verification Model):
- An extension of the Waterfall model.
- Each development phase is associated with a testing phase, forming a V shape.Iterative Model:
- Focuses on building a system incrementally.
- Each iteration builds upon the previous one until the final product is achieved.Spiral Model:
- Combines iterative development with systematic aspects of the Waterfall model.
- Each cycle involves planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation.Big Bang Model:
- All coding is done with minimal planning, and the entire software is integrated and tested at once.RAD Model (Rapid Application Development):
- Emphasizes rapid prototyping and quick feedback.
- Focuses on quick development and delivery.Incremental Model:
- The product is designed, implemented, and tested incrementally until the product is finished.
Each of these models has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of which to use often depends on the specific requirements and constraints of the project at hand.
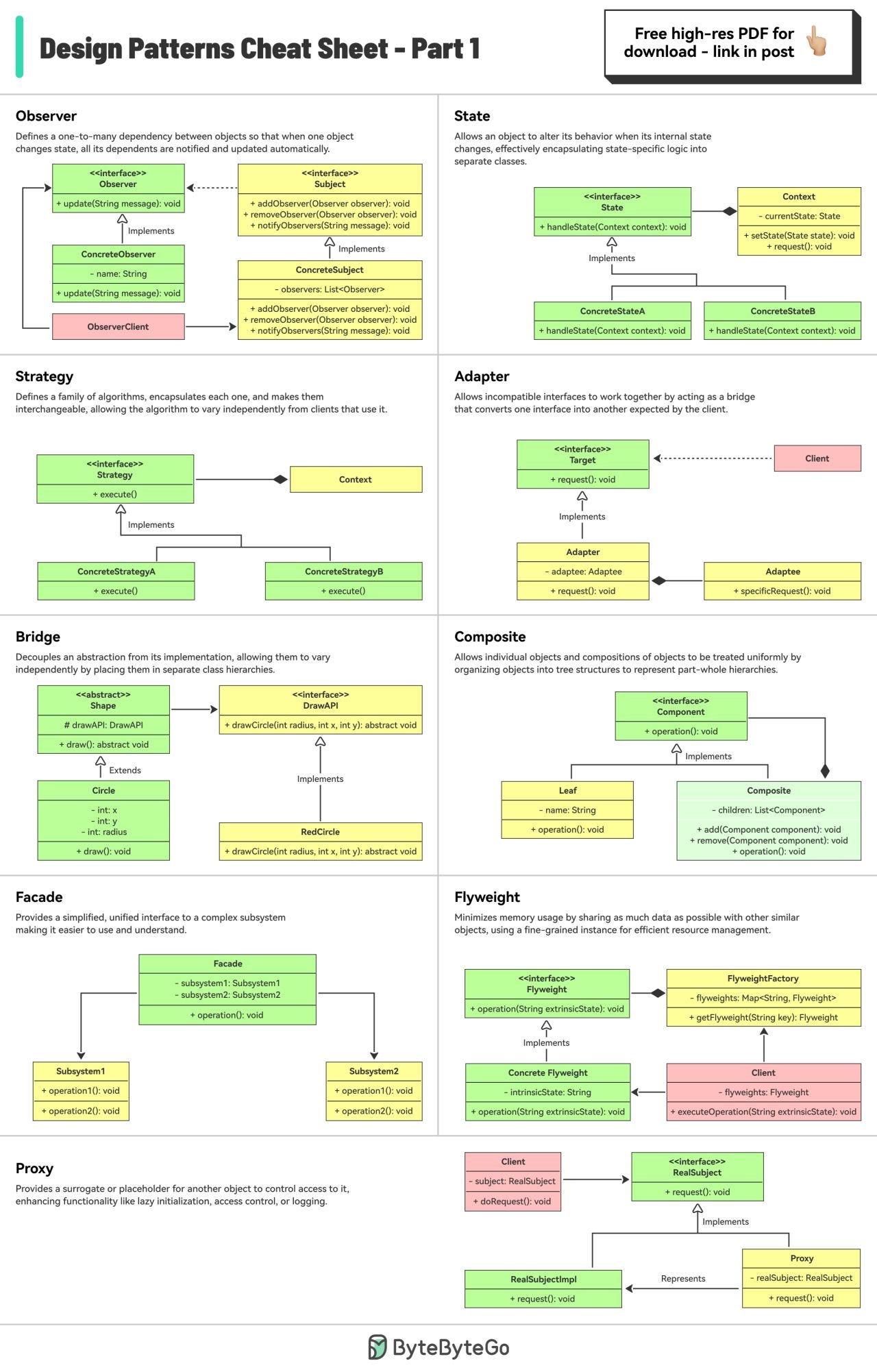
Design Patterns Cheat Sheet - Part 1 and Part 2
The cheat sheet briefly explains each pattern and how to use it.
What's included?
Factory
Builder
Prototype
Singleton
Chain of Responsibility
And many more!
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing hi@bytebytego.com
Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 20 Jul 2024 -
I need to post on your site
--Hello
I need to post on your site https://learn.odoo.com/
can you give 3 do follow if you can give me your best price
i am waiting for your reply
thanks
by "farman ali" <fa6653347@gmail.com> - 06:52 - 20 Jul 2024 -
RE: website error
Hello,
Are you still in the business?
I found a few errors on your website
Would you like me to send over a screenshot of those errors?
Thanks,
by "Krishna" <bmichaell196@gmail.com> - 06:43 - 20 Jul 2024 -
Reminder: You're invited! Join us for a virtual event on tight labor markets in advanced economies
Register now New from McKinsey & Company
Labor markets in advanced economies are exceptionally tight today. This tightness isn’t the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic but rather a sustained trend driven by aging workforces and labor demand outstripping supply. Continued tightness comes at an economic cost, increasing the impetus for business leaders and policymakers to come up with new approaches to boost participation and productivity to offset its impact.
Join us on Tuesday, July 30 at 11:00AM-12:00PM EDT (5:00PM-6:00PM CEST) for a discussion on MGI’s latest research that examines labor market conditions in advanced economies, highlighting dynamics across sectors and occupations, future supply trends, and strategies to mitigate labor shortages.
This virtual event will include a presentation by the authors followed by a panel with leading labor market experts who will discuss:•
Countries and sectors that are most impacted by labor shortages
•
The economic consequences of labor shortages
•
The role of AI and other technology
•
Actions employers and policymakers can take to improve labor supply and productivity
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to our McKinsey Global Institute alert list.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey & Company" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 04:37 - 19 Jul 2024 -
Thank you for supporting ByteByteGo Newsletter
Thank you for reading ByteByteGo Newsletter. As a token of our appreciation, we're offering you a limited-time offer of 20% off a paid subscription.
Redeem special offerHere are the benefits you unlock with a paid subscription:
- An extra deep dive on Thursdays
- Full archive
- Many expense it with team's learning budget
Join the hundreds of other readers who pay for full access to ByteByteGo Newsletter - redeem your special offer today!
Thanks again for reading.
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 01:30 - 19 Jul 2024 -
What’s on your summer reading list?
Only McKinsey
McKinsey’s 2024 annual book recommendations •
CEO-curated reads. What will you read next? McKinsey Global Publishing leader Raju Narisetti returns this year with McKinsey’s annual book recommendations list—a McKinsey Global Publishing tradition—featuring suggestions from 50-plus CEOs and global leaders in media, nonprofits, and other organizations, as well as several McKinsey leaders. Also on the list is The Journey of Leadership: How CEOs Learn to Lead from the Inside Out, by McKinsey senior partners Dana Maor, Kurt Strovink, and Ramesh Srinivasan, with senior partner emeritus Hans-Werner Kaas. The book, being published on September 10, helps leaders hone the qualities that help them find success in a demanding role.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:37 - 19 Jul 2024 -
RE: Consumer Electronics Show - CES 2024 (Post Show)
Hi,
I am just following-up regarding my previous email.
If you are looking for pricing offer, please do let me know.
Thanks,
Becky
From: becky.walters@moreofdata.com <becky.walters@moreofdata.com>
Sent: Tuesday, July 16, 2024 2:41 PM
To: 'info@learn.odoo.com' <info@learn.odoo.com>
Subject: Consumer Electronics Show - CES 2024 (Post Show)I had a chance to review your company profile and thought you might be interested in acquiring an updated Attendee list of Consumer Electronics Show - CES 2024?
Attendees are: - Analyst, Content Developer, Distributor, Buyer, Engineer, Manager/Store Manager/Product Manager, Manufacturer’s Representative, Service Technician, Systems Installer/Integrator & More.
List Contains: Name, Title, Email, Phone, Company Name, Physical Address, City, State, Zip Code, Country, Web Address, Employee Size, Revenue Size and Industry.
Please do let me know your interest. I’d be happy to send over our counts, accuracy, quality, pricing structure and more details on your request.
Waiting for your response
Thank you
Becky Walters - Event Manager
If you don’t want to receive further emails please revert with “Take Out” in the subject
by becky.walters@moreofdata.com - 04:43 - 18 Jul 2024 -
A Crash Course on Relational Database Design
A Crash Course on Relational Database Design
In today's data-driven world, efficient storage and management of information are critical requirements for businesses and organizations of all sizes. Relational databases provide a robust framework for storing and retrieving data based on well-defined relationships between entities. They offer a structured approach to data management, enabling users to:͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreLatest articles
If you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
In today's data-driven world, efficient storage and management of information are critical requirements for businesses and organizations of all sizes.
Relational databases provide a robust framework for storing and retrieving data based on well-defined relationships between entities. They offer a structured approach to data management, enabling users to:
Define tables
Establish relationships
Perform complex queries to extract meaningful insights from the stored information
However, just using a relational database is not enough to gain its benefits.
Effective database design is crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring data integrity, and facilitating efficient data retrieval. The principles of database design, such as normalization, indexing, joins, and relationships, play a vital role in creating a well-structured and performant database.
In this post, we’ll look at the fundamentals of relational databases, exploring their key concepts, management systems, and the principles that underpin effective database design.

Unlock this post for free, courtesy of Alex Xu.
A subscription gets you:
An extra deep dive on Thursdays Full archive Many expense it with team's learning budget Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:36 - 18 Jul 2024 -
Don’t forget to book your spot to accelerate your API platform maturity!
Don’t forget to book your spot to accelerate your API platform maturity!
Join our Scaling API platforms webinar on July 25th to assess and accelerate your API platform maturity.Hi Md Abul,
Would you like to assess and accelerate your API platform maturity? Then join us on July 25th for an action-packed webinar.
Tyk’s Developer Advocate Budha Bhattacharya will join a platform architect and product owner from ACME FinCorp International, a Fortune 500 financial services company at an early stage of its API journey. ACME FinCorp International is exploring ways to mature its platform initiative, delving into Tyk’s API platform maturity model and prioritization framework.
During the webinar, we will:- Provide a brief overview of the API platform maturity model
- Identify the current platform maturity of ACME FinCorp
- Discuss KPIs and what success looks like over 6-12 months
- Choose key strategic and implementation maturity pillars to prioritize
- Define the next steps to achieve desired platform maturity over 6-12 months
If you’re ready to create a playbook for API platform maturity, don’t miss this webinar. Speakers will include Tyk’s Budha Bhattacharya (Developer Advocate), Tamara Evans (Account Director) and Andy Smith (Solution Architect).
We’ll kick off at 10 am EDT/3 pm BST on July 25th. Click the link below to join us.See you soon,
Budha & teamTyk, Huckletree 199 Bishopsgate, Broadgate, London, City of London EC2M 3TY, United Kingdom, +44 (0)20 3409 1911
by "Budhaditya Bhattacharya" <budha@tyk.io> - 06:00 - 18 Jul 2024 -
How tight are advanced economies’ labor markets?
Only McKinsey
Scenarios for labor force participation •
Labor market squeeze. Labor markets in advanced economies remain tighter than at any other time over the past two decades, new McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) research finds. This is a long-term trend that may intensify as workforces age. Without concerted efforts to boost productivity or increases in the workforce through higher participation or immigration, many advanced economies will struggle to maintain GDP growth (to match or exceed the relatively muted economic growth of the past decade), MGI chair Sven Smit and coauthors explain.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:12 - 18 Jul 2024