- Mailing Lists
- in
- SQL vs NoSQL: Choosing the Right Database for An Application
Archives
- By thread 5022
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 134
SQL vs NoSQL: Choosing the Right Database for An Application
SQL vs NoSQL: Choosing the Right Database for An Application
Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
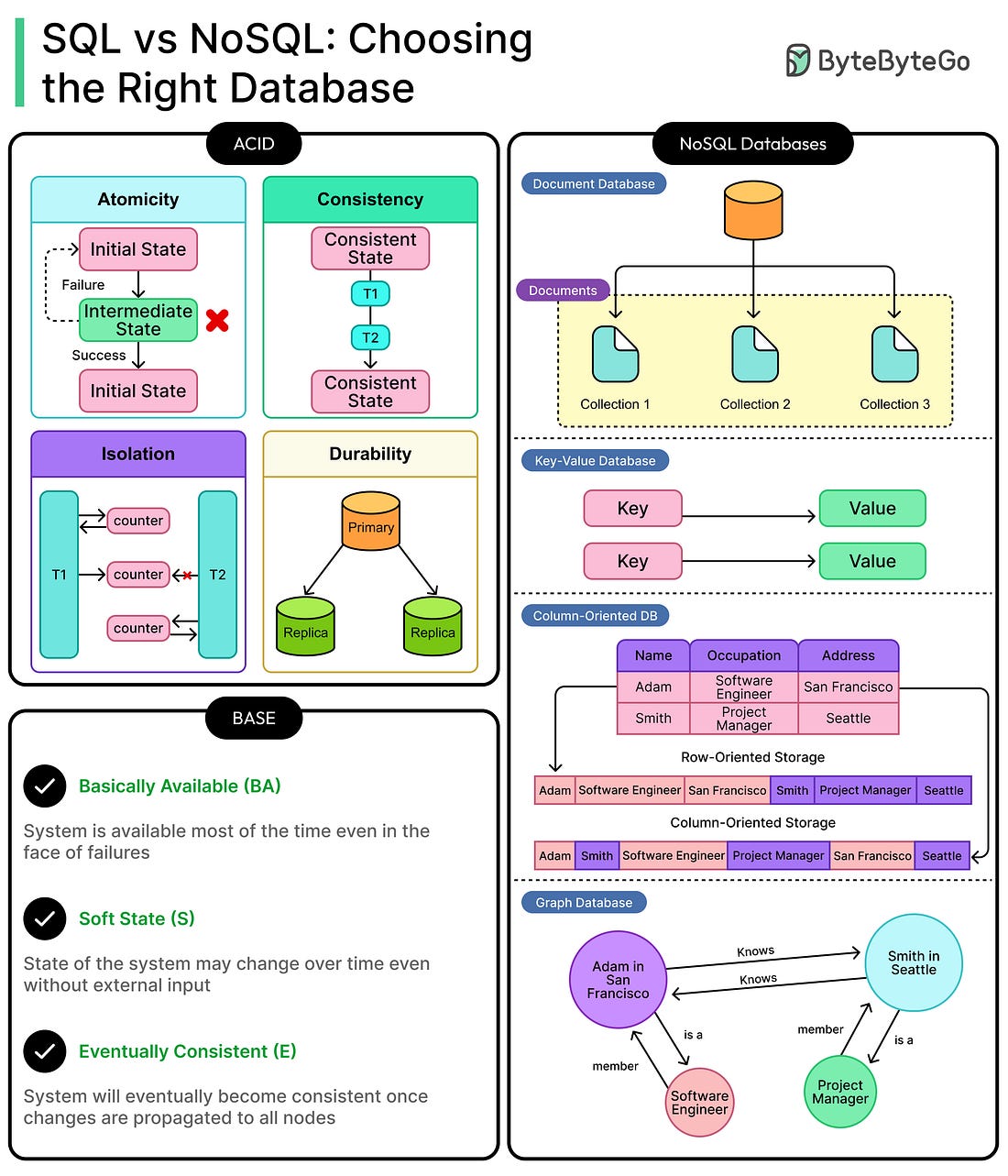
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: Every modern application, from a ride-hailing service to an e-commerce platform, relies on data, and behind that data sits a database. Whether it's storing customer profiles, tracking inventory, or logging user actions, the database is more than just a storage engine. It's the core system that holds an application’s state together. When the database fails, everything else (APIs, front-end, business logic) comes tumbling down. Therefore, choosing the right kind of database is critical, but it isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. Relational databases, such as MySQL and PostgreSQL, have been the default for decades. They offer strong consistency, well-understood query languages, and battle-tested reliability. However, as systems scale and use cases diversify, traditional SQL starts to exhibit problems. That’s where NoSQL enters the picture with a flexible schema design, horizontal scalability, and models tailored to specific access patterns. The promise is to scale fast and iterate freely. However, there are trade-offs in consistency, structure, and operations. Then there’s a growing third category: NewSQL systems such as Google Spanner and CockroachDB. These attempt to bridge the gap by retaining SQL semantics and ACID guarantees, while scaling like NoSQL across regions and nodes. There are also specialized databases that push performance in specific directions. In-memory stores like Redis blur the line between cache and persistence. Search engines like Elasticsearch offer lightning-fast text search and analytics capabilities that relational databases were never built for. The wrong database choice can throttle performance, slow down development, or break under scale. The right one can unlock speed, agility, and reliability. In this article, we break down the core database paradigms, such as SQL and NoSQL, along with specialized database types and how developers can choose the appropriate database for their requirements. Core Models: ACID vs BASE... Continue reading this post for free in the Substack app© 2025 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 5 Jun 2025