- Mailing Lists
- in
- The 6 Most Impactful Ways Redis is Used in Production Systems
Archives
- By thread 5220
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 32
See what's new with Remote's global benefits 🌍🚀
Forward Thinking on the existential issues facing the middle classes in every country with Homi Kharas
The 6 Most Impactful Ways Redis is Used in Production Systems
The 6 Most Impactful Ways Redis is Used in Production Systems
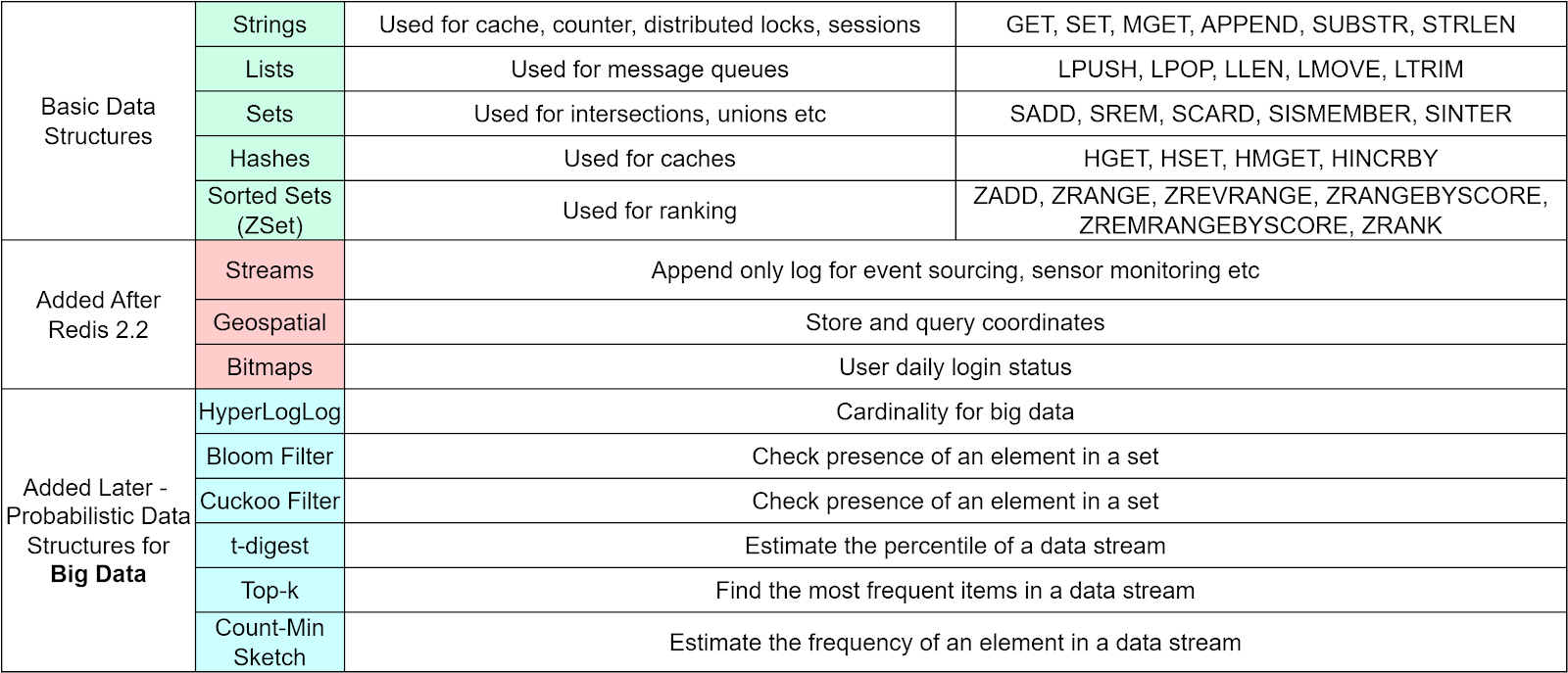
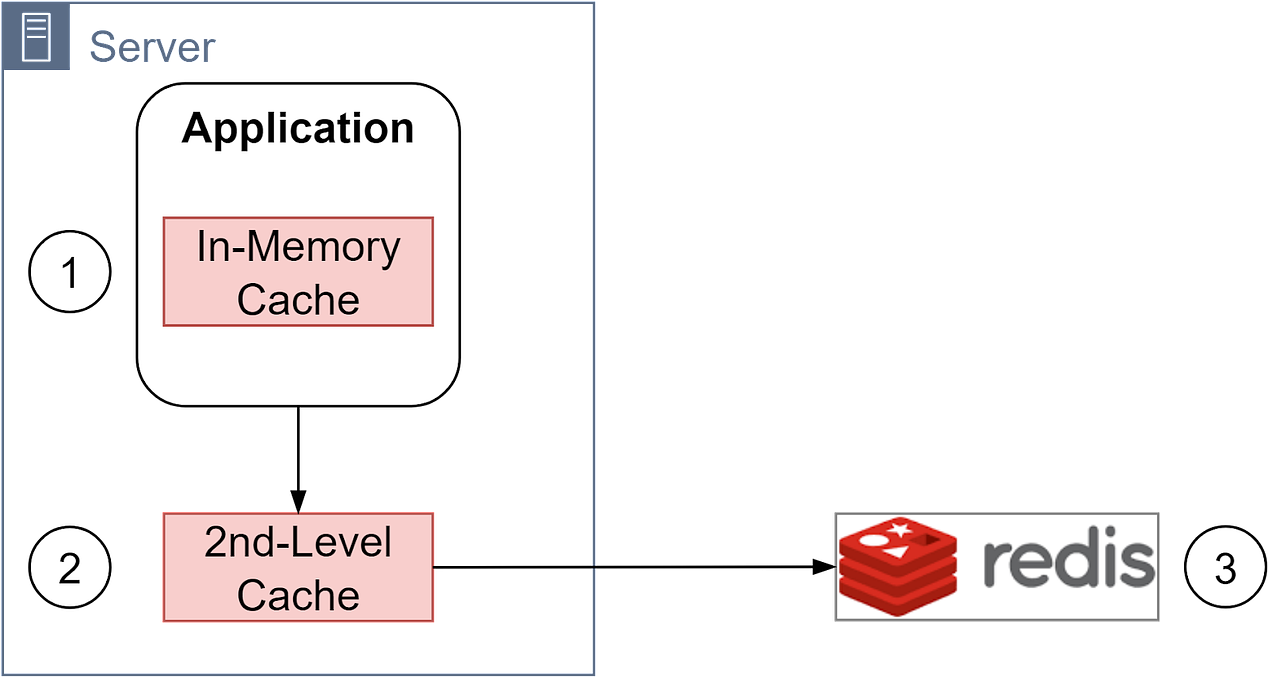
This is a sneak peek of today’s paid newsletter for our premium subscribers. Get access to this issue and all future issues - by subscribing today. Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month. To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: Redis is often referred to as a Swiss Army knife - it's an incredibly versatile in-memory database that can help solve many different problems. Let's say your online game is experiencing slow response times from your database due to rapidly increasing users. Or your e-commerce site needs to quickly display real-time product inventory for flash sales. Or your web analytics need to track page views at massive scale. Redis to the rescue! Its lightning fast speeds and flexible data structures make it a go-to tool for many challenging use cases. In this issue, we'll explore 6 popular Redis use cases including caching, session management, leaderboards, queues, analytics, and more. You'll discover techniques to supercharge your apps. But first, let's do a quick refresher on Redis data structures we covered in our previous issue: Now what makes Redis so fast? Unlike disk-based databases, Redis stores all data in memory and uses a single-threaded design. This allows Redis to achieve extremely high throughput and lightning fast speeds for reads and writes. The performance combined with versatile data structures like the ones above enables Redis to power many data-intensive real-time applications. First up is caching. CacheA cache is an essential part of a system. It provides a shortcut to access hot data and improves performance. A typical cache architecture has three layers:
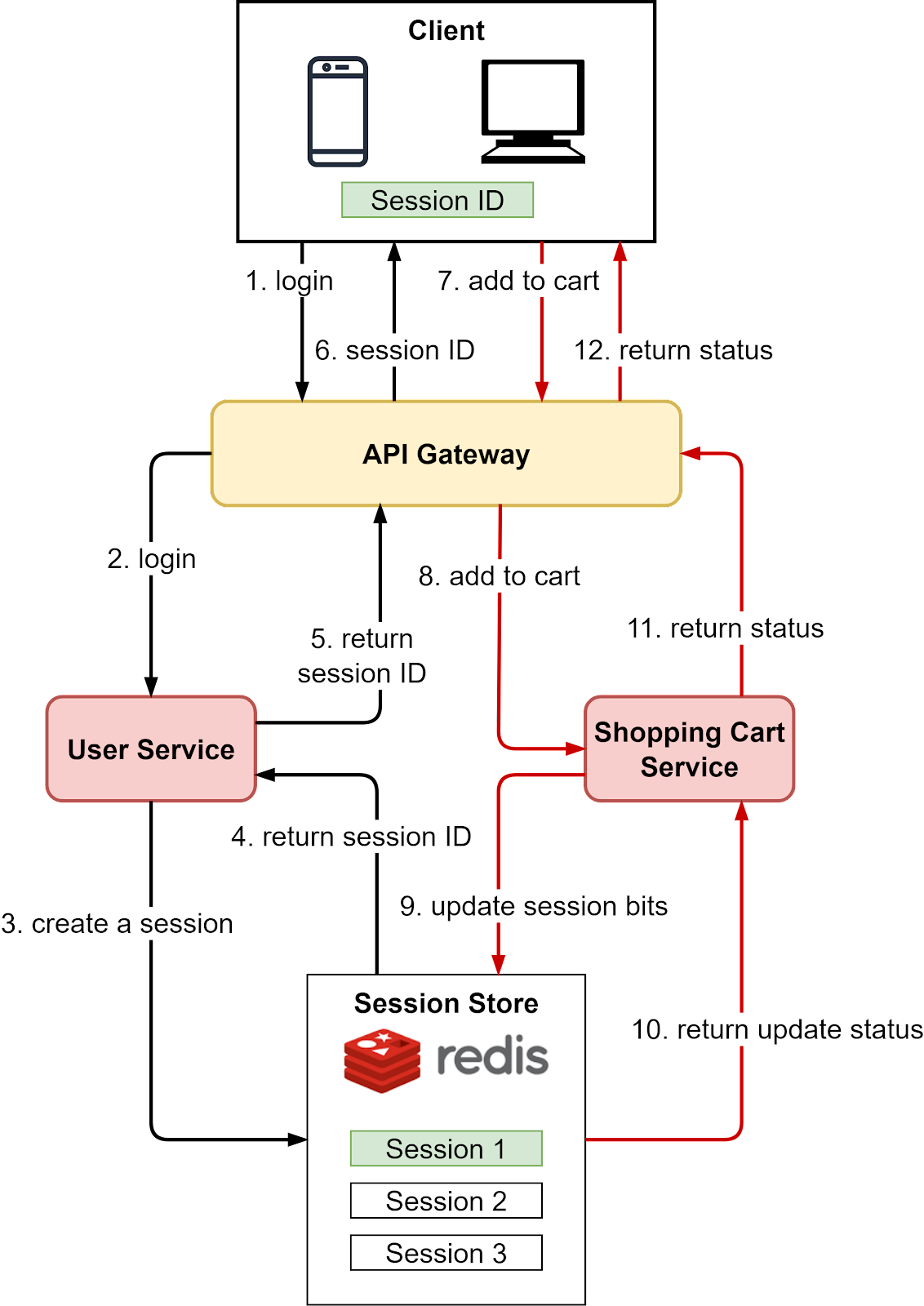
Redis lets you cache different data types like strings for user’s full names, hashes for user profiles, etc. However, the database remains the complete source of truth and holds the full set of data, while Redis caches the hot subsets. Based on the Pareto principle, around 20% of data tends to make up 80% of accesses. So caching the hottest 20% of data in Redis can improve performance for a majority of requests. This 80/20 rule of thumb can guide what data is cached versus stored solely in the database. The cache hierarchy allows managing different data sizes/access patterns efficiently. The first level cache holds a small volume of very hot data. The second level cache holds more data, still frequently accessed. The distributed Redis cache can hold large datasets by sharding across servers. Using Redis as a cache improves performance but introduces complexity around cache coherence. There can be multiple copies of data, so read/write strategies need careful design. Typically one data source is designated as the "source of truth" and writes go there first. The application can implement lazy loading and write-through patterns when using Redis as a cache to keep it updated. Cache aside and read aside are other application-level caching patterns that Redis readily supports. Caching is a classic time vs space tradeoff - we duplicate data across the system to gain speed. Interested readers can check our previous issues on caching best practices. Based on the Pareto principle, 20% of the data in the system is mostly accessed, so this should be good guidance for the caching strategy. Session StoreThe Session Store is a critical component for web applications to maintain state across requests. Popular solutions like Redis provide a fast, scalable session store by keeping session data in-memory. The server uses Redis to store session data and associate it with each user. It assigns every client a unique session ID that is sent on each request to retrieve the correct session. Storing sessions in Redis instead of locally on each app server removes the need for "sticky sessions" when load balancing. Session data in Redis is serialized as JSON or similar format. This enables structured data to be stored like user profiles, recent actions, shopping carts, and CSRF tokens. Sessions should expire after a period of inactivity. This practice improves security and frees up stale resources. The expiration time can be configured based on app needs. The diagram below shows a typical Redis session flow: Steps 1 and 2 - A user login request is sent to the User Service. Steps 3 and 4 - The User Service creates a new session in Redis by generating a unique session ID. Steps 5 and 6 - The User Service sends the session ID back to the client where it is stored locally. Steps 7 and 8 - The user adds a product to their shopping cart. This sends the request to the Shopping Cart Service. Steps 9 and 10 - The Shopping Cart Service retrieves the session data from Redis using the session ID. It updates the session object in Redis by adding the new shopping cart items. Steps 11 and 12 - The Shopping Cart Service returns a success status to the client. Keep reading with a 7-day free trialSubscribe to ByteByteGo Newsletter to keep reading this post and get 7 days of free access to the full post archives.A subscription gets you:
© 2023 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:37 - 12 Oct 2023