- Mailing Lists
- in
- Unlocking the Power of SQL Queries for Improved Performance
Archives
- By thread 5314
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 126
New Relic AI monitoring—the industry’s first APM for AI—now generally available
A microscope on small businesses: Spotting opportunities to boost productivity
Unlocking the Power of SQL Queries for Improved Performance
Unlocking the Power of SQL Queries for Improved Performance
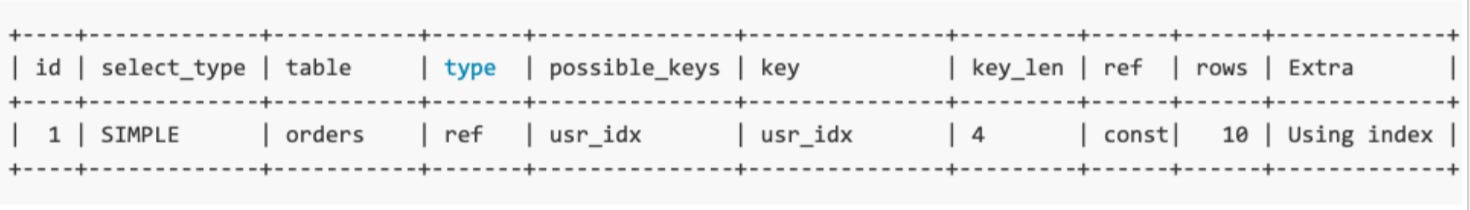
Latest articlesIf you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month. To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing: SQL, or Structured Query Language, is the backbone of modern data management. It enables efficient retrieval, manipulation, and management of data in a Database Management System (DBMS). Each SQL command taps into a complex sequence within a database, building on concepts like the connection pool, query cache, command parser, optimizer, and executor, which we covered in our last issue. Crafting effective queries is essential. The right SQL can enhance database performance; the wrong one can lead to increased costs and slower responses. In this issue, we focus on strategies such as using the Explain Plan, adding proper indexes, and optimizing commands like COUNT(*) and ORDER BY. We also dive into troubleshooting slow queries. While MySQL is our primary example, the techniques and strategies discussed are applicable across various database systems. Join us as we refine SQL queries for better performance and cost efficiency. Explain PlanIn MySQL, the EXPLAIN command, known as EXPLAIN PLAN in systems like Oracle, is a useful tool for analyzing how queries are executed. By adding EXPLAIN before a SELECT statement, MySQL provides information about how it processes the SQL. This output shows the tables involved, operations performed (such as sort, scan, and join), and the indexes used, among other execution details. This tool is particularly useful for optimizing SQL queries, as it helps developers see the query execution plan and identify potential bottlenecks. When an EXPLAIN statement is executed in MySQL, the database engine simulates the query execution. This simulation generates a detailed report without running the actual query. This report includes several important columns:
Let's explore a practical application of the EXPLAIN command using a database table named orders. Suppose we want to select orders with user_id equal to 100. To analyze this query with EXPLAIN, we would use: The output might look like this:  Continue reading this post for free, courtesy of Alex Xu.A subscription gets you:
© 2024 ByteByteGo |
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:38 - 2 May 2024