Archives
- By thread 5376
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 190
-
Samples ready for your spring projects?
Dear info。
Hope this email finds you well.
Just a quick note - we supply stainless steel sheets/coils to different industry companies, with:
• Grades: 304, 316L, 201, 430 and more.
• Thickness: 0.2mm to 12mm (cold-rolled/hot-rolled).
• Finishes: 2B,NO.1,NO.4,HL,8K Mirror, Etched,Embossed,and custom textures.
• Flexible MOQ and competitive pricing.Are you currently sourcing similar materials? Would love to explore how we might help.
Best regards,
Hank
WhatsApp: +86 18316490047
Export Manager | X-METAL
by "Connie" <Connie@xmetalmaterials.com> - 07:16 - 18 Apr 2025 -
Tools for the trade shock
The Shortlist
Emerging ideas for leaders Curated by Alex Panas, global leader of industries, & Axel Karlsson, global leader of functional practices and growth platforms
Welcome to the latest edition of the CEO Shortlist, a biweekly newsletter of our best ideas for the C-suite. This week, we dive into our latest thinking on tariffs and simmering trade tensions. You can reach us with thoughts, ideas, and tariff chat at Alex_Panas@mckinsey.com and Axel_Karlsson@mckinsey.com. Thank you, as ever.
—Alex and Axel
Now they’re here. Now they’re not. Leaders are grappling with day-to-day issues related to the rapidly changing global economic order. Understandably, they are hesitant to make strategic moves given the overwhelming uncertainty of the trade situation. Cindy Levy, Shubham Singhal, and their coauthors argue that traditional forecasting and planning methods are insufficient for this particular set of circumstances. What may help is to establish a geopolitical nerve center: a central hub that tracks, plans, and guides decision-makers in mitigating the impact of tariffs.
This flavor of uncertainty is new. But tariffs are old. Some say the Babylonian king Hammurabi was the first to enact tariffs on foreign goods, in his famous code. The Smoot-Hawley Act of 1930, and the trade war that ensued, has been more in the news lately. In this article from December 2024, our authors look back on the history of tariffs, examine some recent examples, and present a range of responses that executives can take to seize potential opportunities.
We hope you find these ideas novel and insightful. See you in a couple weeks with more McKinsey ideas for the CEO and others in the C-suite.Share these insights
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to The CEO Shortlist newsletter.
Copyright © 2025 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey CEO Shortlist" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 04:26 - 18 Apr 2025 -
High-Quality PCB Equipment & Machines for Your Business
Dear info,
I hope this message finds you well. I am reaching out to introduce our company, a leader in PCB equipment manufacturing. Our company's products cover almost the entire PCB production process, and all are independently developed and manufactured.
We specialize in providing top-notch PCB machines that are designed to meet the various needs of the PCB-making industry. Our equipment is engineered for high productivity, precision, and reliability, enabling businesses like yours to stay competitive.
If you're interested, please don't hesitated to contact me.
Best regards,
ZHONGSHAN MEIDING MACHINERY MANUFACTURING CO.,LTD
by "managersun" <managersun@md-pcbequipment.com> - 02:03 - 18 Apr 2025 -
Make gen AI work for you
On McKinsey Perspectives
Keeping up with gen AI
by "Only McKinsey Perspectives" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:05 - 18 Apr 2025 -
Your Trusted Partner in Rapid Test Products
Dear info,
Hope this message finds you well.
I’m reaching out from Core Technology Co., Ltd., a subsidiary of the American Cordx Union group, with over a decade of expertise in medical diagnostics. Our rapid test products, such as HCG Pregnancy Tests, LH Ovulation Tests, and Influenza A/B + COVID-19 Ag Combo Tests, are used by millions worldwide across 170+ countries.
We pride ourselves on delivering reliable quality at competitive prices, supported by advanced R&D and global manufacturing capabilities.
If this aligns with your needs, I would be happy to discuss how we can support your market goals.
Best regards,
Ashely
Core Technology Co., Ltd.
18601366018
+86 10 69390616
by "Urni Nikuda" <nikudaurni@gmail.com> - 03:41 - 17 Apr 2025 -
shock absorber
Dear info,
Greetings from Henghong Intelligent Equipment Co.,Ltd!
We are professional in R&D,production and sales of automotive shock absorbers.Our team has explored your website and noticed significant synergies between our product lines.With in-depth knowledge of your market,we are eager to share valuable insights and explore potential collaborations with you.
Would you like to accept our catalogue?It could open up new avenues for common development.
Best Regards!
Echo Gao
by "sales5" <sales5@henghongparts.com> - 12:40 - 17 Apr 2025 -
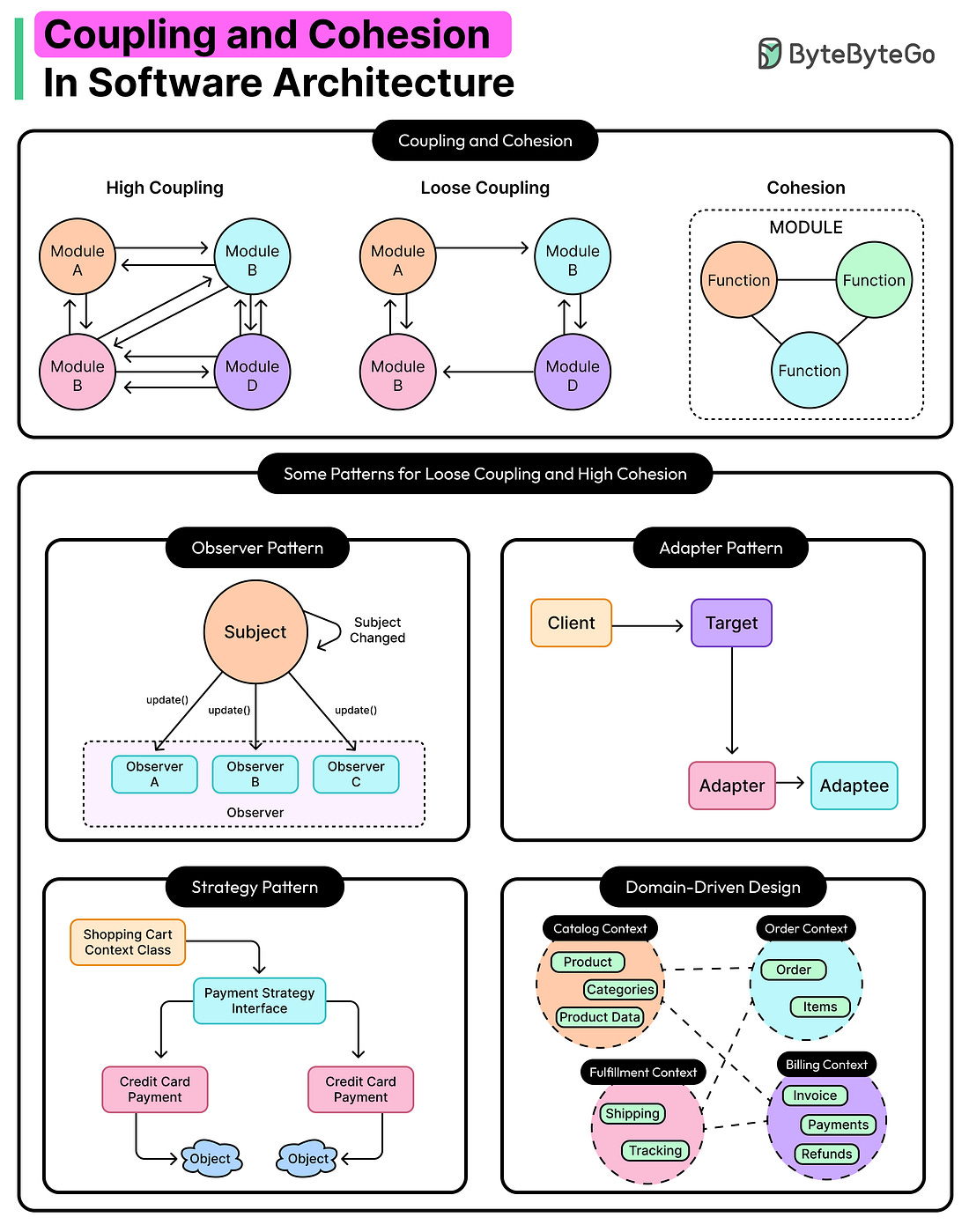
Coupling and Cohesion: The Two Principles for Effective Architecture
Coupling and Cohesion: The Two Principles for Effective Architecture
Every large system that spirals out of control starts the same way: small, functional, and deceptively simple.͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreLatest articles
If you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
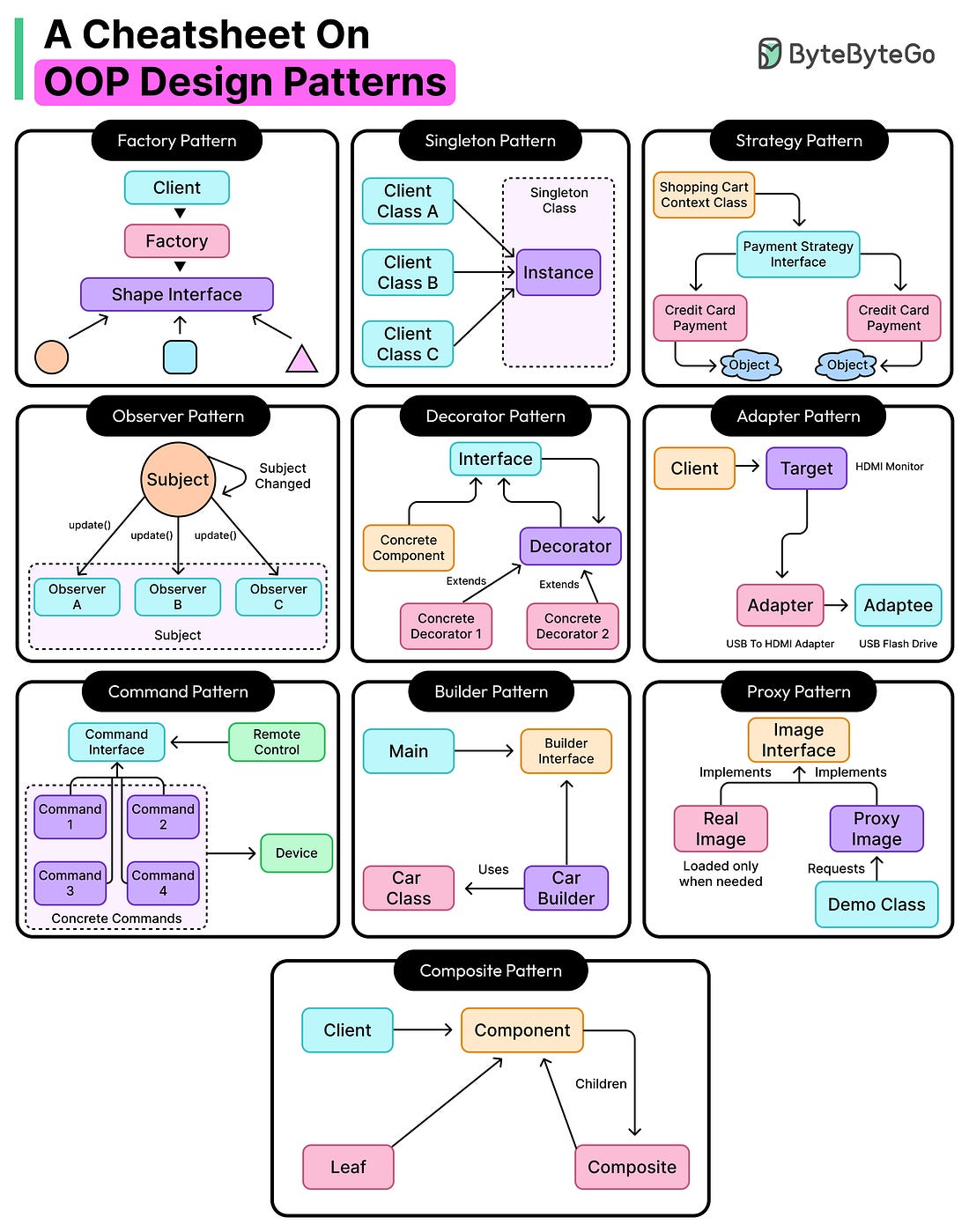
OOP Design Patterns and Anti-Patterns: What Works and What Fails
The Art of REST API Design: Idempotency, Pagination, and Security
Monolith vs Microservices vs Modular Monoliths: What's the Right Choice
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
Every large system that spirals out of control starts the same way: small, functional, and deceptively simple. However, as the system evolves, things spiral out of control.
A feature is added here, a helper function squeezed there, and a “temporary” dependency for some urgent task that never gets removed. Months later, debugging requires going through five layers of indirection, and touching one module can break the entire system.
Behind the scenes of that slow collapse, two invisible forces often play tug-of-war: coupling and cohesion.
Most developers first hear these terms in textbooks or blog posts, often lumped into a “good design” checklist.
High cohesion: good.
Loose coupling: also good.
But beyond the concepts, the practical meaning often gets lost. What does coupling look like? When does cohesion break down in real teams? And why do some projects feel like a breeze to change, while others offer challenges with every pull request?
Coupling and cohesion aren’t abstract guidelines. They are practical engineering realities that define how easily code could evolve, how confidently teams could deploy, and how painful it becomes to onboard a new teammate or fix a bug under pressure.
In this article, we’ll attempt to understand coupling and cohesion in more realistic terms and how they might show up in different architectural styles and patterns.
Understanding Coupling...

Continue reading this post for free in the Substack app
Like
Comment
Restack
© 2025 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 17 Apr 2025 -
Quick estimate
Howdy, Do you have any estimation jobs for us? If so, please share the drawings or illustrations, and we’ll provide you with a quote. Once approved, we can proceed further. Feel free to reach out if you have any questions.Thank you Looking forward to working with you. Kyle Edison
by kyle.hamestimating@gmail.com - 10:21 - 17 Apr 2025 -
Too many resumes. Not enough hires.
Too many resumes. Not enough hires.
Hi MD,
If your hiring pipeline feels overloaded — but still underwhelming — you’re not alone.
Sorting through resumes, chasing down applicants, and switching between tools eats up time most teams don’t have. And still, 38% of hiring leaders say it’s hard to find qualified candidates.
That’s where Remote Recruit comes in.
It’s built to take the weight off your team — starting with AI-powered sourcing that filters out noise and surfaces top talent fast. You’ll go from job post to shortlist in less time, without the clutter of job boards and manual screening.
You can even onboard globally through our Employer of Record (EOR) service — no entity setup needed.
I’ve seen firsthand how much time this saves. It’s why I believe so strongly in giving teams like yours the tools to move fast and hire with confidence.
👉 Try AI-powered sourcing free for 7 days
Best,
Gillian O’Brien
General Manager, Recruit
Remote






You received this email because you are subscribed to
News & Offers from Remote Europe Holding B.V
Update your email preferences to choose the types of emails you receive.
Unsubscribe from all future emailsRemote Europe Holding B.V
Copyright © 2025 Remote Europe Holding B.V All rights reserved.
Kraijenhoffstraat 137A 1018RG Amsterdam The Netherlands
by "Gillian at Remote" <hello@remote-comms.com> - 10:09 - 17 Apr 2025 -
Upcoming Tyk webinars: AI readiness & 5.8 release
Upcoming Tyk webinars: AI readiness & 5.8 release
Hi Md Abul, want to find out what's on?Hi Md Abul,
With 2025 in full-swing, here’s a reminder of our upcoming webinars for you:
AI, APIs, and the path to AI-readiness: Structuring the AI supply chain for enterprise adoption
📅 Date: April 24, 2025
⏰ Time: 10 AM EST / 3 PM BST
📍 Location: Zoom - register hereJoin us to explore the new capabilities of Tyk 5.8 and how they can amplify OpenAPI-powered API definitions, enhancing security, governance, and workflows.
Tyk 5.8: OAS-native API management for secure, interoperable and governance-first API experience
📅 Date: May 8, 2025
⏰ Time: 10 AM EST / 3 PM BST
📍 Location: Zoom - register hereDig into the importance of AI structuring a robust AI supply chain, and get an introduction to Tyk AI Studio, a governance-first solution for managing AI interactions.
Want to stay in the loop of more events for the API community? Follow us on social media below.
Got queries about events? Contact us at communities@tyk.io
See you there!
Budha and team
Tyk, Huckletree 199 Bishopsgate, Broadgate, London, City of London EC2M 3TY, United Kingdom, +44 (0)20 3409 1911
by "Budhaditya Bhattacharya" <budha@tyk.io> - 10:04 - 17 Apr 2025 -
would you like to check free samples of solar cables and connectors--slocable joyce
Hi Dear info,
Are you interested in saving some money? Are you interested in good quality and nice price? And are you interested in small order with fast delivery?
If yes,pls click here and contact me by email sales4@slocable.com.cn or phone +8618025117626
Thanks and best regards!
Joyce

by "market9" <market9@slocablevip.com> - 09:12 - 17 Apr 2025 -
Premium Lamination & Silicon Cores Available
Dear Manager,
I am Sandy from Jiangyin Chuangjia Electrical Co., Ltd. We are a leading manufacturer of transformer cores (EI/UI/By drawing), lamination cores, and silicon cores.We are interested in exploring potential collaboration opportunities and providing you with high-quality products tailored to your needs.
Below is some basic information of our company:
Company Name: JIANGYIN CHUANGJIA ELECTRICAL CO., LTD
Address:ADD: NO.102 XICHENG ROADLINGANG STREET, JIANGYIN,JIANGSU PROVINCE, CHINA.
Business License number: 913202817532007529
Year Established: 2003
Certificate: ISO 9001 approved.
Industry, Type of products: Silicon steel core, transformer core,motor lamination(stator&rotor),CRGO/CRNO slit coils.
Business Type: Manufacturer
The quantity of production:50000 tons per year.
Main Market: Brazil, Spain, Peru, Thailand, Indonesia, Egypt, Turkey, Kuwait, Syria, Oman, India, Bangladesh, Jordan, Lebanon,United Arab Emirates,dominican and so on.Please let us know if you’re interested in learning more about our offerings.
Best Regard,
Sandy(wechat&whatsapp+86 159 9532 9060)
Jiangyin Chuangjia Electrical Co.,ltd
Web:www.siliconsteelcore.com
https://jycjdq.en.alibaba.com/
by "sales15" <sales15@stampingcore.com> - 06:38 - 17 Apr 2025 -
You're Invited! Product Expert Series: Intelligent Observability for Business Uptime
New Relic
Join us for our Product Expert Series: Intelligent Observability for Business Uptime.
This is your chance for a live demo and Q&A with the team behind agentic integrations, predictions, response intelligence, and more innovations for minimizing downtime. Let them show you how you can:- Use agentic AI to streamline: Bring observability insights from New Relic to GitHub, Amazon Q Business, ServiceNow, and more.
- Speed up diagnosing problems: AI points to root cause and suggests remediation steps, based on system-wide analysis (because it knows what’s dependent on what).
- Proactively prevent issues: Gain early warnings to prevent issues, based on analysis of historical trends.
This live webinar is the ideal format to ask questions live, discuss your use cases, and see how Intelligent Observability improves your results.
Register Now 
View in browser
This email was sent to info@learn.odoo.com. Update your email preferences.For information about our privacy practices, see our Privacy Policy.
Need to contact New Relic? You can chat or call us at +44 20 3859 9190
Strand Bridge House, 138-142 Strand, London WC2R 1HH
© 2025 New Relic, Inc. All rights reserved. New Relic logo are trademarks of New Relic, Inc.
by "New Relic" <emeamarketing@newrelic.com> - 04:59 - 17 Apr 2025 -
Join us for the Agentforce World Tour Broadcast | 29 May
Join us for the Agentforce World Tour Broadcast | 29 May
Discover Agentforce, the Digital Labour Platform at SalesforceDiscover Agentforce, the Digital Labour Platform at Salesforce
29 May 2025
9:00 a.m. BKT/ICT | 10:00 a.m. SGTRegister now 29 May 2025
9:00 a.m. BKT/ICT | 10:00 a.m. SGTRegistration is now open for the
Agentforce World Tour Broadcast
Join us for the Agentforce World Tour Broadcast and take your business to the next level with groundbreaking innovation.
It’s time to power up with Agentforce - you’ll find new ways to deepen customer and employee relationships, and boost growth and productivity, by activating digital labour for every team in your company.
Be inspired by the Agentforce keynote and hear remarkable stories of customer success and gain unique insights from our local Trailblazers and thought leaders.
Broadcast date and time: 29 May 2025, 09:00 a.m. BKT/ICT, 10:00 a.m. SGT
Duration: 60 mins
Experience the groundbreaking benefits of Agentforce - the agentic layer and Digital Labour Platform at Salesforce, to take your business to the next level.
We can’t wait to welcome you!Register now Captions will be available during the broadcast for Traditional Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, and Bahasa Indonesia. Your unique viewing link for the broadcast event will be sent to you in a confirmation email upon registering.
© 2025 Salesforce, Inc.
Salesforce.com Singapore Pte Ltd. 5 Temasek Boulevard #13-01 Suntec Tower 5 Singapore 038985
General Inquiries: +65 6302 5700


This email was sent to info@learn.odoo.com
Manage Preferences to Unsubscribe | View as webpage | Privacy Statement
Powered by Salesforce Marketing Cloud
by "Salesforce Events" <aseanevents@salesforce.com> - 03:02 - 17 Apr 2025 -
How can leaders tackle expanding trade controls and tariffs?
On McKinsey Perspectives
Why your business needs a nerve center Brought to you by Alex Panas, global leader of industries, & Axel Karlsson, global leader of functional practices and growth platforms
Welcome to the latest edition of Only McKinsey Perspectives. We hope you find our insights useful. Let us know what you think at Alex_Panas@McKinsey.com and Axel_Karlsson@McKinsey.com.
—Alex and Axel
•
Tariff turbulence. While geopolitical tensions have been rising over several years, the surge in trade controls and reciprocal tariffs has been sudden and intense. The effect on businesses is both significant and unevenly distributed—and will likely remain so, McKinsey Senior Partners Cindy Levy and Shubham Singhal and coauthors explain. In the automotive industry, for example, the amount of components sourced from different countries varies by car model, causing ripple effects throughout automakers’ supply chains. Many other industries are facing similarly complex disruptions.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey Perspectives newsletter, formerly known as Only McKinsey.
Copyright © 2025 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey Perspectives" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:30 - 17 Apr 2025 -
High-Quality Valves for Industrial Applications
Put your preheader text here


Dear Company,
I am writing this email as a foreign trade salesman of Bogong Valve Co., Ltd. We are a valve company located in Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China, specializing in manufacturing various types of valves, such as gate valves, check valves, globe valves, butterfly valves, and ball valves. With more than two decades of manufacturing experience, we have API, EAC, and TS certifications, ensuring that we are at the forefront of the manufacturing industry. Our valves are of high quality and reasonable price, and enjoy a high reputation in China.
We have been working with you and providing our services. We would be very grateful for the opportunity to quote you or send you a technical drawing. Please rest assured that we are committed to providing quality services to meet your needs.
If you are interested, please contact postmaster@bogongvalve.com or Whatsapp: +8615267791204. Or visit our Google site http://bogongvalve.com/ for more information.
We guarantee to provide you with a satisfactory price quotation in a timely manner.
Thank you for considering choosing Bogong Valve Co., Ltd. to meet your valve needs.
Sincerely,
Tony Xiang
Button 
by "sales03" <sales03@BogongValves.com> - 07:31 - 16 Apr 2025 -
Introduction of HISAN: Your trusted partners for Weld Overlay Wear Plates
Dear info,
I hope this message finds you well.
I am writing to introduce our esteemed company, HISAN (Tianjin) Co., Ltd, an ISO9001 certified manufacturer specializing in high-quality weld overlay wear plates. Our extensive range of products includes various grades and thicknesses, meticulously designed to cater to diverse working conditions.
Our facility, covering 11,000 square meters, boasts a monthly production capacity of 12 containers of wear plates. Among our offerings, the Grade HS200 plates have garnered significant popularity due to their exceptional quality and performance.
We take pride in our commitment to delivering reliable and cost-effective solutions to meet your needs. Should you require any further information or have specific inquiries, please do not hesitate to reach out.
Best Regards
HISAN(Tianjin) Co., Ltd
by "Kiyo Harscher" <blaisegudd501@gmail.com> - 12:44 - 16 Apr 2025 -
Achilles Coaching Sport Santé , vous utilisez quoi pour la musique ?
Bonjour,
Une question rapide : comment gérez-vous l’ambiance musicale chez Achilles Coaching Sport Santé ?
Beaucoup de commerces utilisent des radios FM ou Spotify, mais cela pose parfois des problèmes : publicité, musique pas adaptée ou frais cachés.
J’accompagne plusieurs entreprises sur ce sujet, et j’aimerais bien avoir votre avis.
Qu’en diriez-vous d’en discuter ? 😊
Romain
by "Romain Rigaud" <romain.rigaud@license-jamendo.fr> - 08:36 - 16 Apr 2025 -
RE: Looking for a Professional Mexican Agent
Dear agent,
Greetings from Crystal and the entire GLA family. We hope this message finds you well.
I would like to extend a sincere invitation to you to become a part of the GLA platform. As we experience a growing demand from/to Mexico among our GLA members, your participation would be highly valuable in helping us meet and address these requirements effectively.
Above 75% of GLA Members are first-class agents with wide range of primary resources. GLA fulfills all your needs for your business development and resources integration, in terms of finding reliable agents and getting huge volume of inquiries from/to your area.
Besides, We are planning to hold the 12th GLA Global Logistics Conference:
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>Event Name: The 12th GLA Global Logistics Conference
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>Host By: GLA Global Logistics Alliance
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>Event Date: May 15 - 18, 2025 (4 days)
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>Host City: Dubai, UAE
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>Expected Attendee: 1500+
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>From: 130+ countries
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>1-2-1 Meeting: 51 times per pax
The biggest promotion for the 12th GLA Conference is now open till 25th April 2025! Please don’t miss this opportunity to attend the conference as a GLA member.
If you want to know more about GLA, please just feel free to contact me.
Best regards,
Crystal LEE
GLA overseas department
Mobile/ Whatsapp:
(86) 190-7616-6927
Email:
Company:
GLA Co.,Ltd
Website:
Address:
No. 2109, 21st Floor, HongChang, Plaza, No. 2001, Road Shenzhen, China
The 12th GLA Conference - Dubai during 15th-18th May 2025 – click here for registration
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>The 11th GLA Conference in Bangkok Thailand, online album
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>The 10th GLA Conference in Dubai UAE, online album
<![if !supportLists]>Ø <![endif]>The 9th GLA Conference in Hainan China, online album
【Notice Agreement No 7】
7. GLA president reserves the right to cancel or reject membership or application. Company shall cease to be a member of GLA if:
a) the Member does not adhere to GLA terms and conditions
b) the Member gives notice of resignation in writing to the GLA.
c) No good reputation in the market.
d) Have bad debt records in the GLA platform or in the market
by "Crystal LEE" <member72@glafamily.com> - 08:08 - 16 Apr 2025 -
How global companies can succeed in India
On McKinsey Perspectives
What leaders should know Brought to you by Alex Panas, global leader of industries, & Axel Karlsson, global leader of functional practices and growth platforms
Welcome to the latest edition of Only McKinsey Perspectives. We hope you find our insights useful. Let us know what you think at Alex_Panas@McKinsey.com and Axel_Karlsson@McKinsey.com.
—Alex and Axel
•
Business hot spot. The world has taken notice of India’s promises and possibilities as a global business hub, thanks to the country’s skilled workforce, large consumer base, and improving infrastructure. Indeed, over the next decade, India offers many opportunities for multinational companies, explain McKinsey Global Managing Partner Bob Sternfels, McKinsey India Managing Partner Rajat Dhawan, and their coauthors. Yet companies in India may face complex regulations and other challenges. What sets successful global companies in India apart from the rest?
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey Perspectives newsletter, formerly known as Only McKinsey.
Copyright © 2025 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey Perspectives" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:42 - 16 Apr 2025