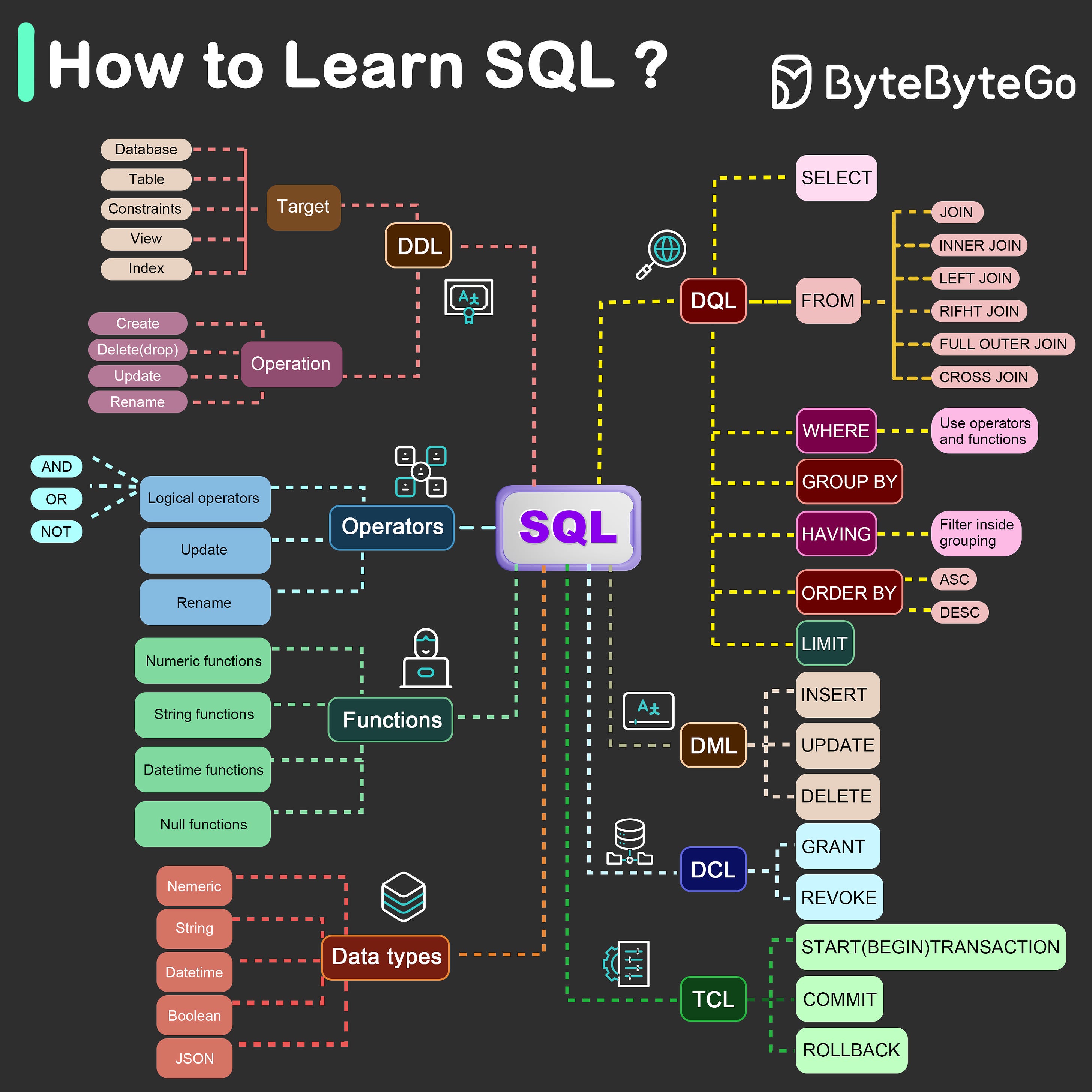
Archives
- By thread 5362
-
By date
- June 2021 10
- July 2021 6
- August 2021 20
- September 2021 21
- October 2021 48
- November 2021 40
- December 2021 23
- January 2022 46
- February 2022 80
- March 2022 109
- April 2022 100
- May 2022 97
- June 2022 105
- July 2022 82
- August 2022 95
- September 2022 103
- October 2022 117
- November 2022 115
- December 2022 102
- January 2023 88
- February 2023 90
- March 2023 116
- April 2023 97
- May 2023 159
- June 2023 145
- July 2023 120
- August 2023 90
- September 2023 102
- October 2023 106
- November 2023 100
- December 2023 74
- January 2024 75
- February 2024 75
- March 2024 78
- April 2024 74
- May 2024 108
- June 2024 98
- July 2024 116
- August 2024 134
- September 2024 130
- October 2024 141
- November 2024 171
- December 2024 115
- January 2025 216
- February 2025 140
- March 2025 220
- April 2025 233
- May 2025 239
- June 2025 303
- July 2025 175
-
EP112: What is a deadlock?
EP112: What is a deadlock?
This week’s system design refresher: Top 9 Most Popular API Protocols (Youtube video) What is a deadlock? What’s the difference between Session-based authentication and JWTs? Top 6 ElasticSearch Use Cases Top 9 Cases Behind 100% CPU Usage SPONSOR US͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreThis week’s system design refresher:
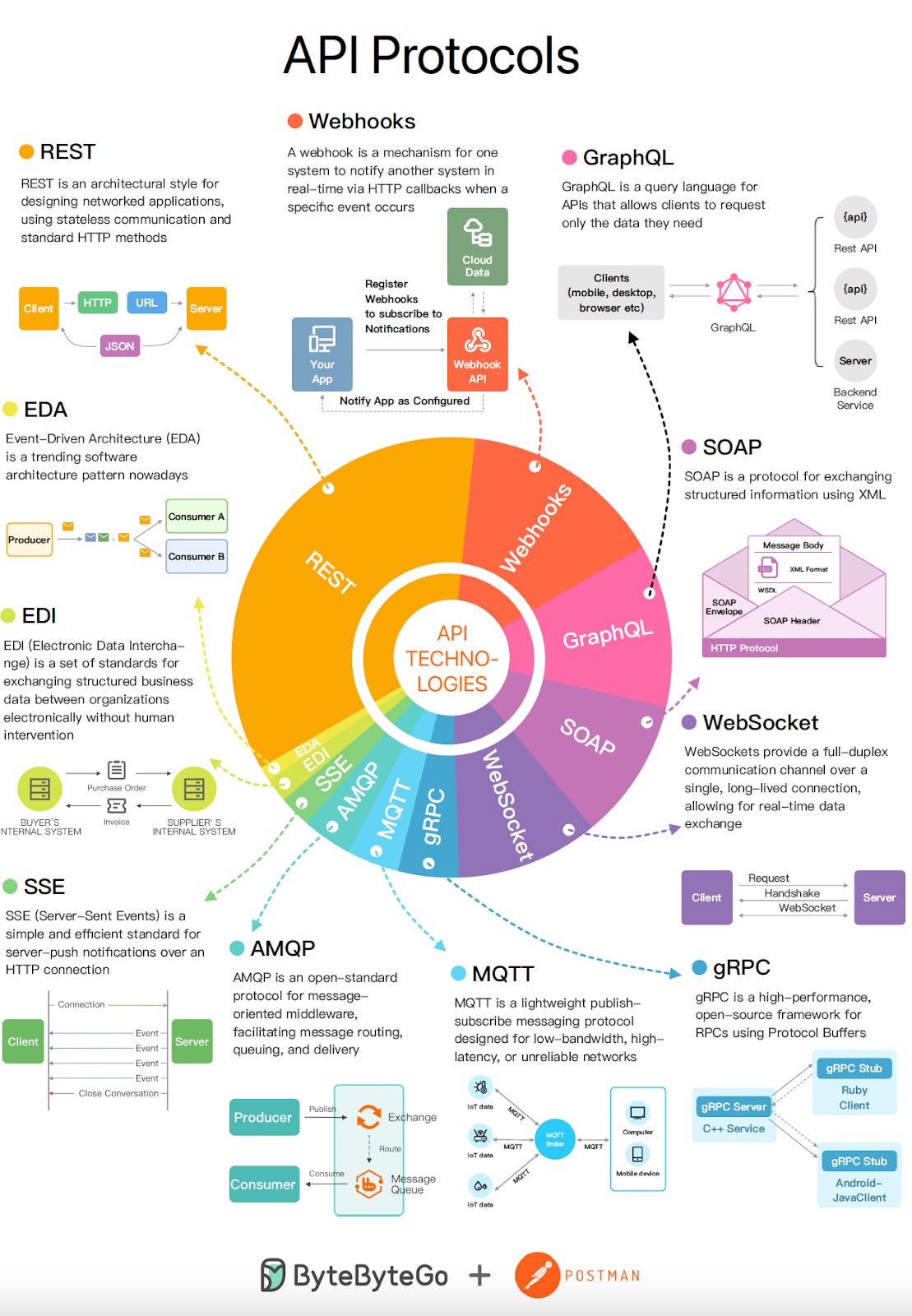
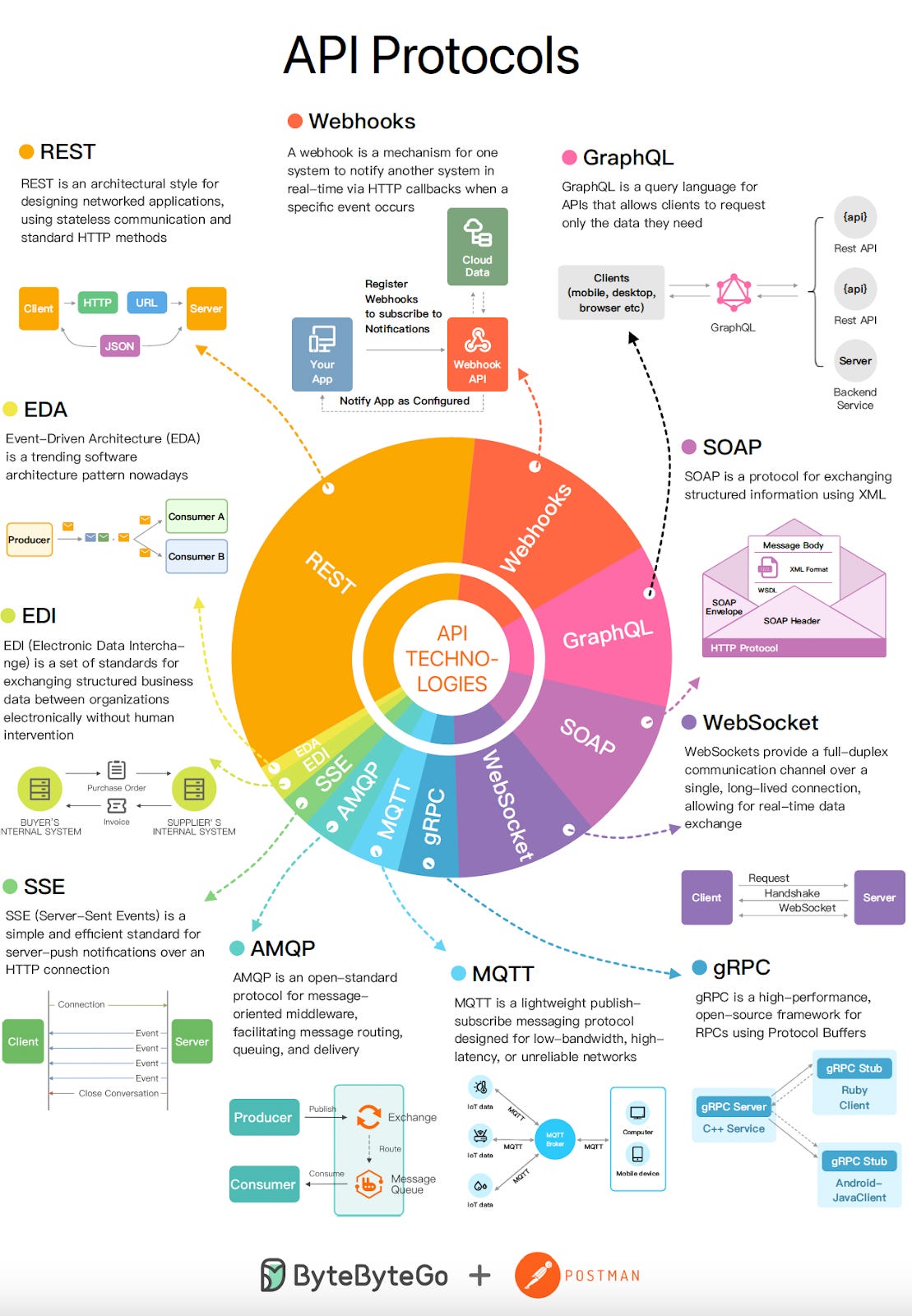
Top 9 Most Popular API Protocols (Youtube video)
What is a deadlock?
What’s the difference between Session-based authentication and JWTs?
Top 6 ElasticSearch Use Cases
Top 9 Cases Behind 100% CPU Usage
SPONSOR US
[Complimentary Download] Gartner Market Guide: Software Engineering Intelligence (SEI) Platforms (Sponsored)
Engineering teams are rapidly adopting Software Engineering Intelligence (SEI) Platforms to improve productivity and value delivery. According to Gartner’s recent Market Guide, use of SEI platforms by engineering organizations will rise to 50% by 2027, compared to 5% in 2024. LinearB was recognized by Gartner as a representative vendor, so we’re offering ByteByteGo readers a complimentary copy.
Learn how you can unlock the transformative potential of SEI platforms by leveraging key features like:
Extensive data from DevOps tools for critical metrics and insights.
Customizable dashboards that highlight pivotal trends and inform strategic decisions.
Insights into KPIs that showcase your team's achievements.
Top 9 Most Popular API Protocols
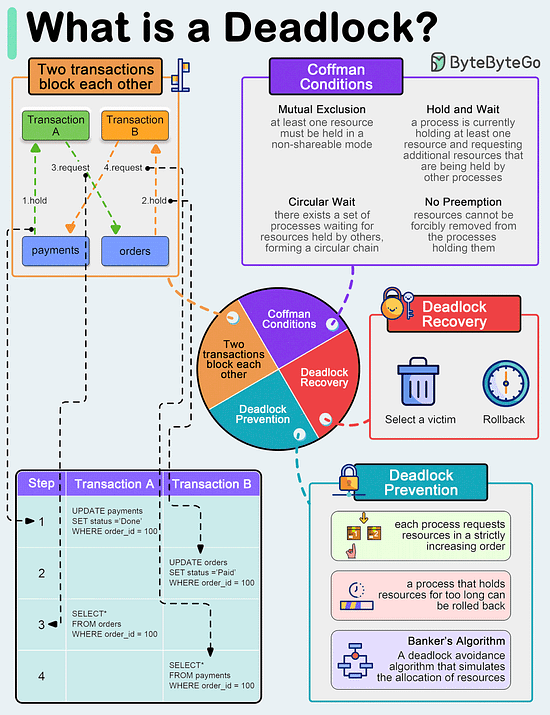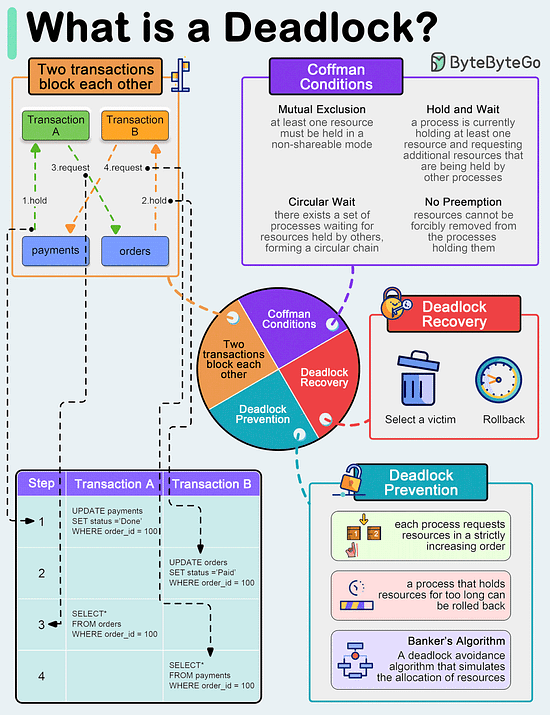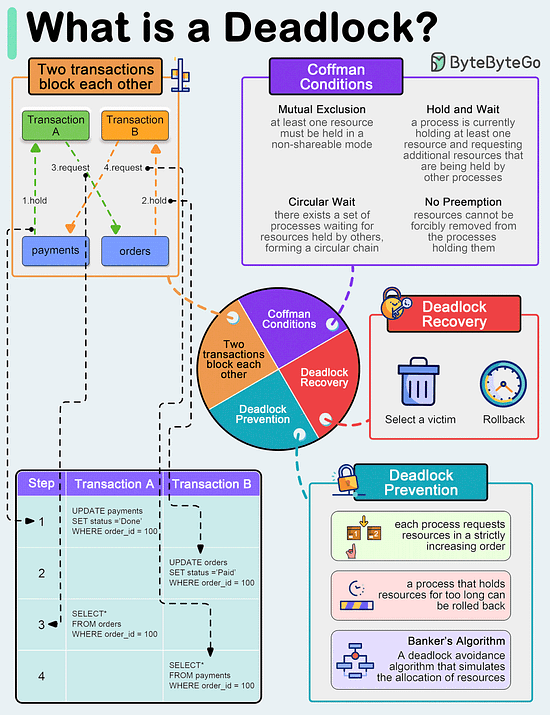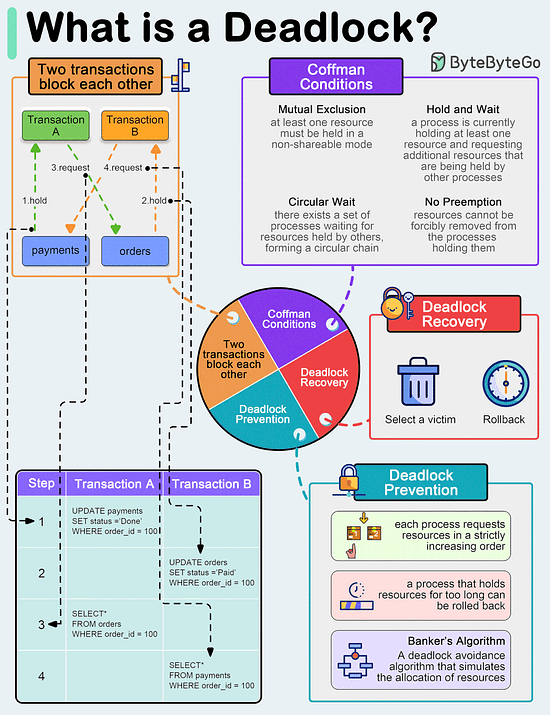
What is a deadlock?
A deadlock occurs when two or more transactions are waiting for each other to release locks on resources they need to continue processing. This results in a situation where neither transaction can proceed, and they end up waiting indefinitely.
Coffman Conditions
The Coffman conditions, named after Edward G. Coffman, Jr., who first outlined them in 1971, describe four necessary conditions that must be present simultaneously for a deadlock to occur:
- Mutual Exclusion
- Hold and Wait
- No Preemption
- Circular WaitDeadlock Prevention
- Resource ordering: impose a total ordering of all resource types, and require that each process requests resources in a strictly increasing order.
- Timeouts: A process that holds resources for too long can be rolled back.
- Banker’s Algorithm: A deadlock avoidance algorithm that simulates the allocation of resources to processes and helps in deciding whether it is safe to grant a resource request based on the future availability of resources, thus avoiding unsafe states.Deadlock Recovery
- Selecting a victim: Most modern Database Management Systems (DBMS) and Operating Systems implement sophisticated algorithms for detecting deadlocks and selecting victims, often allowing customization of the victim selection criteria via configuration settings. The selection can be based on resource utilization, transaction priority, cost of rollback etc.
- Rollback: The database may roll back the entire transaction or just enough of it to break the deadlock. Rolled-back transactions can be restarted automatically by the database management system.
Over to you: have you solved any tricky deadlock issues?
Latest articles
If you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
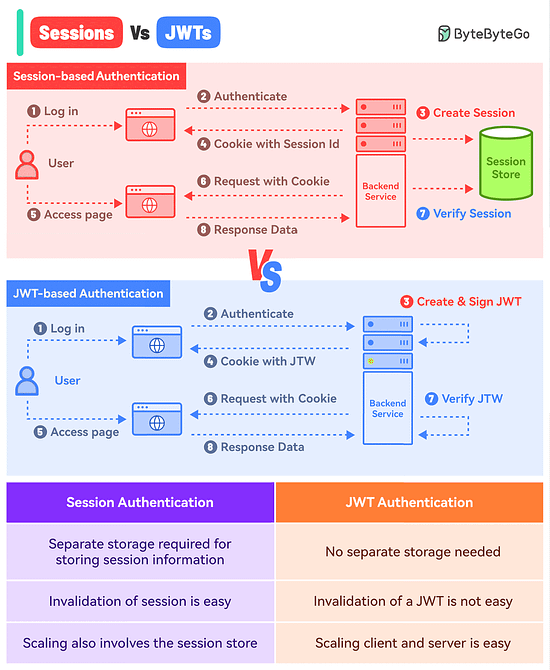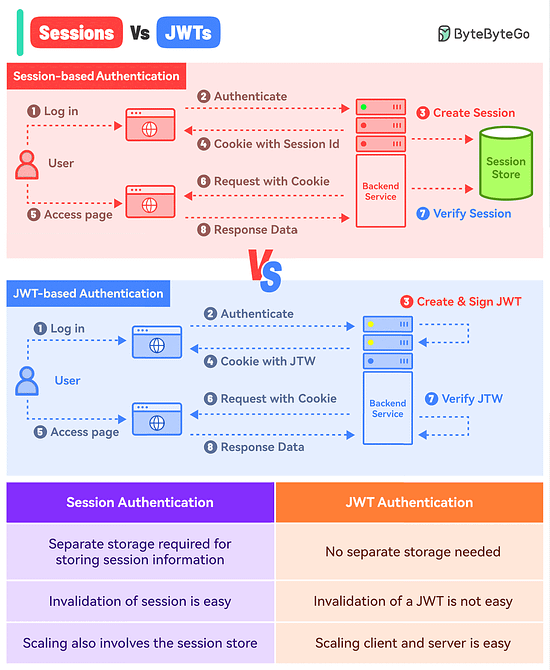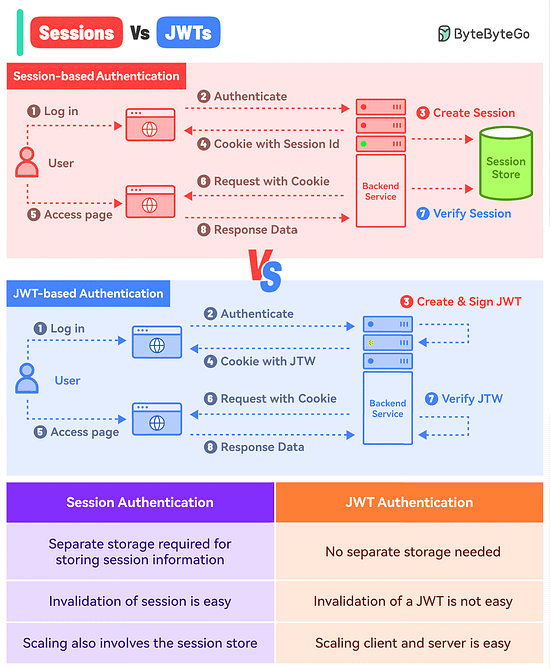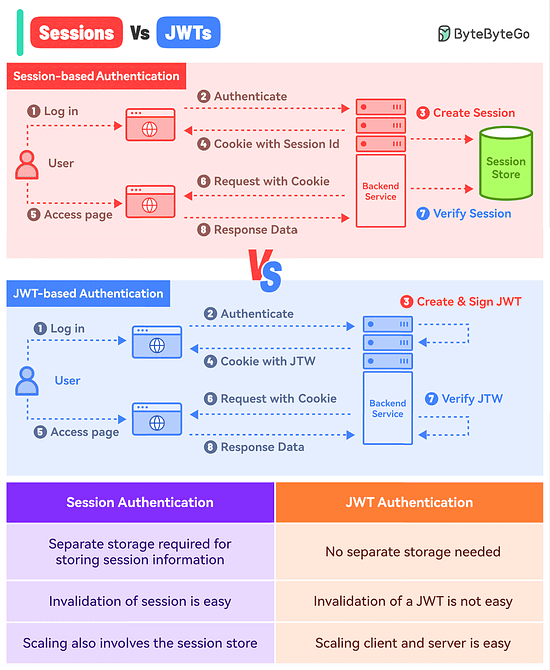
What’s the difference between Session-based authentication and JWTs?
Here’s a simple breakdown for both approaches:
Session-Based Authentication
In this approach, you store the session information in a database or session store and hand over a session ID to the user.
Think of it like a passenger getting just the Ticket ID of their flight while all other details are stored in the airline’s database.
Here’s how it works:The user makes a login request and the frontend app sends the request to the backend server.
The backend creates a session using a secret key and stores the data in session storage.
The server sends a cookie back to the client with the unique session ID.
The user makes a new request and the browser sends the session ID along with the request.
The server authenticates the user using the session ID.
JWT-Based Authentication
In the JWT-based approach, you don’t store the session information in the session store.
The entire information is available within the token.
Think of it like getting the flight ticket along with all the details available on the ticket but encoded.
Here’s how it works:The user makes a login request and it goes to the backend server.
The server verifies the credentials and issues a JWT. The JWT is signed using a private key and no session storage is involved.
The JWT is passed to the client, either as a cookie or in the response body. Both approaches have their pros and cons but we’ve gone with the cookie approach.
For every subsequent request, the browser sends the cookie with the JWT.
The server verifies the JWT using the secret private key and extracts the user info.
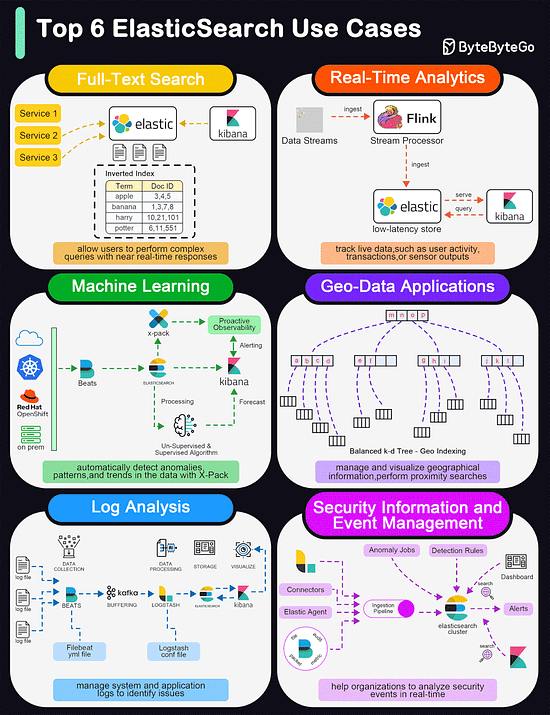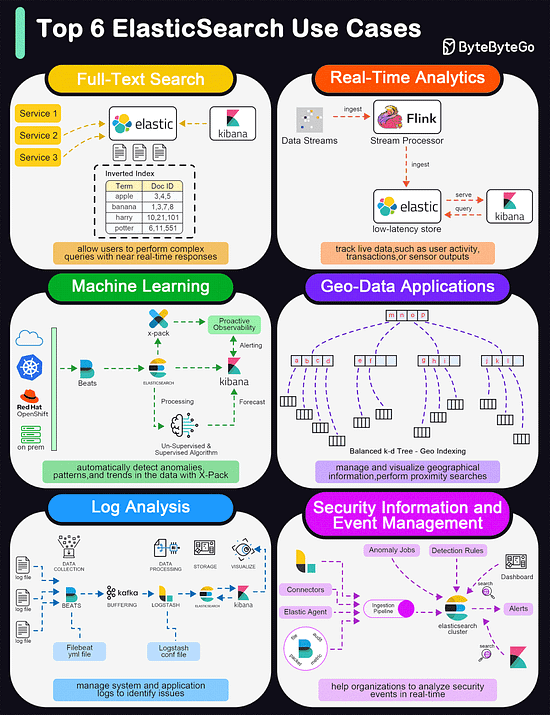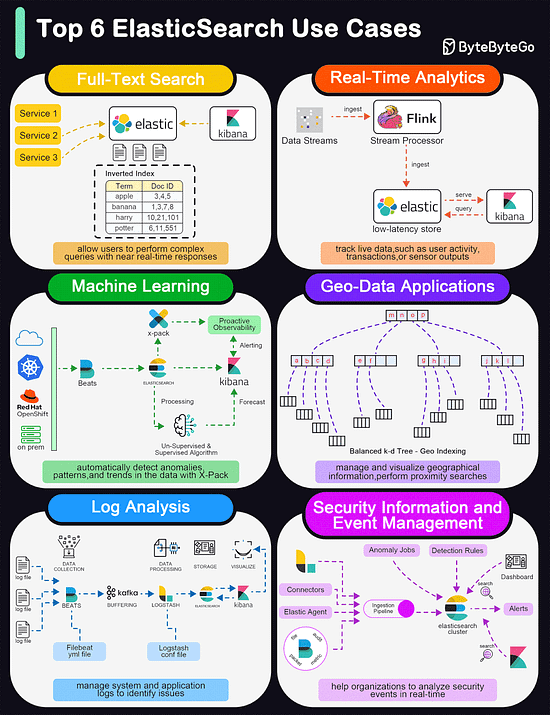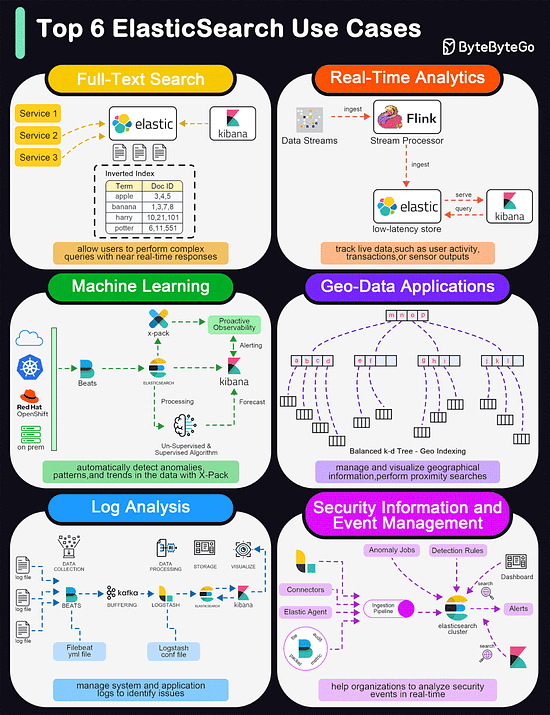
Top 6 ElasticSearch Use Cases
Elasticsearch is widely used for its powerful and versatile search capabilities. The diagram below shows the top 6 use cases:
Full-Text Search
Elasticsearch excels in full-text search scenarios due to its robust, scalable, and fast search capabilities. It allows users to perform complex queries with near real-time responses.Real-Time Analytics
Elasticsearch's ability to perform analytics in real-time makes it suitable for dashboards that track live data, such as user activity, transactions, or sensor outputs.Machine Learning
With the addition of the machine learning feature in X-Pack, Elasticsearch can automatically detect anomalies, patterns, and trends in the data.Geo-Data Applications
Elasticsearch supports geo-data through geospatial indexing and searching capabilities. This is useful for applications that need to manage and visualize geographical information, such as mapping and location-based services.Log and Event Data Analysis
Organizations use Elasticsearch to aggregate, monitor, and analyze logs and event data from various sources. It's a key component of the ELK stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), which is popular for managing system and application logs to identify issues and monitor system health.Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Elasticsearch can be used as a tool for SIEM, helping organizations to analyze security events in real time.
Over to you: What did we miss?
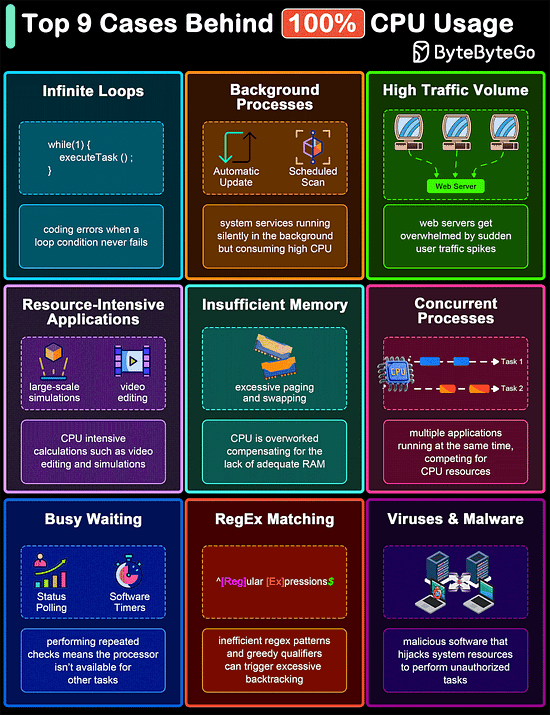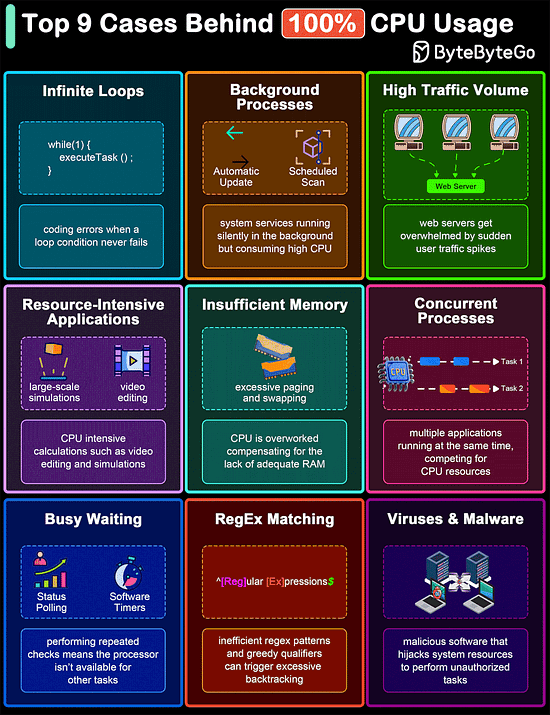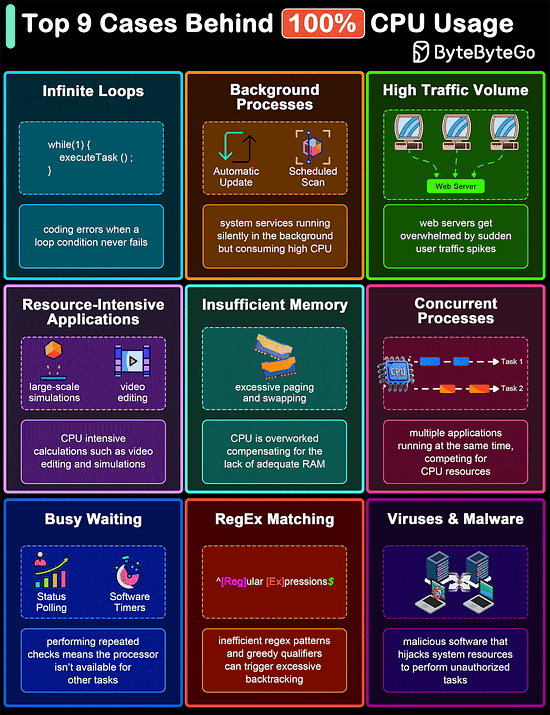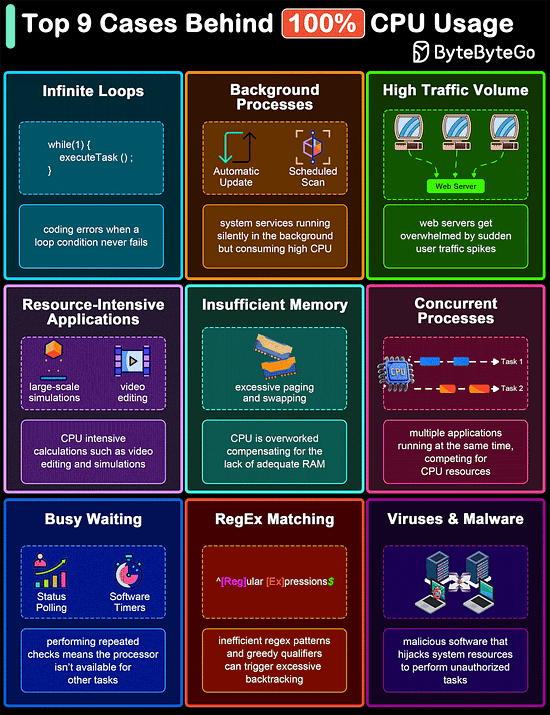
Top 9 Cases Behind 100% CPU Usage
The diagram below shows common culprits that can lead to 100% CPU usage. Understanding these can help in diagnosing problems and improving system efficiency.
Infinite Loops
Background Processes
High Traffic Volume
Resource-Intensive Applications
Insufficient Memory
Concurrent Processes
Busy Waiting
Regular Expression Matching
Malware and Viruses
Over to you: Did we miss anything important?
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 500,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing hi@bytebytego.com
Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 18 May 2024 -
Reminder: Join us for a McKinsey Live webinar on productivity through tech investment
Register now
by "McKinsey & Company" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 02:43 - 17 May 2024 -
Consumer Electronics Show - CES 2024 (Post Show)
Hi,
The verified & updated contacts attendees list of Consumer Electronics Show - CES 2024 is available with us.
Attendees are: - Analyst, Content Developer, Distributor, Buyer, Engineer, Manager/Store Manager/Product Manager, Manufacturer’s Representative, Service Technician, Systems Installer/Integrator & More.
List includes: - Contact Name, Email address, Phone Number, Mailing Address, Job Title etc.
If you are interested in the list, I shall share the counts & cost details.
Best Regards,
Terry Baker - Marketing and Event Coordinator
If you don’t want to receive further emails please revert with “Take Out” in the subject
by terry.baker@datasmining.com - 01:18 - 17 May 2024 -
Thrive or dive: How workers respond to gen AI
The Shortlist
Four new insights Curated by Liz Hilton Segel, chief client officer and managing partner, global industry practices, & Homayoun Hatami, managing partner, global client capabilities
You’ve bought your AI chips, or maybe you’ve upgraded your cloud contract. You’ve started to rethink your IT stack. But is that enough? In our experience, it’s never just about the tech. To extract full value from today’s technologies, companies need much more than hardware and software. They need new ways of thinking about talent, growth, leadership, and change management. This edition of the CEO Shortlist highlights several of the elements needed to get the most out of generative AI and quantum computing. We hope you enjoy the read.
—Liz and Homayoun
Gen AI wealth is built on workplace health. The savviest among us are already using gen AI to knock out busywork. So why are heavy gen AI users increasingly likely to leave their jobs due to burnout? It’s likely because the work gen AI can’t do takes more mental energy to complete—and the elite employees who do it need time to recharge to keep performing at their best. Healthy working cultures will matter even more in the future than they have in the past.
Keep busy with five actions to maximize employee well-being in “To defend against disruption, build a thriving workforce,” a new article by Aaron De Smet, Brooke Weddle, and colleagues.Put away your magic wand. Organizational growth doesn’t happen just like that. Executives at the helm of high-growth organizations actively choose growth every day—especially amid uncertainty. We’ve seen a much steeper growth curve in companies that made bold bets during downturns, including on new technologies, than in those that played it safe.
But don’t mistake bold for reckless. Learn to walk the line with “Six strategies for growth outperformance,” the latest episode of McKinsey’s Inside the Strategy Room podcast, featuring Jill Zucker and colleagues.The quantum advantage. No, it’s not the latest Bond movie. It’s what the world’s leading companies are pursuing through investment and research in quantum computing, sensing, and communication. Our third annual Quantum Technology Monitor reviews the burgeoning opportunities, the flow of new investments, and the startling technological advances.
Leap into the Monitor’s key takeaways with “Steady progress in approaching the quantum advantage,” by Rodney Zemmel and colleagues.Time is money. When it comes to new technologies such as gen AI, speed is a strategy. But whoever invented time isn’t making more of it, as business leaders know well. Our new research reveals six ways that CFOs and other top leaders find the time to not just do their core jobs but also serve as thought partners to CEOs on topics well beyond finance, including new technologies.
Set your watch to “Six ways CFOs find the time to unlock their full potential,” by Ankur Agrawal and colleagues.We hope you find these ideas inspiring and helpful. See you next time with four more McKinsey ideas for the CEO and others in the C-suite.
Share these insights
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to The CEO Shortlist newsletter.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey CEO Shortlist" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 04:07 - 17 May 2024 -
Google 1st page?
Hi,
I found your detail on Google.com and I have looked at your website but noticed that you aren't at the top of Google search.
I can fix that for you and make your company more profitable.
If you are interested, let me know, and I will send you the cost and details about our company. Sincerely,
Geeta Jaiswal,SEO Professional (India)
by "Geeta Jaiswal" <anjalisinghwebsolution@outlook.com> - 03:32 - 17 May 2024 -
How might featuring more Asians and Pacific Islanders advantage Hollywood?
Only McKinsey
API consumers’ untapped potential Brought to you by Liz Hilton Segel, chief client officer and managing partner, global industry practices, & Homayoun Hatami, managing partner, global client capabilities
•
Surge in API on-screen presence. As the entertainment industry undergoes a transformation, studios have the chance to adopt a more inclusive casting approach and broaden their content to appeal to the Asian and Pacific Islander (API) community. While there’s been a remarkable upswing in API on-screen representation in US-distributed films, there’s a long way to go for API on- and off-screen professionals to reach parity with their peers. Moreover, US API consumers still feel their stories are not authentically portrayed. They could be convinced to spend more on entertainment if this pain point is addressed, note McKinsey senior partner Kabir Ahuja and coauthors.
—Edited by Querida Anderson, senior editor, New York
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:47 - 17 May 2024 -
Wide Range of GPS tracking software products that are easy to white-label and customize for your business needs
Wide Range of GPS tracking software products that are easy to white-label and customize for your business needs
Telematics solutions that will supercharge your businessTelematics Solutions We Offer

Uffizio Technologies Pvt. Ltd., 4th Floor, Metropolis, Opp. S.T Workshop, Valsad, Gujarat, 396001, India
by "Sunny Thakur" <sunny.thakur@uffizio.com> - 08:02 - 16 May 2024 -
A Crash Course in GraphQL
A Crash Course in GraphQL
The complexity of software applications has grown by leaps and bounds over the years. This has led to a rise in the number of interfaces between various systems, resulting in an ever-growing API footprint. While APIs have revolutionized the connectivity between systems, the explosion of integrations between clients and servers often leads to maintenance problems. Even minor backend changes take more implementation time since developers must analyze and test more. Despite all the effort, there are still high chances that issues creep into the application.͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreLatest articles
If you’re not a subscriber, here’s what you missed this month.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
The complexity of software applications has grown by leaps and bounds over the years.
This has led to a rise in the number of interfaces between various systems, resulting in an ever-growing API footprint.
While APIs have revolutionized the connectivity between systems, the explosion of integrations between clients and servers often leads to maintenance problems. Even minor backend changes take more implementation time since developers must analyze and test more. Despite all the effort, there are still high chances that issues creep into the application.
Refactoring the application interfaces is one way to address growing maintenance costs. However, this is costly, and there’s no guarantee that we won’t encounter similar issues as the system evolves.
What’s the solution to this problem?
GraphQL is a tool that brings a major change in how clients and servers interact. While it’s not a silver bullet, it can be a sweet spot between a complete application overhaul and doing absolutely nothing
In this issue, we’ll explore GraphQL's features and concepts, compare it to REST API and BFFs, and discuss its advantages and disadvantages.
What is GraphQL?...

Continue reading this post for free, courtesy of Alex Xu.
A subscription gets you:
An extra deep dive on Thursdays Full archive Many expense it with team's learning budget Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:36 - 16 May 2024 -
RE: DIA Global 2024
Hi,
I’m curious to know if would you be interested in our mailing lists.?
Could you please just hit me back with a number 1-2-3 that best describes your response?
1.Interested to see Count & Cost.
2.Too busy, email me again in a month, please.
3.Please close my tab, I’m not interested…
Looking back to hear from you.
Marketing Analyst - Laurie Young
Please let me know if you have any particular goals in mind so that I can adjust the list.
From: laurie.young@planetmaillinglist.com <laurie.young@planetmaillinglist.com>
Sent: Tuesday, May 14, 2024 5:41 PM
To: 'info@learn.odoo.com' <info@learn.odoo.com>
Subject: DIA Global 2024Greetings,
An attendees list for the Drug Information Association Annual Meeting - DIA Show is available tailored to meet your marketing needs.
List Includes: Company Name, Contact Name, Verified E-mail id’s, Tel.no, URL/Website, Title/Designation.
Can I send you cost of full lists.? If you are interested.
Marketing Manager – Laurie Young
Let me know if you have any particular targets in mind so that I can customize the list.
by laurie.young@planetmaillinglist.com - 10:52 - 16 May 2024 -
[Online workshop] Maximising performance with integrated APM and infrastructure monitoring
New Relic
 Register for this free online workshop on the 30th May at 10am BST/11am CEST to learn more about the integration of APM and infrastructure monitoring, and discover how they enhance operational visibility, mitigate risks and deliver valuable insights from application and system data.
Register for this free online workshop on the 30th May at 10am BST/11am CEST to learn more about the integration of APM and infrastructure monitoring, and discover how they enhance operational visibility, mitigate risks and deliver valuable insights from application and system data.
Attend this session and learn how to:- Use new UI components in APM and infrastructure to locate issues, troubleshoot faster and uncover observability gaps
- Understand the UI bridges between APM and infrastructure that connect performance in your environments
- Work with updated filter capabilities in Infrastructure to view relevant parts of your ecosystem, and create powerful saved views
- Correlate infrastructure, application performance and utilisation metrics side by side.
Register now Need help? Let's get in touch.



This email is sent from an account used for sending messages only. Please do not reply to this email to contact us—we will not get your response.
This email was sent to info@learn.odoo.com Update your email preferences.
For information about our privacy practices, see our Privacy Policy.
Need to contact New Relic? You can chat or call us at +44 20 3859 9190.
Strand Bridge House, 138-142 Strand, London WC2R 1HH
© 2024 New Relic, Inc. All rights reserved. New Relic logo are trademarks of New Relic, Inc

by "New Relic" <emeamarketing@newrelic.com> - 05:12 - 16 May 2024 -
Pre-production Samples
Dear info,
Pls find attached inventory list that you forwarded to our purchase dept. Please clarify if these list is valid. Good customer has some purchase other with us for a big project.
Best regards,
Helen Li
Sr. Specialist, Supplies I Office Depot Merchandising (Shenzhen) Co. Ltd.
9/F, Block A, World Finance Center, No. 4003 Shennan Dong Road,
Louhu District, Shenzhen, China, P.C:518001
广东省深圳市罗湖区深南东路4003号世界金融中心A栋9层 /
邮编:518001 Tel: +86 755 8284 6770 I helen.mei-li@
officedepot.com CONFIDENTIALITY NOTICE: The information contained in this email and attached document(s) may contain confidential information that is intended only for the addressee(s). If you are not the intended recipient, you are hereby advised that any disclosure, copying, distribution or the taking of any action in reliance upon the information is prohibited If you have received this email in error, please immediately notify the sender and delete it from your system
by "Helen Mei-Li" <Helen.Mei-Li@OfficeDepot.com> - 04:56 - 16 May 2024 -
Can semiconductor leaders keep up with surging chip demand?
Only McKinsey
Scenarios for demand in 2030 Brought to you by Liz Hilton Segel, chief client officer and managing partner, global industry practices, & Homayoun Hatami, managing partner, global client capabilities
•
Surging need for chips. As generative AI (gen AI) applications take the world by storm, demand for computational power is soaring, McKinsey senior partner Mark Patel, whose expertise includes QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and coauthors reflect. Can the semiconductor sector keep up? To guide semiconductor leaders, McKinsey has developed several scenarios for gen AI’s effect in the B2B and B2C markets. Every scenario involves a massive increase in compute—and thus wafer—demand.
—Edited by Belinda Yu, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:36 - 16 May 2024 -
Canal delays are making waves
Re:think
Coping with ocean cargo delays FRESH TAKES ON BIG IDEAS
ON CANAL CARGO
Canal slowdowns could create rough seas for global tradeJohn Murnane
When delays recently afflicted two major canals—the Panama Canal, due to a drought that created low water levels, and the Suez Canal, due to conflict in the Red Sea region—it was the latest in a long line of supply chain complications that have occurred since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nowadays, supply chain executives are aware that they need to be ready for anything. There was even a previous canal shutdown in 2021 when a ship ran aground in the Suez. As a result, these canal slowdowns haven’t been quite the shock that they might have been in the past.
That said, trade route disruptions have consequences. Different trade lanes and types of cargo face different challenges. Companies dealing in items with tightly time-constrained supply chains and high value per volume—such as electronics—could start using air carriers to keep operating smoothly. Some sectors—such as automotive, pharmaceuticals, and high-end retail—could see inventory shortages, which could frustrate consumers. Higher transport costs could also be passed on to those consumers. Companies might investigate sourcing items from new locations that are less affected by canal delays; maybe some manufacturing gets shifted from Asia to, say, Angola. However, it can take 18 months or more to negotiate new sourcing, and the newly sourced item might not be identical to the previous version.
Lower-value goods could be profoundly affected because their transportation costs are high compared with their total value. Some bulk-commodity trade lanes that rely on the canals might not even be viable if cargo transit cost and duration both increase dramatically. For instance, flows of grain from Europe into Eastern Africa that move straight through the Suez on barges might make less sense if they need to make a longer journey around the southern tip of Africa using a different type of ship that can handle that trickier passage. The refrigerated-fruit trade from the west coast of South America could also face serious challenges if markets on the far side of the Panama Canal are no longer accessible. Ultimately, the chunk of trade involved is big enough to affect macroeconomics. Canal delays could show up in GDP numbers or inflation rates. The delays could also affect carbon emissions. More items might be sent by air, which creates higher emissions rates than ocean shipping. And even when items are sent by sea, rerouted ships will, in many cases, have to make longer passages and try to sail at faster speeds to make up time, which burns more fuel.“For some companies, these canal slowdowns could present growth opportunities.”
I’ve laid out a bunch of downsides. But for some companies, these canal slowdowns could present growth opportunities. Maybe a company can gain more share in a market because a dominant competitor’s easy routing through the Suez has been disrupted. Maybe a manufacturer on the west coast of Africa, not reliant on the Suez for transport, is suddenly more attractive to European customers. There could be new success stories as companies realize that logistics can be a strategic advantage.
For decades before the pandemic, moving goods by ship anywhere in the world was generally very easy and inexpensive. Even at large companies, there were sometimes only one or two people left handling logistics because it was mostly just a procurement function. Companies are now starting to see that they need the capacity to handle disruptions and that logistics can be a competitive strength when done right.
This is a critical moment for companies to modernize their logistics capabilities, particularly by taking advantage of digital advancements that enable sharper insights and smarter execution. Elevating the role of logistics within a company and integrating logistics leaders into global strategy teams can lead to faster decision making and broader impact. Companies can view logistics as a means of differentiation and value creation, not just as a cost to minimize.ABOUT THIS AUTHOR
John Murnane is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
MORE FROM THIS AUTHOR
UP NEXT
Kana Enomoto on employee well-being
Burnout and mental health disorders are pervasive and complex issues. Organizations that invest in employee well-being now may become tomorrow’s employers of choice.
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to our McKinsey Quarterly alert list.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey Quarterly" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 02:39 - 15 May 2024 -
A new issue of the McKinsey Quarterly is here
Sign up now for instant access Productivity and the next age of abundance
The newest issue of the McKinsey Quarterly explores productivity and the next age of abundance. In our cover story, “The productivity imperative,” McKinsey’s Ezra Greenberg, Asutosh Padhi, and Sven Smit argue that there is a three-sided productivity opportunity that allows companies to invest in a brighter future and boost growth and profitability.
Other features include:•
how to implement gen AI with speed and safety
•
how leaders can address stalled global cooperation
•
the difficulty—and potential—behind adopting climate technology
•
the trends defining the $1.8 trillion global wellness market
This edition is available in an immersive online reading experience we’ve recently unveiled for our flagship publication. Sign up for a free digital Quarterly membership to access it.
A membership to the digital edition of the McKinsey Quarterly also includes downloads of our top reports in the McKinsey Insights Store as well as access to all digital issues of the Quarterly.
This email contains information about McKinsey’s research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this email because you subscribed to our McKinsey Quarterly alert list.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "McKinsey & Company" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 04:57 - 15 May 2024 -
What can generative AI do for CFOs?
On Point
CFOs, meet gen AI Brought to you by Liz Hilton Segel, chief client officer and managing partner, global industry practices, & Homayoun Hatami, managing partner, global client capabilities
•
Testing the waters. Gen AI holds the potential to generate value, but this doesn’t happen automatically. Finance chiefs can’t plug and play with gen AI; the technology must be trained with data sets that are themselves first curated to ensure applicable outputs. Executives still dipping their toes into gen AI waters can find many solutions online to get a feel for how large language models work, McKinsey senior partner Ben Ellencweig and colleagues note. CFOs may want to prioritize particular use cases in the finance function that can produce useful outcomes with gen AI initiatives.
—Edited by Sarah Thuerk, editor, Atlanta
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 11:06 - 14 May 2024 -
Taskeye - Field Employee Task Tracking Software Offering Real-Time Visibility into Employees Activities on the Field.
Taskeye - Field Employee Task Tracking Software Offering Real-Time Visibility into Employees Activities on the Field.
A Versatile Platform is Designed to Cater to the Unique Needs of Various Field Domains.Experience the power of our field employe task tracking software that offers real-time visibility into employees’ activities on the field. With our innovative device-less tracking system, effortlessly monitor the workforce and optimize their performance like never before.



Advanced tool to reduce workload and increase employee productivity.

Uffizio Technologies Pvt. Ltd., 4th Floor, Metropolis, Opp. S.T Workshop, Valsad, Gujarat, 396001, India
by "Sunny Thakur" <sunny.thakur@uffizio.com> - 08:00 - 14 May 2024 -
DIA Global 2024
Greetings,
An attendees list for the Drug Information Association Annual Meeting - DIA Show is available tailored to meet your marketing needs.
List Includes: Company Name, Contact Name, Verified E-mail id’s, Tel.no, URL/Website, Title/Designation.
Can I send you cost of full lists.? If you are interested.
Marketing Manager – Laurie Young
Let me know if you have any particular targets in mind so that I can customize the list.
by laurie.young@planetmaillinglist.com - 05:46 - 14 May 2024 -
Important: Platform migration on May 18, 7-9 am UTC 🔧
Remote
Important: Platform migration on May 18, 7-9 am UTC 🔧
Hello 👋
On May 18 at 7am UTC, we are migrating our servers to improve the reliability and security of our services.
During this 2-hour window, you may experience temporary unavailability of Remote, including employ.remote.com, our mobile app and all supporting services.
We appreciate your patience and are committed to ensuring this process is as seamless as possible.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, do not hesitate to reach out through our chat support, email us at help@remote.com, or visit our status page. We’re here to help!
Thank you,
Your Remote team.ℹ️ This is a system notification sent to all users, even those who have unsubscribed from marketing emails. For more details, refer to this article.
.
by "Remote" <no-reply@remote.com> - 03:03 - 14 May 2024 -
How Facebook served billions of requests per second Using Memcached
How Facebook served billions of requests per second Using Memcached
Creating stronger passwords with AuthKit (Sponsored) A common cause of data breaches and account hijacking is customers using weak or common passwords. One way to mitigate this risk is to inform new users about the strength of their passwords as they create them.͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ Forwarded this email? Subscribe here for moreCreating stronger passwords with AuthKit (Sponsored)
A common cause of data breaches and account hijacking is customers using weak or common passwords.
One way to mitigate this risk is to inform new users about the strength of their passwords as they create them.
To solve this problem, Dropbox created zxcvbn, an open-source library that calculates password strength based on factors like entropy, dictionary checks, and pattern recognition.
If you want an easy way to implement user password security in your app, check out AuthKit, an open-source login box that incorporates zxcvbn and other best practices to provide a much more secure onboarding experience for new users.There are two absolute truths about running a social network at the scale of Facebook:
First, it cannot go down.
Second, it cannot run slow.
These two factors determine whether people are going to stay on your social network or not.
Even a few people leaving impacts the entire user base because the users are interconnected. Most people are online because their friends or relatives are online and there’s a domino effect at play. If one user drops off due to issues, there are chances that other users will also leave.
Facebook had to deal with these issues early on because of its popularity. At any point in time, millions of people were accessing Facebook from all over the world.
In terms of software design, this meant a few important requirements:
Facebook had to support real-time communication.
They had to build capabilities for on-the-fly content aggregation.
Scale to handle billions of user requests.
Store trillions of items across multiple geographic locations.
To achieve these goals, Facebook took up the open-source version of Memcached and enhanced it to build a distributed key-value store.
This enhanced version was known as Memcache.
In this post, we will look at how Facebook solved the multiple challenges in scaling memcached to serve billions of requests per second.
Introduction to Memcached
Memcached is an in-memory key-value store that supports a simple set of operations such as set, get, and delete.
The open-source version provided a single-machine in-memory hash table. The engineers at Facebook took up this version as a basic building block to create a distributed key-value store known as Memcache.
In other words, “Memcached” is the source code or the running binary whereas “Memcache” stands for the distributed system behind it.
Technically, Facebook used Memcache in two main ways:
Query Cache
The job of the query cache was to reduce the load on the primary source-of-truth databases.
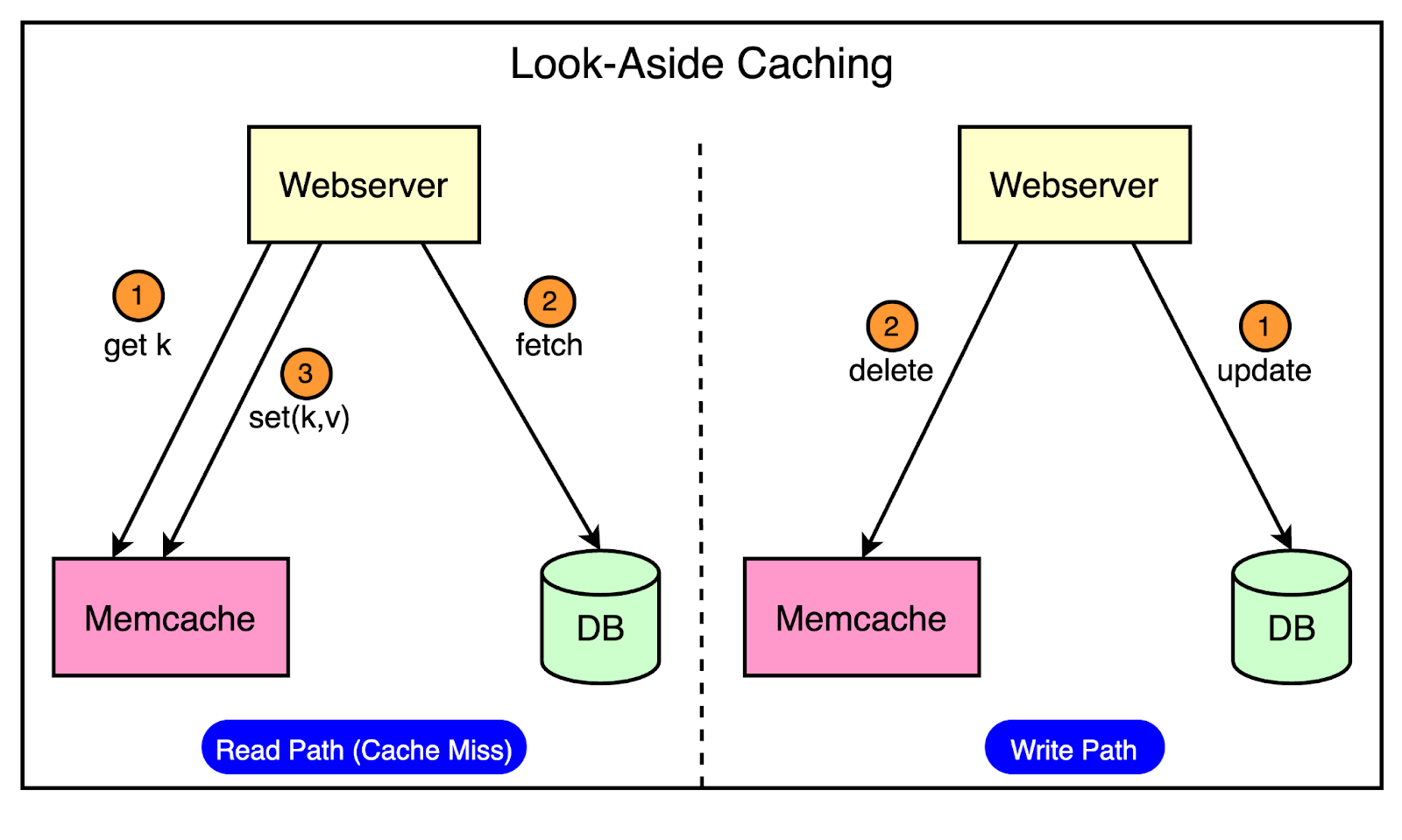
In this mode, Facebook used Memcache as a demand-filled look-aside cache. You may have also heard about it as the cache-aside pattern.
The below diagram shows how the look-aside cache pattern works for the read and write path.
The read path utilizes a cache that is filled on-demand. This means that data is only loaded into the cache when a client specifically requests it.
Before serving the request, the client first checks the cache. If the desired data is not found in the cache (a cache miss), the client retrieves the data from the database and also updates the cache.
The write path takes a more interesting approach to updating data.
After a particular key is updated in the database, the system doesn’t directly update the corresponding value in the cache. Instead, it removes the data for that key from the cache entirely. This process is known as cache invalidation.
By invalidating the cache entry, the system ensures that the next time a client requests data for that key, it will experience a cache miss and be forced to retrieve the most up-to-date value directly from the database. This approach helps maintain data consistency between the cache and the database.
Generic Cache
Facebook also leverages Memcache as a general-purpose key-value store. This allows different teams within the organization to utilize Memcache for storing pre-computed results generated from computationally expensive machine learning algorithms.
By storing these pre-computed ML results in Memcache, other applications can quickly and easily access them whenever needed.
This approach offers several benefits such as improved performance and resource optimization.
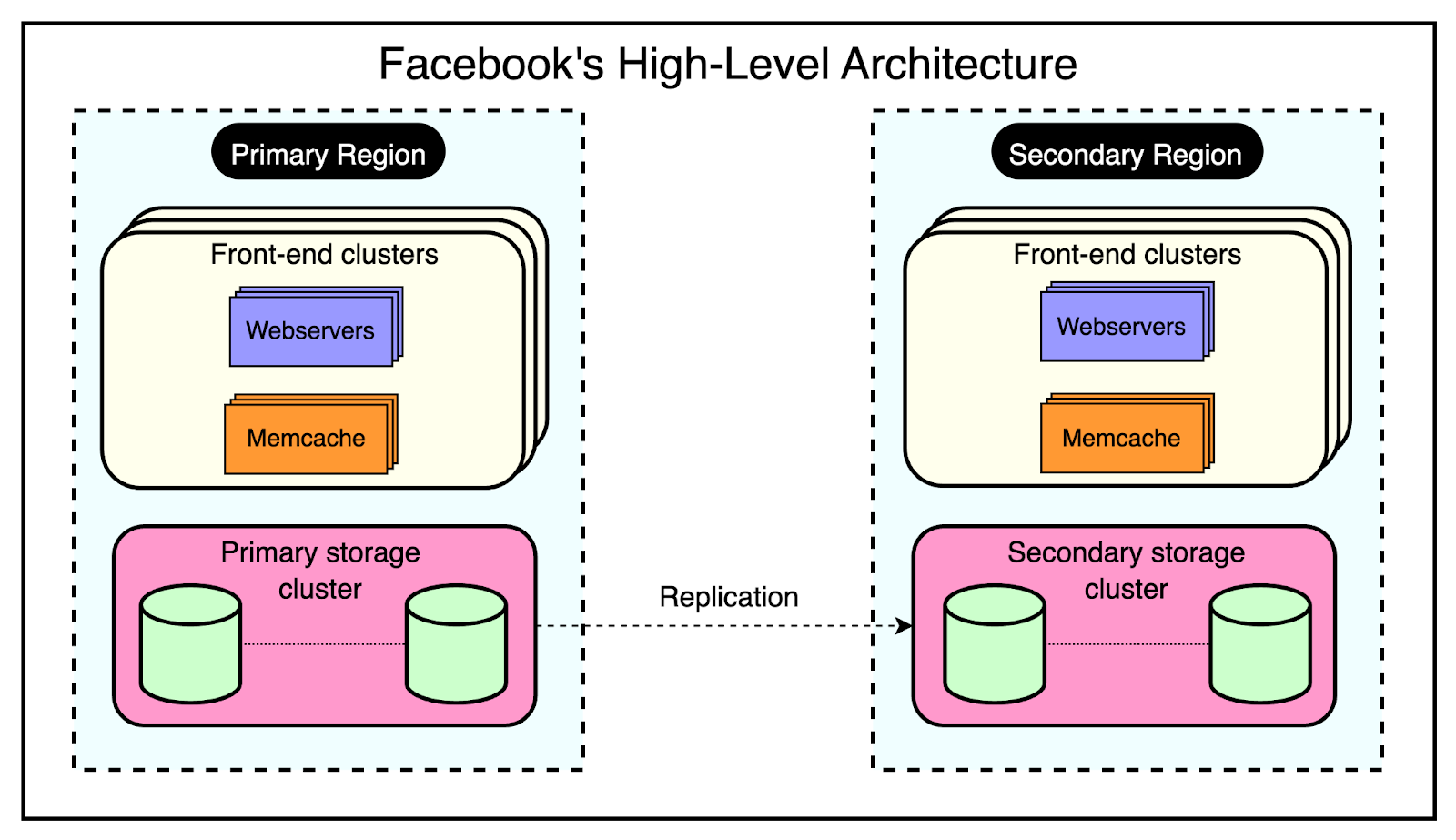
High-Level Architecture of Facebook
Facebook’s architecture is built to handle the massive scale and global reach of its platform.
At the time of their Memcached adoption, Facebook’s high-level architecture consisted of three key components:
1 - Regions
Facebook strategically places its servers in various locations worldwide, known as regions. These regions are classified into two types:
Primary Region: The primary region is responsible for handling the majority of user traffic and data management.
Secondary Region: Multiple secondary regions are distributed globally to provide redundancy, load balancing, and improved performance for users in different geographical areas.
Each region, whether primary or secondary, contains multiple frontend clusters and a single storage cluster.
2 - Frontend Clusters
Within each region, Facebook employs frontend clusters to handle user requests and serve content. A frontend cluster consists of two main components:
Web Servers: These servers are responsible for processing user requests, rendering pages, and delivering content to the users.
Memcache Servers: Memcache servers act as a distributed caching layer, storing frequently accessed data in memory for quick retrieval.
The frontend clusters are designed to scale horizontally based on demand. As user traffic increases, additional web and Memcache servers can be added to the cluster to handle the increased load.
3 - Storage Cluster
At the core of each region lies the storage cluster. This cluster contains the source-of-truth database, which stores the authoritative copy of every data item within Facebook’s system.
The storage cluster takes care of data consistency, durability, and reliability.
By replicating data across multiple regions and employing a primary-secondary architecture, Facebook achieves high availability and fault tolerance.
The below diagram shows the high-level view of this architecture:
One major philosophy that Facebook adopted was a willingness to expose slightly stale data instead of allowing excessive load on the backend.
Rather than striving for perfect data consistency at all times, Facebook accepted that users may sometimes see outdated information in their feeds. This approach allowed them to handle high traffic loads without crumbling under excessive strain on the backend infrastructure.
To make this architecture work at an unprecedented scale of billions of requests every day, Facebook had to solve multiple challenges such as:
Managing latency and failures within a cluster.
Managing data replication within a region.
Managing data consistency across regions.
In the next few sections, we will look at how Facebook handled each of these challenges.
Within Cluster Challenges
There were three important goals for the within-cluster operations:
Reducing latency
Reducing the load on the database
Handling failures
1 - Reducing Latency
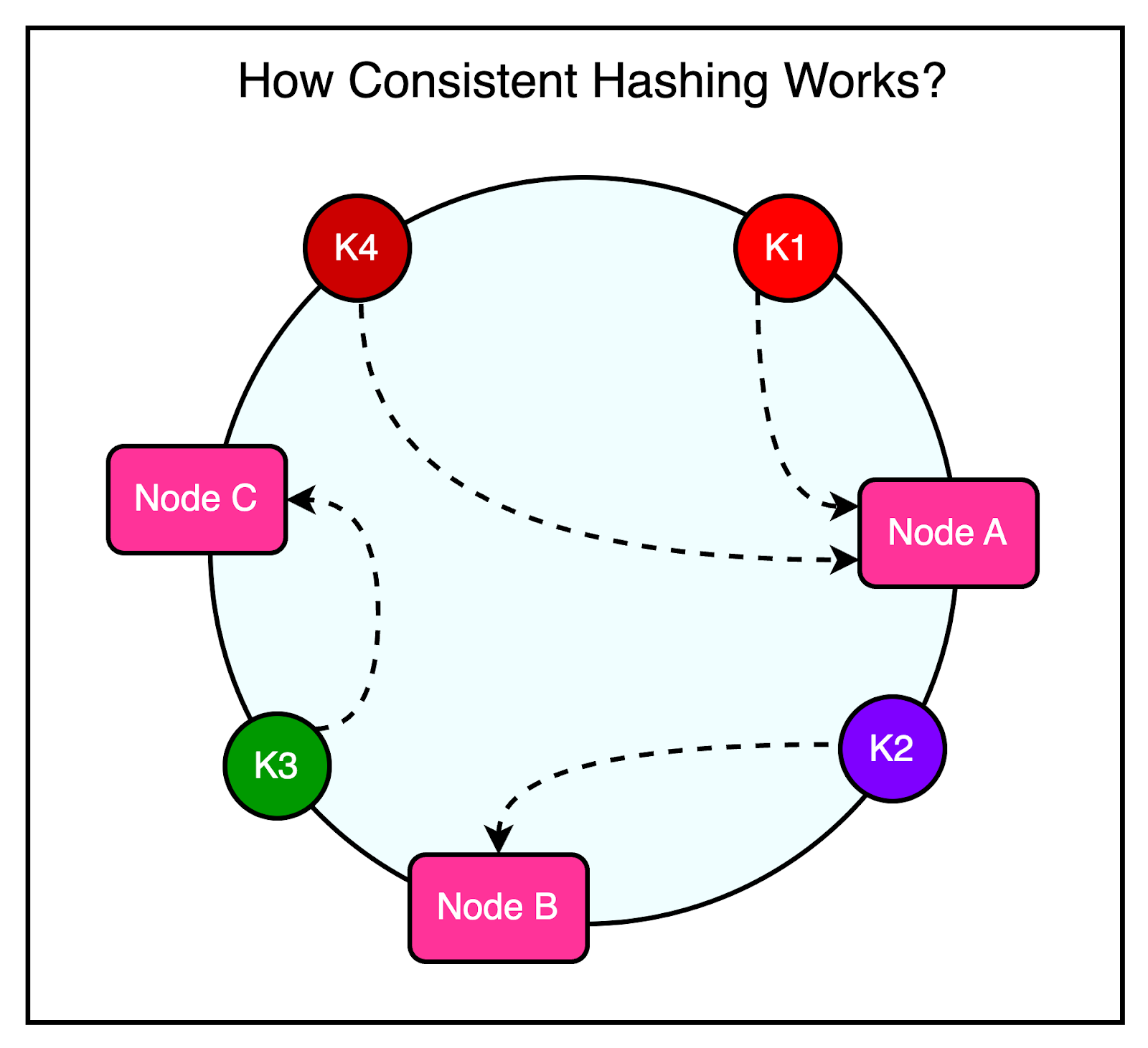
As mentioned earlier, every frontend cluster contains hundreds of Memcached servers, and items are distributed across these servers using techniques like Consistent Hashing.
For reference, Consistent Hashing is a technique that allows the distribution of a set of keys across multiple nodes in a way that minimizes the impact of node failures or additions. When a node goes down or a new node is introduced, Consistent Hashing ensures that only a small subset of keys needs to be redistributed, rather than requiring a complete reshuffling of data.
The diagram illustrates the concept of Consistent Hashing where keys are mapped to a circular hash space, and nodes are assigned positions on the circle. Each key is assigned to the node that falls closest to it in a clockwise direction.
At Facebook's scale, a single web request can trigger hundreds of fetch requests to retrieve data from Memcached servers. Consider a scenario where a user loads a popular page containing numerous posts and comments.
Even a single request can require the web servers to communicate with multiple Memcached servers in a short timeframe to populate the necessary data.
This high-volume data fetching occurs not only in cache hit situations but also when there’s a cache miss. The implication is that a single Memcached server can turn into a bottleneck for many web servers, leading to increased latency and degraded performance for the end user.
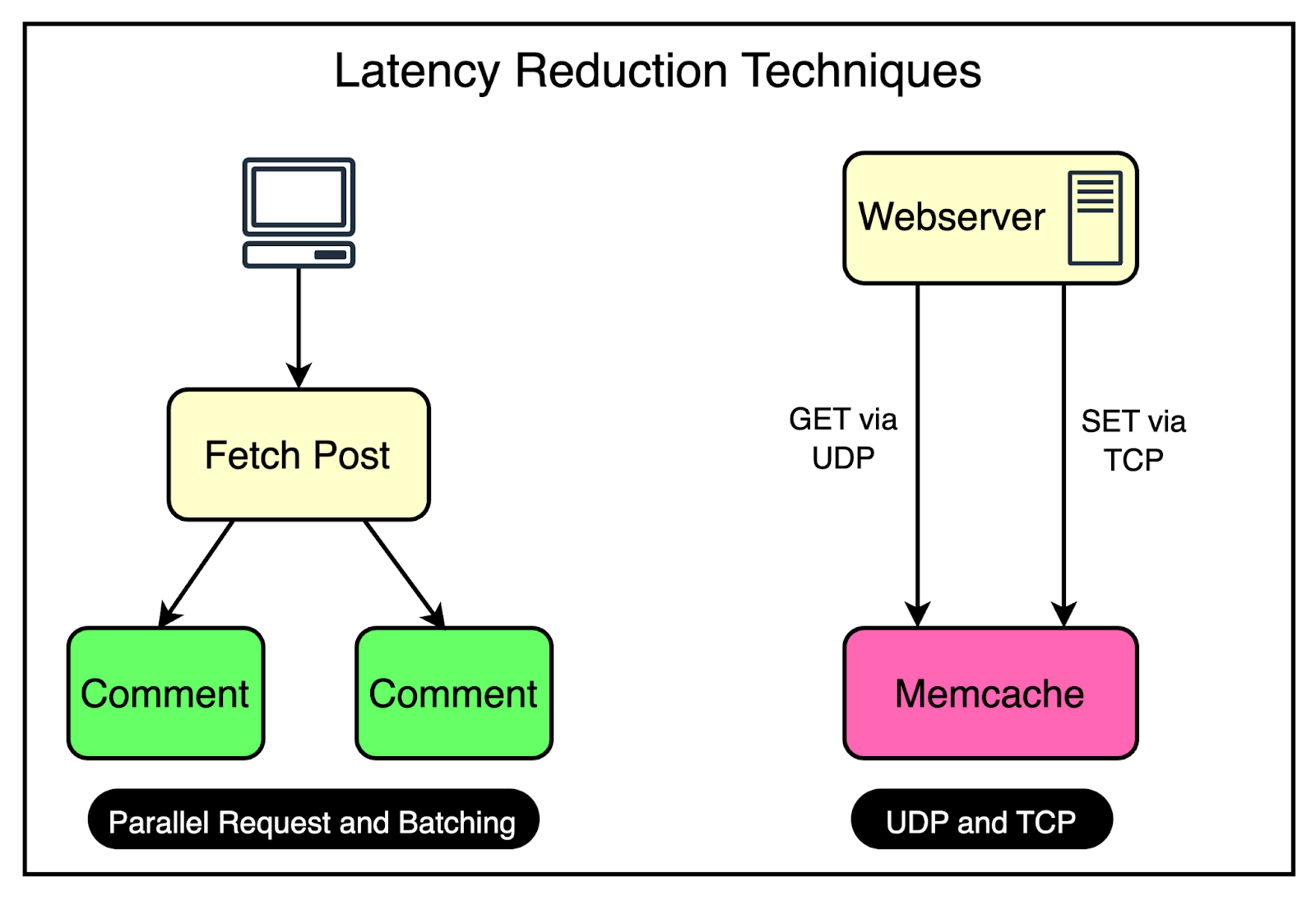
To reduce the possibility of such a scenario, Facebook uses a couple of important tricks visualized in the diagram.
Parallel Requests and Batching
To understand the concept of parallel requests and batching, consider a simple analogy.
Imagine going to the supermarket every time you need an item. It would be incredibly time-consuming and inefficient to make multiple trips for individual items. Instead, it’s much more effective to plan your shopping trip and purchase a bunch of items together in a single visit.
The same optimization principle applies to data retrieval in Facebook's frontend clusters.
To maximize the efficiency of data retrieval, Facebook constructs a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) that represents the dependencies between different data items.
The DAG provides a clear understanding of which data items can be fetched concurrently and which items depend on others.
By analyzing the DAG, the web server can determine the optimal order and grouping of data fetches. It identifies data items that can be retrieved in parallel, without any dependencies, and groups them in a single batch request.
Using UDP
Facebook employed a clever strategy to optimize network communication between the web servers and the Memcache server.
For fetch requests, Facebook configured the clients to use UDP instead of TCP.
As you may know, UDP is a connectionless protocol and much faster than TCP. By using UDP, the clients can send fetch requests to the Memcache servers with less network overhead, resulting in faster request processing and reduced latency.
However, UDP has a drawback: it doesn’t guarantee the delivery of packets. If a packet is lost during transmission, UDP doesn’t have a built-in mechanism to retransmit it.
To handle such cases, they treated UDP packet loss as a cache miss on the client side. If a response isn’t received within a specific timeframe, the client assumes that the data is not available in the cache and proceeds to fetch it from the primary data source.
For update and delete operations, Facebook still used TCP since it provided a reliable communication channel that ensured the delivery of packets in the correct order. It removed the need for adding a specific retry mechanism, which is important when dealing with update and delete operations.
All these requests go through a special proxy known as mcrouter that runs on the same machine as the webserver. Think of the mcrouter as a middleman that performs multiple duties such as data serialization, compression, routing, batching, and error handling. We will look at mcrouter in a later section.
2 - Reducing Load
The most important goal for Memcache is to reduce the load on the database by reducing the frequency of data fetching from the database.
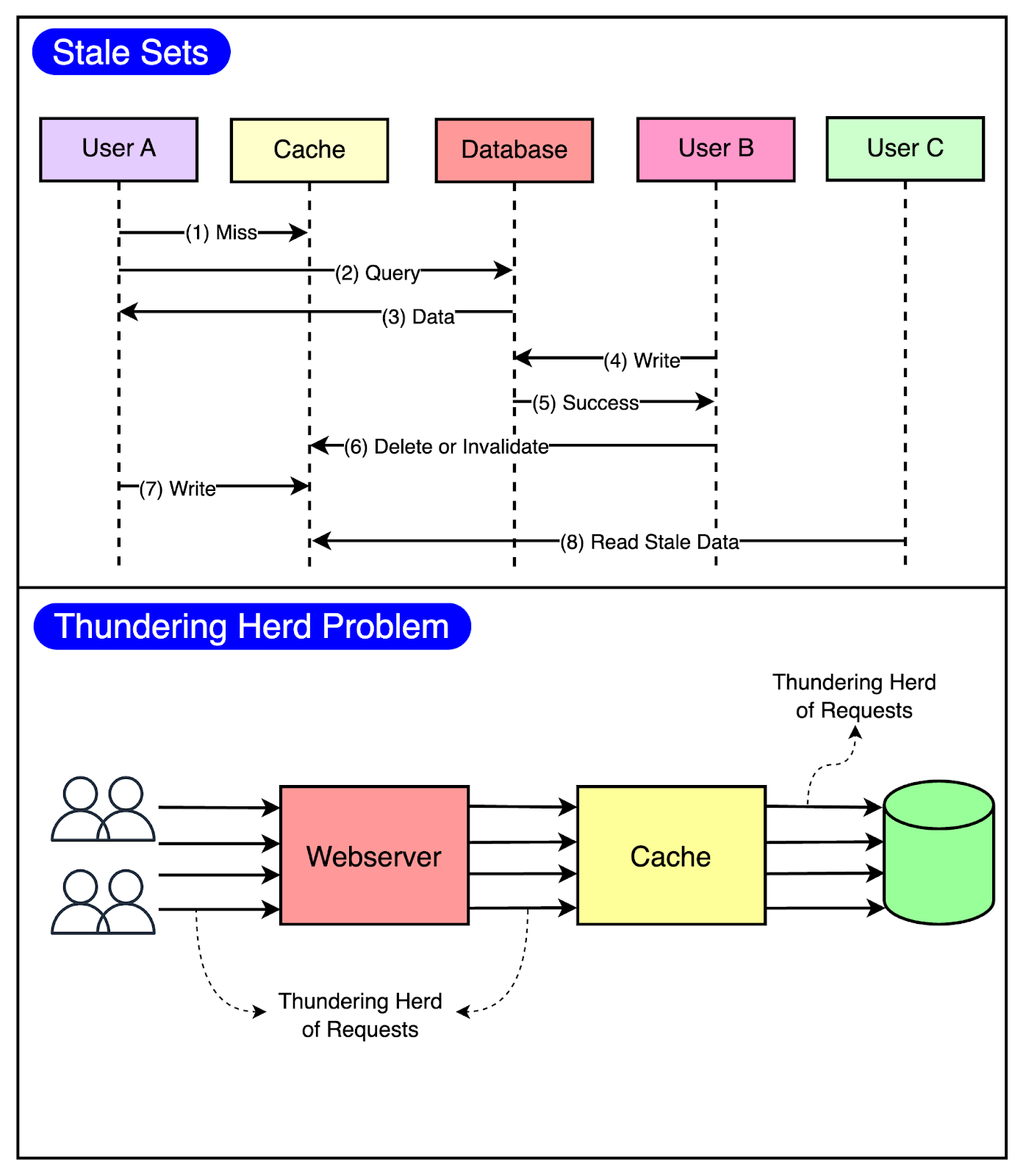
Using Memcache as a look-aside cache solves this problem significantly. But at Facebook’s scale, two caching-related issues can easily appear.
Stale Set: This happens when the cache is set with outdated data and there’s no easy way of invalidating it.
Thundering Herd: This problem occurs in a highly concurrent environment when a cache miss triggers a thundering herd of requests to the database.
The below diagram visualizes both of these issues.
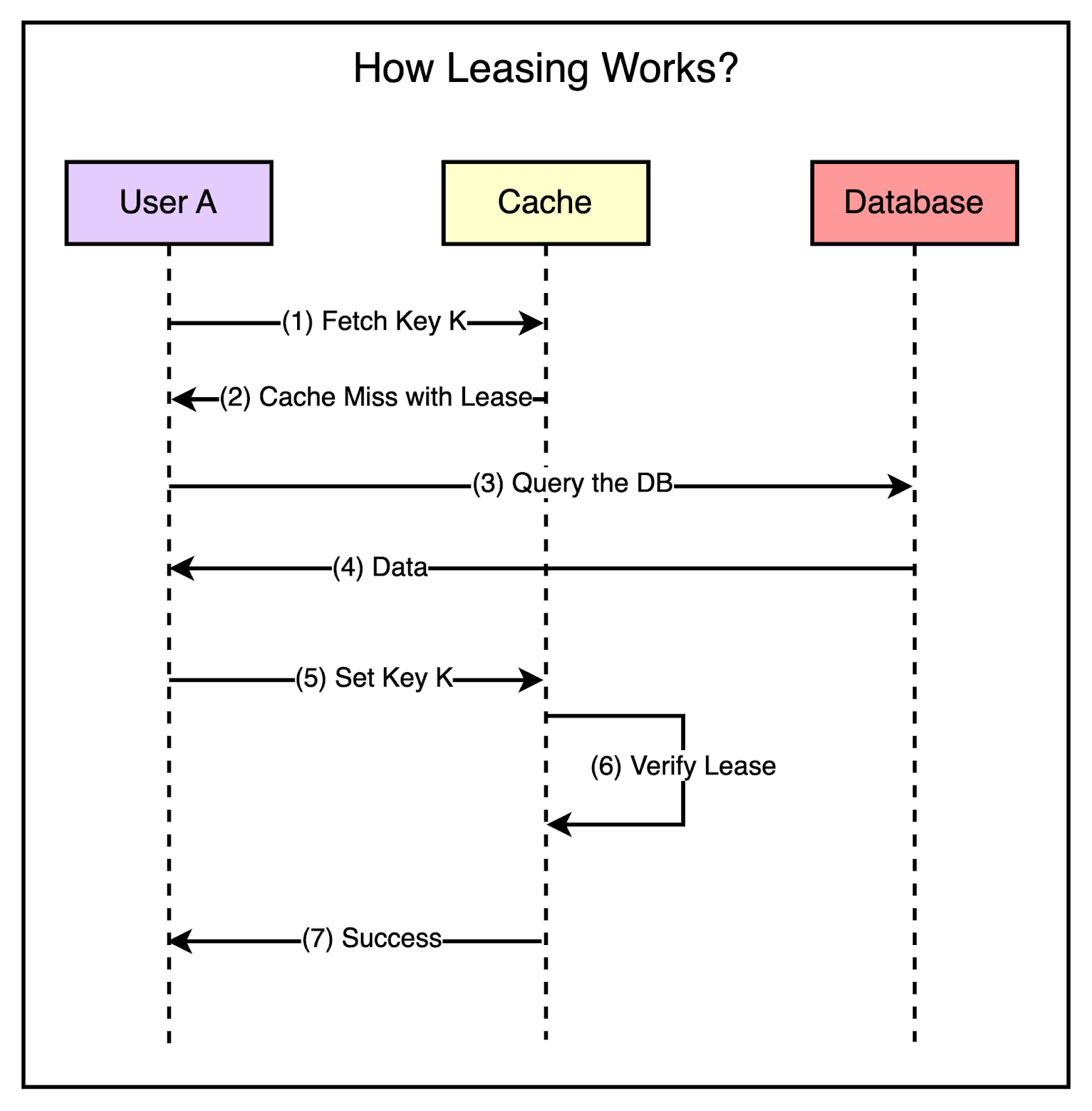
To minimize the probability of these two critical issues, Facebook used a technique known as leasing.
Leasing helped solve both stale sets and thundering herds, helping Facebook reduce peak DB query rates from 17K/second to 1.3K/second.
Stale Sets
Consider that a client requests memcache for a particular key and it results in a cache miss.
Now, it’s the client’s responsibility to fetch the data from the database and also update memcache so that future requests for the same key don’t result in a cache miss.
This works fine most of the time but in a highly concurrent environment, the data being set by the client may get outdated by the time it gets updated in the cache.
Leasing prevents this from happening.
With leasing, Memcache hands over a lease (a 64-bit token bound to a specific key) to a particular client to set data into the cache whenever there’s a cache miss.
The client has to provide this token when setting the value in the cache and memcache can verify whether the data should be stored by verifying the token. If the item was already invalidated by the time the client tried to update, Memcache will invalidate the lease token and reject the request.
The below diagram shows the concept of leasing in a much better manner.
Thundering Herds
A slight modification to the leasing technique also helps solve the thundering herd issue.
In this modification, Memcache regulates the rate of issuing the lease tokens. For example, it may return a token once every 5 seconds per key.
For any requests for the key within 5 seconds of the lease token being issued, Memcache sends a special response requesting the client to wait and retry so that these requests don’t hit the database needlessly. This is because there’s a high probability that the client holding the lease token will soon update the cache and the waiting clients will get a cache hit when they retry.
Latest articles
If you’re not a paid subscriber, here’s what you missed.
To receive all the full articles and support ByteByteGo, consider subscribing:
3 - Handling Failures
In a massive-scale system like Facebook, failures are an inevitable reality.
With millions of users using the platform, any disruption in data retrieval from Memcache can have severe consequences. If clients are unable to fetch data from Memcache, it places an excessive load on the backend servers, potentially leading to cascading failures in downstream services.
Two Levels of Failure
Facebook faced two primary levels of failures when it comes to Memcache:
Small-Scale Outages: A small number of hosts may become inaccessible due to network issues or other localized problems. While these outages are limited in scope, they can still impact the overall system performance.
Widespread Outages: In more severe cases, an entire cluster may go down, affecting a significant percentage of the Memcache hosts. Such widespread outages create a greater threat to the stability and availability of the system.
Handling Widespread Outages
To mitigate the impact of a cluster going down, Facebook diverts web requests to other functional clusters.
By redistributing the load, Facebook ensures that the problematic cluster is relieved of its responsibilities until it can be restored to health.
Automated Remediation for Small Outages
For small-scale outages, Facebook relies on an automated remediation system that automatically detects and responds to host-level issues by bringing up new instances to replace the affected ones.
However, the remediation process is not instantaneous and can take some time to complete. During this time window, the backend services may experience a surge in requests as clients attempt to fetch data from the unavailable Memcache hosts.
The common way of handling this is to rehash keys and distribute them among the remaining servers.
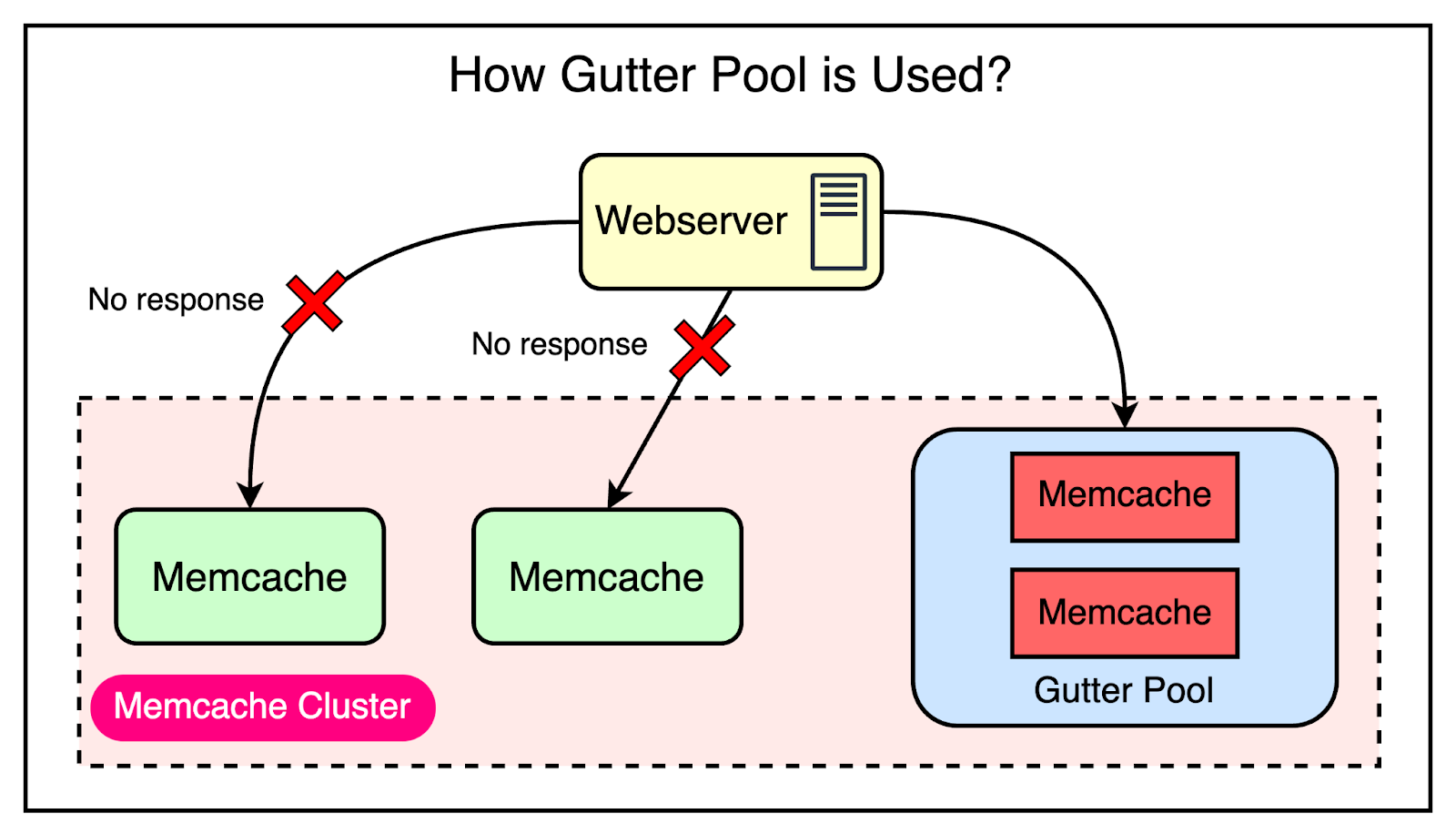
However, Facebook’s engineering team realized that this approach was still prone to cascading failures. In their system, many keys can account for a significant portion of the requests (almost 20%) to a single server. Moving these high-traffic keys to another server during a failure scenario could result in overload and further instability.
To mitigate this risk, Facebook went with the approach of using Gutter machines. Within each cluster, they allocate a pool of machines (typically 1% of the Memcache servers) specifically designated as Gutter machines. These machines are designed to take over the responsibilities of the affected Memcache servers during an outage.
Here’s how they work:
If a Memcache client receives no response (not even a cache miss), the client assumes that the server has failed and issues a request to the Gutter pool.
If the request to the Gutter pool returns a cache miss, the client queries the database and inserts the data into the Gutter pool so that subsequent requests can be served from Memcache.
Gutter entries expire quickly to remove the need for invalidations.
The below diagram shows how the Gutter pool works:
Though there are chances of serving stale data, the backend is protected. Remember that this was an acceptable trade-off for them when compared to availability.
Region Level Challenges
At the region level, there were multiple frontend clusters to deal with and the main challenge was handling Memcache invalidations across all of them.
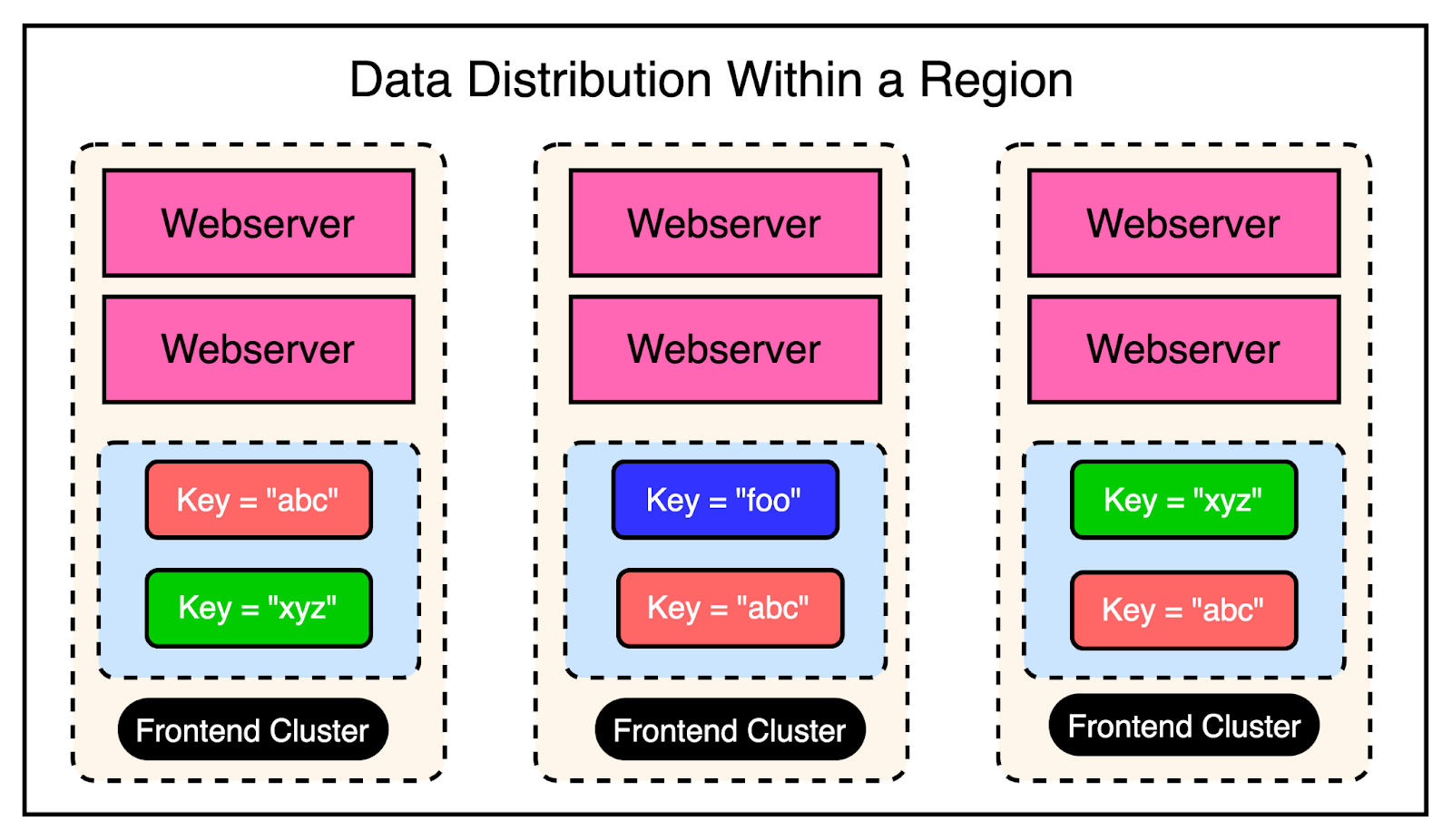
Depending on the load balancer, users can connect to different front-end clusters when requesting data. This results in caching a particular piece of data in multiple clusters.
In other words, you can have a scenario where a particular key is cached in the Memcached servers of multiple clusters within the region. The below diagram shows this scenario:
As an example, the keys “abc” and “xyz” are present in multiple frontend clusters within a region and need to be invalidated in case of an update to their values.
Cluster Level Invalidation
Invalidating this data at the cluster level is reasonably simpler. Any web server that modifies the data is responsible for invalidating the data in that cluster. This provides read-after-write consistency for the user who made the request. It also reduces the lifetime of the stale data within the cluster.
For reference, read-after-write consistency is a guarantee that if a user makes some updates, he/she should always see those updates when they reload the page.
Region Level Invalidation
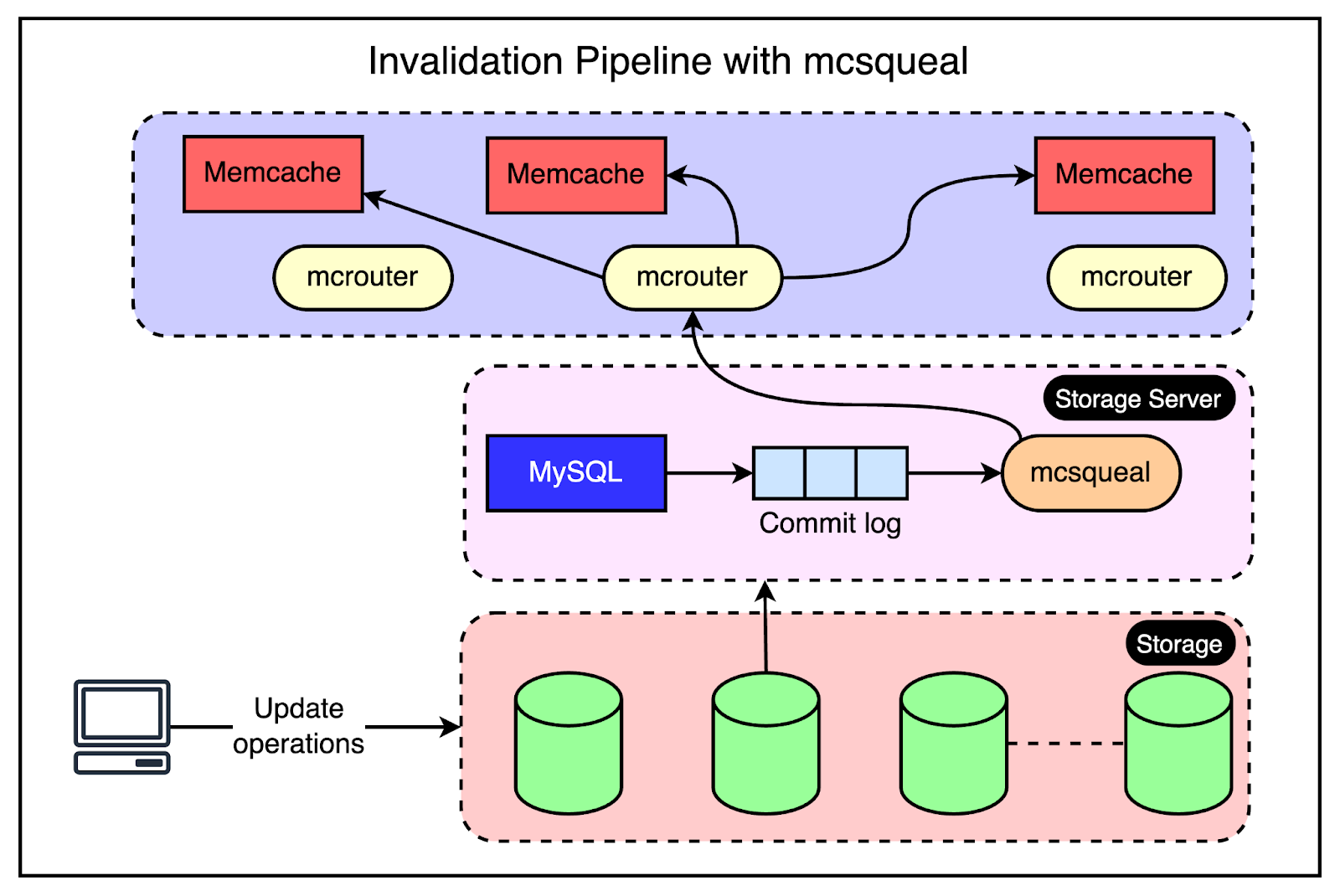
For region-level invalidation, the invalidation process is a little more complex and the webserver doesn’t handle it.
Instead, Facebook created an invalidation pipeline that works like this:
An invalidation daemon known as mcsqueal runs on every database server within the storage cluster.
This daemon inspects the commit log, extracts any deletes, and broadcasts them to the Memcache deployments in every frontend cluster within the region.
For better performance, mcsqueal batches these deletes into fewer packets and sends them to dedicated servers running mcrouter instances in each cluster.
The mcrouter instance iterates over the individual deletes within the batch and routes them to the correct Memcache server.
The below diagram explains this process.
Challenges with Global Regions
Operating at the scale of Facebook requires them to run and maintain data centers globally.
However, expanding to multiple regions also creates multiple challenges. The biggest one is maintaining consistency between the data in Memcache and the persistent storage across the regions.
In Facebook’s region setup, one region holds the primary databases while other geographic regions contain read-only replicas. The replicas are kept in sync with the primary using MySQL’s replication mechanism.
However, when replication is involved, there is bound to be some replication lag. In other words, the replica databases can fall behind the primary database.
There are two main cases to consider when it comes to consistency here:
Writes from the Primary Region
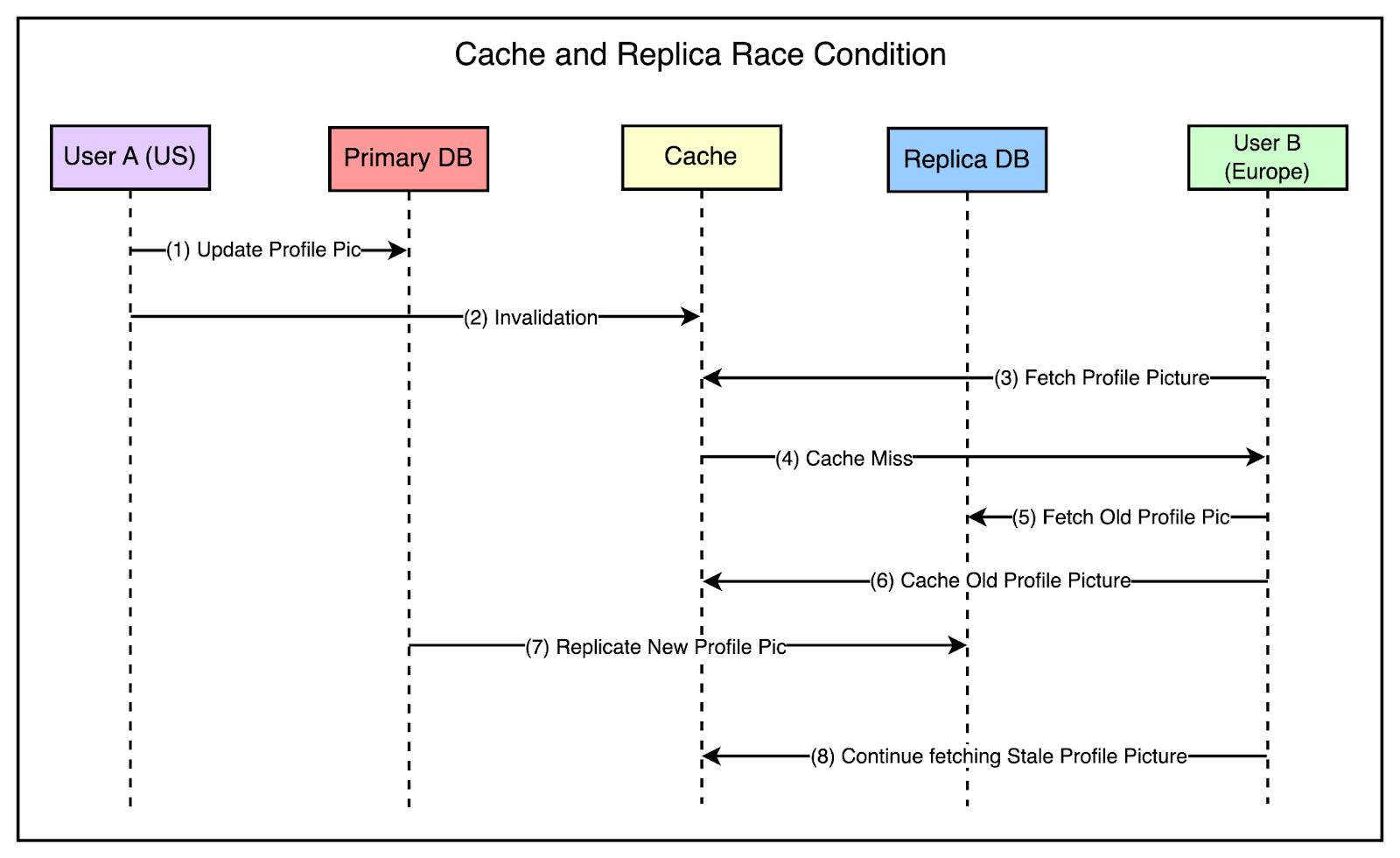
Let’s say a web server in the primary region (US) receives a request from the user to update their profile picture.
To maintain consistency, this change needs to be propagated to other regions as well.
The replica databases have to be updated.
Also, the Memcache instances in the secondary regions need to be invalidated.
The tricky part is managing the invalidation along with the replication.
If the invalidation arrives in the secondary region (Europe) before the actual change is replicated to the database in the region, there are chances of a race condition as follows:
Someone in the Europe region tries to view the profile picture.
The system fetches the information from the cache but it has been invalidated.
Data is fetched from the read-only database in the region, which is still lagging. This means that the fetch request gets the old picture and sets it within the cache.
Eventually, the replication is successful but the cache is already set with stale data and future requests will continue fetching this stale data from the cache.
The below diagram shows this scenario:
To avoid such race conditions, Facebook implemented a solution where the storage cluster having the most up-to-date information is responsible for sending invalidations within a region. It uses the same mcsqueal setup we talked about in the previous section.
This approach ensures that invalidations don’t get sent prematurely to the replica regions before the change has been fully replicated in the databases.
Writes from the Non-Primary Region
When dealing with writes originating from non-primary regions, the sequence of events is as follows:
User updates their profile picture from a secondary region. While reads are served from the replica or secondary regions, the writes go to the primary region.
After the writes are successful, the changes also need to be replicated in the secondary region as well.
However, there’s a risk that before the replication catches up, a read request on the replica region may fetch and cache stale data in Memcache.
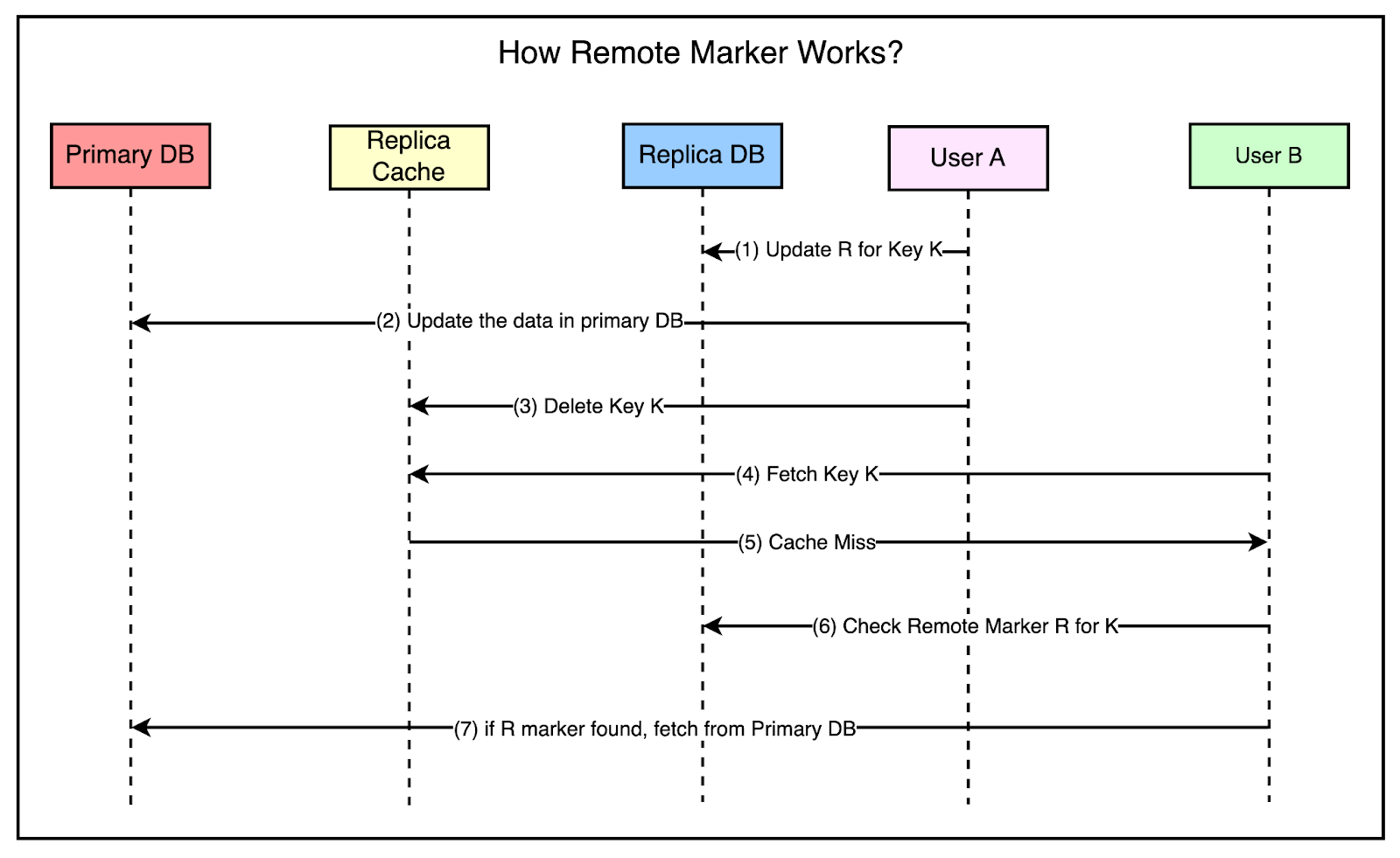
To solve this problem, Facebook used the concept of a remote marker.
The remote marker is used to indicate whether the data in the local replica is potentially stale and it should be queried from the primary region.
It works as follows:
When a client web server requests to update the data for key K, it sets a remote marker R for that key in the replica region.
Next, it performs the write to the primary region.
Also, the key K is deleted from the replica region’s Memcache servers.
A read request comes along for K in the replica region but the webserver would get a cache miss.
It checks whether the remote marker R exists and if found, the query is directed to the primary region.
The below diagram shows all the steps in more detail.
At this point, you may think that this approach is inefficient because they are first checking the cache, then the remote marker, and then making the query to the primary region.
In this scenario, Facebook chose to trade off latency for a cache miss in exchange for a reduced probability of reading stale data.
Single Server Optimizations
As you can see, Facebook implemented some big architectural decisions to scale Memcached for their requirements. However, they also spent a significant time optimizing the performance of individual Memcache servers.
While the scope of these improvements may seem small in isolation, their cumulative impact at Facebook’s scale was significant.
Here are a few important optimizations that they made:
Automatic Hash Table Expansion
As the number of stored items grows, the time complexity of lookups in a hash table can degrade to O(n) if the table size remains fixed. This reduces the performance.
Facebook implemented an automatic expansion mechanism for the hash table. When the number of items reaches a certain threshold, the hash table automatically doubles in size, ensuring that the time complexity of the lookups remains constant even as the dataset grows.
Multi-Threaded Server Architecture
Serving a high volume of requests on a single thread can result in increased latency and reduced throughput.
To deal with this, they enhanced the Memcache server to support multiple threads and handle requests concurrently.
Dedicated UDP Port for Each Thread
When multiple threads share the same UDP port, contentions can occur and lead to performance problems.
They implemented support for each thread to have its own dedicated UDP port so that the threads can operate more efficiently.
Adaptive Slab Allocator
Inefficient memory allocation and management can lead to fragmentation and suboptimal utilization of system resources.
Facebook implemented an Adaptive Slab Allocator to optimize memory organization within each Memcache server. The slab allocator divides the available memory into fixed-size chunks called slabs. Each slab is further divided into smaller units of a specific size.
The allocator dynamically adapts the slab sizes based on the observed request patterns to maximize memory utilization.
Conclusion
Facebook’s journey in scaling Memcached serves as a fantastic case study for developers and engineers. It highlights the challenges that come up when building a globally distributed social network that needs to handle massive amounts of data and serve billions of users.
With their implementation and optimization of Memcache, Facebook demonstrates the importance of tackling scalability challenges at multiple levels. From high-level architectural decisions to low-level server optimizations, every aspect plays an important role in ensuring the performance, reliability, and efficiency of the system.
Three key learning points to take away from this study are as follows:
Embracing eventual consistency is the key to performance and availability. However, every decision has to be taken based on a good understanding of the trade-offs.
Failures are inevitable and it’s critical to design your system for failures.
Optimization can be done at multiple levels.
References:
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 500,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing hi@bytebytego.com
Like
Comment
Restack
© 2024 ByteByteGo
548 Market Street PMB 72296, San Francisco, CA 94104
Unsubscribe
by "ByteByteGo" <bytebytego@substack.com> - 11:35 - 14 May 2024 -
How can tokenization be used to speed up financial transactions?
On Point
4 steps to asset tokenization Brought to you by Liz Hilton Segel, chief client officer and managing partner, global industry practices, & Homayoun Hatami, managing partner, global client capabilities
•
Blockchain’s benefits. Tokenization is the process of creating a digital representation of a real thing. It could transform the financial-services industry by allowing asset holders to reap the benefits of blockchain, such as 24/7 operations and data availability, McKinsey partner Anutosh Banerjee and coauthors explain. Potential benefits of tokenization in the industry include cheaper and nimbler infrastructure, democratization of access, faster transaction settlement, and operational cost savings.
•
Catching on. Financial-services companies are already beginning to tokenize cash. However, it’s not yet happening on a scale that could be considered a tipping point. Since tokenization debuted five years ago, many financial-services companies have considerably expanded their digital-asset teams and capabilities. As tokenization matures, it could become increasingly useful in financial transactions. See our McKinsey Explainer for four steps typically involved in asset tokenization.
—Edited by Jana Zabkova, senior editor, New York
This email contains information about McKinsey's research, insights, services, or events. By opening our emails or clicking on links, you agree to our use of cookies and web tracking technology. For more information on how we use and protect your information, please review our privacy policy.
You received this newsletter because you subscribed to the Only McKinsey newsletter, formerly called On Point.
Copyright © 2024 | McKinsey & Company, 3 World Trade Center, 175 Greenwich Street, New York, NY 10007
by "Only McKinsey" <publishing@email.mckinsey.com> - 01:37 - 14 May 2024




















.png?width=1200&upscale=true&name=Frame%201%20(2).png)